The Sea floor: Layers of the earth
advertisement

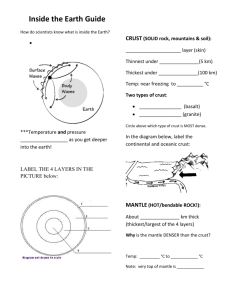
THE SEA FLOOR: LAYERS OF THE EARTH Ms. Springstroh Why study the sea floor in this class? Over time, geological processes greatly influence marine habitats. Sculpt the shoreline Determine water depth Control the substrate on the ocean floor (rock, sand, mud, etc) Create new underwater mountains for organisms to live on Oceans Cover 71% of the earth’s surface Regulate earth’s climate and atmosphere Fun facts about the oceans Northern Hemisphere = 61% ocean Southern Hemisphere = 80% ocean Pacific ocean: deepest, largest, almost as large as all the others combined Arctic ocean is the smallest and shallowest Because all of the oceans are connected, they are sometimes referred to as a single “world ocean”. Formation of the earth Big Bang 13.7 billion years ago Cosmic explosion which produced dust Dust particles from the big bang collided with each other Created larger particles More collisions lead to even larger particles These collisions created the earth (4.5 billion years ago) and other planets When the earth was created… It was probably molten (liquified by heat) This allowed the materials within the earth to settle according to density. Density Density = object’s mass__ object’s volume Remember: mass is similar to weight volume is how much space an object takes up Which do you think is more dense? A pound of styrofoam or a pound of lead? lead Density (continued) Less dense materials float, or rise on top of, more dense materials Which object in this picture is more dense? The water Density (continued) When the earth was molten, where would you find the most dense material? In the center of the planet Where would you find the lightest material? Toward the surface of the planet Layers of the earth Extremely high pressure and temperatures formed the core Innermost layer of the earth Composed mostly of iron Estimated to be 7,200°F Made of two parts: Inner core (solid) Outer core (liquid) Swirling motions of iron-containing material in the outer core might be what produces earth’s magnetic field Layers of the earth (continued) Outside of the core is the earth’s mantle Solid, but very hot, so it can flow like a liquid Contains the upper mantle and the lower mantle Outside of the mantle is the earth’s crust Outer-most layer of the earth Very thin Contains the oceans and the continents Earth’s crust There are two types of crust: Oceanic crust Made of a mineral called basalt Covered with water (the oceans) Continental crust Made of granite Oceanic crust is more dense than continental crust. This makes sense, because oceanic crust is “below sea level” and covered with water, and the continents lie high and dry above sea level. Asthenosphere and Lithosphere The asthenosphere is closer to the earth’s core and contains part of the upper mantle The lithosphere is closer to the surface of the earth and contains the rest of the upper mantle and all of the crust On your drawing, label and color the following: Inner core Outer core Lower Mantle Upper Mantle Continental Crust Oceanic Crust Asthenosphere Lithosphere