Student Growth Goals
advertisement

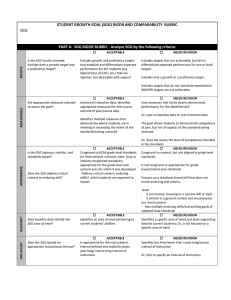
Student Growth Goals: An Introduction Presented by: Cam Kitchen, Administrator Jodi Lee, Teacher Jenna Miller, Teacher Kelli Shurtliff, Human Resources Robin Troche, Teacher & NCEA Erin Whitlock, OEA Student Growth Goals Agenda for Today Introduction to Oregon's Framework Introduction to Student Growth Goals (SGG) Analysis of Baseline data Draft Student Growth Goals Determining Levels of Performance Aligning Practice to Support SGG Student Growth Goals Targets I can explain the difference between a growth goal and achievement goal. I can list, model and explain the five steps in the student growth goal setting process. I can summarize the goal parameters/expectations for a variety of teaching assignments. After analyzing a data set, I can write a SMART student growth goal. Student Growth Goals 3 Framework Required Elements Teacher Evaluation Oregon Framework for Teacher Evaluation and Support Measures are ways/tools to gather evidence in our evaluation and professional growth systems (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) Standards of Professional Practice Differentiated Performance Levels Multiple Measures Evaluation and Professional Growth Cycle Aligned Professional Learning (4 levels) Student Growth Goals Multiple Measures Oregon teacher Oregon teacher evaluations must evaluations must include measures include measures from three three categories ofof categories evidence: evidence: (C) Student Learning and Growth (A)Professional Practice Aligned totothe Aligned the standards ofof standards professional professional practice practice (B)Professional Responsibilities Student Growth Goals Multiple Measures (A) Professional Practice Evidence of effectiveness of planning, delivery of instruction, and assessment of student learning •Multiple Observations •Artifact analysis (B) Professional Responsibilities Evidence of teachers’ progress toward their own professional goals and contribution to school wide goals, including collegial learning •Professional Goal •Self-Assessment Student Growth Goals Multiple Measures (C) Student Learning and Growth “Student growth” defined as “the change in student achievement between two or more points in time.” Teachers, in collaboration with their supervisors/evaluators, will establish Student Growth Goals and select evidence from a variety of valid measures and regularly assess progress It is just practice this year! Student Growth Goals Process Point #1 Answer this question as a table and have someone record your answers on the Process Worksheet (yellow): •Considering the information we have heard this far, what are our building-level needs? Record all questions on your table's Questions Sheet (blue) Student Growth Goals Multiple Measures of Student Learning Measures of student learning and growth includes three types of measures: Types of Measures of Student Learning (aligned to standards) Examples include, but are not limited to: 1 State or national standardized tests Oregon Assessment of Knowledge and Skills (OAKS), SMARTER Balanced (when adopted), English Language Proficiency Assessment (ELPA), Extended Assessments 2 Common national, international, regional, district-developed measures ACT, PLAN, EXPLORE, AP, IB, DIBELS, C-PAS, other national measures; or common assessments approved by the district or state as valid, reliable and able to be scored comparably across schools or classrooms 3 Classroom-based or school-wide measures Student performances, portfolios, products, projects, work samples, tests 3 Other school-wide or Graduation rate, attendance rate, drop-out rate, district-wide measures discipline data, college ready indicators (PSAT, Category AP/IB) Multiple Measures DEFINITIONS FOR 2013-2014 SCHOOL YEAR Teacher: Any individual holding a Teacher Standards and Practices Commission (TSPC) teaching license and instructing students 50% or more of their contracted day. Administrator: Any individual holding a TSPC Administrator license who serves as a principal or an assistant principal in a school building for 50% or more of their contracted day. Student Growth Goals Multiple Measures (C) Teachers Student Growth Goals (SGGs) Write two SGGs minimum Two of the three categories of Student Learning Measures must be used (last slide) If you are ELA (reading)/Math, Grades 4-8 & 11 • 1 of your 2 goals must use OAKS data • Your other goal must use student learning measures from category 2 or 3 If you are not ELA (reading)/Math Grades 4-8 & 11 • Your goals must include student learning measures from two of the three categories Student Growth Goals Multiple Measures (C) Admin Student Growth Goals Write two goals minimum One goal must use OAKS data •Building-level data in reading and math, including all disaggregated groups of students Should align to Achievement Compact goals where applicable Student Growth Goals Growth Goals vs. Achievement Goals Start with baseline data Intended to include all students regardless of ability level Students can show various levels of growth- students may have individualized finish lines Does not consider baseline data Student