Urogenital triangle in female + Perineal pouches
advertisement
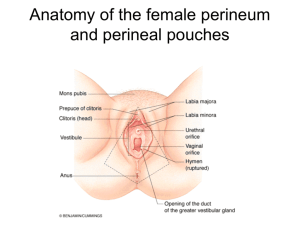
1. Describe the boundaries & contents of urogenital triangle in female. 2. Recite the parts of the female external genital organs. 3. Identify its parts and openings present in it. 4. Discuss the features of each part 5. Discuss the contents of the perineal pouches in female and male. 6. Enumerate the structures piercing the perineal membrane. BOUNDARIES : • • • Anteriorly : Symphysis pubis Posteriorly : Transverse line passing through the 2 ischial tuberosities. Laterally : Ischiopubic rami & ischial tuberosities. CONTENTS : • Lower part of urethra & vagina. • External genitalia (vulva). Mons pubis : a collection of fat overlying the pubis. Labia majora.: Two folds of skin containing fatty tissue and covered with hair Located on either side of the vaginal opening, extending from the mons pubis to the perineum Labia minora.: › Two thin folds of tissue located within the folds of the labia majora Extends from the clitoris downward toward the perineum Clitoris.: › Short, elongated organ composed of erectile tissue › Located just behind the upper junction of the labia minora › Homologous to the penis Vestibule of vagina: The interval between the two labia minora. Vagina & urethra open into it through urethral orifice anteriorly and vaginal orifice (Also known as the vaginal introitus), posteriorly. Bartholin’s glands › Located on either side of the vaginal orifice Secrete a mucous substance that lubricates the vagina Indifferent Male Female Gonad Testis Ovary Appendix testis Fallopian tubes Prostatic utricle Uterus, upper vagina Mesonephric tubules Efferent ducts, Paradidymis Epoophoron, Paroöphoron Mesonephric duct (Wolffian duct) Rete testis Rete ovarii Mesonephric duct Epididymis Gartner's duct Mesonephric duct Vas deferens Mesonephric duct Seminal vesicle Urogenital sinus Prostate Urogenital sinus Bladder, urethra Paramesonephric duct (Mullerian duct) Paramesonephric duct Skene's glands Bladder, urethra, Urogenital sinus Cowper's or Bulbourethral gland Bartholin's gland Labioscrotal folds Scrotum Labia majora Urogenital folds Spongy urethra Labia minora Genital tubercle Penis Clitoris Genital tubercle Bulb of penis Vestibular bulbs Genital tubercle Glans penis Clitoral glans Genital tubercle Crus of penis Clitoral crura Prepuce Foreskin Clitoral hood Peritoneum Processus vaginalis Canal of Nuck Gubernaculum Gubernaculum testis Round ligament of uterus It is the space between the deep membranous layer of superficial fascia and the perineal membrane. BOUNDARIES: Inferiorly: membranous layer of superficial fascia (Colle`s fascia). Superiorly: perineal membrane. Laterally: ischiopubic rami 1- Bulbs of vestibule: on each side of vaginal orifice. • 2- Crura of clitoris. • 3- Superficial perineal muscles: • A-Bulbospongiosus muscle, surrounds orifice of vagina and covers vestibular bulb. • • B- Ischiocavernosus muscle, covers crus of clitoris on each side. • • • • C- Superficial transverse perineal muscles. 4- Greater vestibular glands: on each side of vaginal orifice. 5- Perineal body 6- Perineal branch of pudendal nerve suppling muscles & skin. Bulbospongiosus Ischiocavernosus 1- Root (bulb and crura) of the penis and associated muscles (ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus). 2- Proximal (bulbous) part of the spongy urethra. 3- Superficial transverse perineal muscles. 4- Deep perineal branches of the internal pudendal vessels and pudendal nerves. Bulbospongiosus Ischiocavernosus It is a completely closed space deep to the perineal membrane. BOUNDARIES: Inferiorly: Inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm (Perineal membrane) Superiorly: Superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm Laterally: Inferior portion of obturator internus fascia Contents of Deep Perineal Pouch in female • 1- Part of urethra . • 2- Part of vagina. • 3- Sphincter urethrae muscle, which is pierced by urethra & vagina. • 4- Deep transverse perineal muscles • 5- Internal pudendal vessels. • 6- Dosal nerve of clitoris. 1- membranous part of the urethra, 2- the sphincter urethrae, 3- the bulbourethral glands, 4- the deep transverse perineal muscles, the internal pudendal vessels and their branches, and 5- the dorsal nerves of the penis. 1- In the centre: a- Membranous urethra in male b- urethra and vagina in female 2- On both sides of the urethra: a- ducts of bulbourethral glands of male b- artery to bulb 3- Anteriorly a-Deep and dorsal arteries of penis or clitoris b- Dorsal nerve of penis or clitoris 4- Posteriorly: Scrotal or labial vessels and nerves BOUNDARIES: • Anteriorly: Transverse line passing through the 2 ischial tuberosities. • Posteriorly : coccyx. • Laterally : ischial tuberosity & sacrotuberous lig. overlapped by gluteus maximus. CONTENTS: • Lower part of Anal canal (upper part lies in pelvis). Ano-coccygeal body (or raphe) : a fibrofatty mass that extends from anus to tip of coccyx. • • Ischiorectal fossa on each side. • A fascial lined wedgeshaped space on each side of the anal canal. Boundaries: • Base: Skin of the perineum. • Medial wall: Levator ani & anal canal. • Lateral wall: Obturator internus, covered with pelvic fascia. • Contents: • Dense fat. • Pudendal nerve & internal pudendal vessels within the pudendal canal • Inferior rectal nerve & vessels crossing the fossa to reach anal canal. • Pudendal Canal: • A fascial canal formed by obturator fascia, located on the lateral wall of the ischiorectal fossa, • on the medial side of the ischial tuberosity. • Contains pudendal nerve and internal pudendal vessels Anococcygeal Body The anococcygeal body is a complex musculotendinous structure situated between the anterior aspect of the coccyx and the posterior wall of the anorectal canal Receives insertion of fibers of levator ani muscle Thank You & Good Luck