goals are a “one-size-fit-all” All students are expected to cross the same finish line regardless of where they start Student Growth Goals Example Goals Growth Ex: •By June of 2014, all students will grow in one trait of writing by one level as measured by the state level writing rubric for ___ grade. Achievement Ex: •By June of 2014, all students will be proficient in one trait of writing as measured by the state level writing rubric for ___ grade. Student Growth Goals SGG Characteristics Course-level requirements: •Elementary: year-long Entire class is covered •Secondary: length of actual class/course Biggest amount of students possible (common preps) •Targeted SGG Can only do if the first goal already meets Course-level requirements Subgroups of students •All goals are for the “intact group” Have “pre-” and “post-” data for students Student Growth Goals Process Point #2 Answer this question as a table and have someone record your answers on the Process Worksheet (yellow): •Considering the information we have heard this far, what are our potential roadblocks? Record all questions on your table's Questions Sheet (blue) Student Growth Goals So, what data sources will you use? Student Growth Goals Data Source Possibilities Common Assessments Interim Assessments District Assessments Student Portfolios Projects Products Student Performances Classroom Assessments Student Growth Goals Data Source Possibilities Common Assessments Interim Assessments District Assessments Student Portfolios Projects Products Student Performances Student Growth Goals Classroom Assessments Student Learning Measures Measures of student learning and growth include three types of measures: Category Types of Measures of Student Learning (aligned to standards) 1 State or national standardized tests 2 Common national, international, regional, district-developed measures 3 Classroom-based or school-wide measures 3 Other school-wide or district-wide measures For my content area of: _____________________ Examples include, but are not limited to: What does a SGG look like? SGGs are detailed, measurable goals for student growth •Specific timeframe •Collaboratively developed •Based on student learning needs ID'd via baseline data •Step-by-step process to follow •Regular review/assessment of progress •The objective in a SGG is a SMART goal Student Growth Student Growth GoalsGoals SMART Goal Process S M A R T Specific- The goal addresses student needs within the content. MeasurableAn appropriate instrument or measure is selected to assess the goal, and a concrete criteria AppropriateThe goal is clearly related to the role and responsibilities of the teacher. Realistic- The goal is attainable. Time-boundThe goal is contained to a single school year/course. The goal is measurable and uses an appropriate instrument. The goal is standardsbased and directly related to the subject and students that the teacher teaches. The goal is doable, but rigorous and stretches the outer bounds of what is attainable. The goal is bound by a timeline that is definitive and allows for determining goal attainment. The goal is focused on a specific area of need. Student Growth Goals Unacceptable SGGs 80% of students will pass the end-of-course exam. Students scoring 80 or lower on the pre-assessment will increase their scores by at least 10 points. Any students scoring 81 or higher on the pre-assessment will maintain their scores. Student Growth Goals Student Growth Goals Unacceptable SGGs: 80% of students will pass the end-of-course exam. Does not show growth Timeframe is partially unclear Students scoring 80 or lower on the pre-assessment will increase their scores by at least 10 points. Any students scoring 81 or higher on the pre-assessment will maintain their scores. Students scoring at 50 need to make greater gains Growth is non-existent for students at 81+, who may also need to be challenged with higher goal and/or additional assessment to illustrate growth No mention of post-assessment No specific time frame Student Growth Goals Student Growth Goals Acceptable Student Growth Goals Unacceptable Student Growth Goals By June ‘14, 15 of 25 students will meet their typical Given the OAKS Reading Assessment at __ grade, growth target within -3 RIT scores and the 85% of students will achieve a score of ___ or remaining 10 students will show growth within -5- above. 7 RIT of their target (with at least 1 RIT growth) as measured by the OAKS Reading Assessment at __ grade at or above the 50%ile (typical growth). By Spring ’13, all English Language Learners scoring a 1-3 on the ELPA will increase one level or more as measured by the ELPA assessment. Students scoring higher than a 3 will show at least 10% growth as measured by a teacher-developed pre/post-language test. At least 18 of 21 students achieve a score of 4 or higher on the Music Mastery Rubric By June ’14, each student will improve their Oral Reading fluency rate by at least 40wpm as measured by the Spring ORF easyCBM assessment. At least 17 of 20 students achieve a score of 3 or higher on the AP Chemistry exam. Student Growth Goals Process Point #3 Answer this question as a table and have someone record your answers on the Process Worksheet (yellow): •Considering the information we have heard this far, what are our potential opportunities? Record all questions on your table's Questions Sheet (blue) Student Growth Goals Let’s Take A Brain Break! Student Growth Goals SGG Evaluation Cycle I SGG Development Process V Summative Conference: Discussion of impact on practice and summative rating/professional growth IV Summative Conference: Final review of SGG & Scoring II SGG Initial Collaborative Goal Meeting III SGG Mid-Course Review Student Growth Goals I – SGG Development Generally includes the following 5 steps: 1. Identify core content and standards 2. Gather and analyze student data 3. Determine the focus of the SGG (St/course) 4. Select or develop an assessment(s) 5. Develop a SMART goal statement and rationale: Student Growth Goals Let’s Write a Student Growth Goal Student Growth Goals Step 1: Identify Core Content & Standards Step 1: ID Core Content & Standards Step 2: Gather & Analyze Student Data Step 3: Determine focus of SGG Step 4: Select or develop assessment Student Growth Goals Step 5: Develop a SMART Goal statement and rationale Step 1: ID Core Content & Standards Guiding Questions: •What national or state standards are addressed by the course? •What are the essential skills and content knowledge that students will need in order to be successful next year? •In which of these essential skills and content knowledge are students struggling? •What are the specific academic concepts, skills or behaviors the SGG will target? Student Growth Goals Step 2: Gather & Analyze Student Data Step 1: ID Core Content & Standards Step 2: Gather & Analyze Student Data Step 3: Determine focus of SGG Step 4: Select or develop assessment Student Growth Goals Step 5: Develop a SMART Goal statement and rationale Step 2: Gather & Analyze Student Data You need to KNOW your students abilities before you develop the goal. Student Growth Goals Step 2: Gather & Analyze Student Data Other data that is important to consider could include: •Attendance data •Demographics information •Student support needs IEP ELL •Any others that you can think of? Student Growth Goals Student Indicator 1 Indicator 2 Indicator 3 Student 1 2 2 1 Student 2 3 3 4 Student 3 1 1 1 Student 4 2 2 1 Student 5 3 2 2 Student 6 3 2 2 Student 7 2 1 1 Student 8 1 1 1 Student 9 3 3 3 Student 10 2 2 1 Student 11 3 2 2 Student 12 3 3 3 Student 13 1 1 1 Student 14 3 3 4 Student 15 3 2 2 Student 16 2 2 2 Student 17 1 1 1 Student 18 3 3 2 Student 19 3 3 4 Student 20 2 1 1 Baseline Data On your template: 1. Complete the baseline data information 2.Where are my (your) students now? 3.Based on the data, have a conversation at your table about what needs to happen in your classroom as far as student learning Student Growth Goals Process Point #4 Answer this question as a table and have someone record your answers on the Process Worksheet (yellow): •Considering the information we have heard this far, what are our burning questions? Record all questions on your table's Questions Sheet (blue) Student Growth Goals Step 3: Determine focus of SGG Step 1: ID Core Content & Standards Step 2: Gather & Analyze Student Data Step 3: Determine focus of SGG Step 4: Select or develop assessment Student Growth Goals Step 5: Develop a SMART Goal statement and rationale Step 3: Determine focus of SGG Remember that: •Elementary: year-long & entire class is covered •Secondary: length of actual class/course & biggest amount of students possible (common preps) Tiered targets within a course-level SGG •If data analysis shows wide range of skill/ability •Different targets for different groups of students •Can choose to have individual targets as well Student Growth Goals Examples of Tiered Targets Goal 1.From Oct to January, all students will meet their target score as measured by the American Government pre-/post-assessment: Baseline Score Range Target Score on Post-Test 20-30 70 31-50 77 51-70 85 71-85 90 86-95 96 2.From Fall ‘13 to Spring ’14, all students at __ level will improve their reading fluency by 25 wpm, students at __ level improve by 35 wpm, and Sts at __ will improve by 40wpm, as measured by an ORF assessment. Student Growth Goals OAKS & Growth Goals It is just practice this year 2013-14 Not about: •How many kids “meet” or “exceed” OAKS •How much I “grow” the number of kids who meet/exceed Based on OAKS Growth targets •Oregon Growth Model – DO NOT USE FOR SGG In 3-years or by 11th grade, these targets aim to get students to “Meets” •Typical Growth Model – Use this model with trend data to help you write goal Based on prior year's score, this is what 50%ile typically score in their current year Student Growth Goals OAKS & Growth Goals Reading - 3rd to 4th Grade Growth 3rd Grade 4th Grade Typical Score Target Growth 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 210 210 210 210 210 211 211 211 212 212 200 200 200 201 201 202 203 204 204 205 3rd Grade 4th Grade Typical Score Target Growth 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 213 214 214 214 215 215 216 216 216 217 Student Growth Goals 207 208 210 211 212 213 214 214 215 216 Example OAKS Goal – 4th Grade By June 2014: •50% of 4th grade students will meet their growth target (see attached data) as measured by OAKS-Reading 4th grade exam; this is using the typical growth (50%ile) model. Additionally, students who do not meet or exceed their growth target will be within at least -7 RIT scores of their target (so all students are expected to show growth). •100% of students will grow by at least 30% on the pre-/-post comprehension test, with at least half of students growing by 50%. Student Growth Goals Example OAKS Goal – 11th Grade By June 2014 •55% of 11th grade students in my class who have not yet passed OAKS-Math (and will thus be taking it again) will demonstrate growth on the OAKS Math for 11th grade at or above the 50%ile (typical growth). Since statistically only about 50% of students hit this growth target, having over 50% hit it is quite rigorous. I will expect all students who do not hit the target to be within at least 5-7 RIT scores of their typical growth target and still show growth. Student Growth Goals Step 4: Select or develop an assessment Step 1: ID Core Content & Standards Step 2: Gather & Analyze Student Data Step 3: Determine focus of SGG Step 4: Select or develop assessment Student Growth Goals Step 5: Develop a SMART Goal statement and rationale Step 4: Select or develop an assessment Guiding Questions: •Is this assessment the best way to measure student progress toward the objective? •Does this assessment allow all students to demonstrate developmentally appropriate growth? •Does this assessment follow district and state guidelines? •How will I ensure assessments are graded in a fair and unbiased manner? Student Growth Goals Step 5: Develop SMART Goal Statement Step 1: ID Core Content & Standards Step 2: Gather & Analyze Student Data Step 3: Determine focus of SGG Step 4: Select or develop assessment Student Growth Goals Step 5: Develop a SMART Goal statement and rationale Step 5: Develop SMART Goal Statement Growth goals developed with specific indicators of growth Guiding Questions: •How was the baseline data used to inform the growth goal? •Are tiered targets appropriate for the student population included in the SGG? •Are expectations rigorous yet realistic? Rationale for growth goal was well developed Guiding Questions: •How will this goal address student needs? •Why is this goal important? •What baseline data informed this goal? •How will attainment of this goal help the student learn necessary content for future grade levels? Student Growth Goals Process Point #5 Answer this question as a table and have someone record your answers on the Process Worksheet (yellow): •Considering the information we have heard this far, what are our next steps in-building? Record all questions on your table's Questions Sheet (blue) Student Growth Goals Draft Your Goal Draft a goal based on baseline data Make sure it is growth: • All students • Considers baseline • Is not an achievement goal Make sure it is S.M.A.R.T. THEN… • Rotate to another group's goal • Give them feedback on their goal using the criteria above Student Growth Goals A Possible Goal Student Learning Objective Statement: For the 2012 – 13 school year, 100% of students will make measurable progress in writing. Each student will improve by one performance level in two or more indicators of the rubric. A good goal statement is one that is… Specific Measurable Appropriate Realistic Time-bound Student Growth Goals Strategies for the Goal Students will…. I will…. use a writer’s notebook for writing practice, specifically developing ideas and focusing on specific audiences for specific purposes. implement strategies learned during Rigor and Relevance training and develop writing prompts for students to use in their writer’s notebooks. refine my implementation of the standards, researching and implementing engaging and rigorous teaching strategies that deepen student understanding of organizational structures and uses in their own writing. refine my use of ongoing formative assessment to impact daily instruction by teaching students to lead classroom discussions and peer reviews. I will incorporate these in practice. analyze organizational structure of narrative, informational/explanatory, and argumentative writing and apply to their own writing. participate in peer response groups to give/receive feedback on audience awareness, purpose, and idea development. Student Growth Goals District Expectations Elementary • Two SGGs and professional goals by Oct 15th Secondary • If you teach a year-long course, two SGGs and professional goals by Oct 15th. • If you teach a semester or quarter class a minimum of professional goals and SGGs timeframe identified (+ goal if applicable to first term) by Oct 15th. Student Growth Goals Target Check I can explain the difference between a growth goal and achievement goal. I can list, model and explain the five steps in the student growth goal setting process. I can summarize the goal parameters/expectations for a variety of teaching assignments. After analyzing a data set, I can write a SMART student growth goal. Student Growth Goals 55