Region 19: Perineum Perineum --diamond shaped space occupying
advertisement

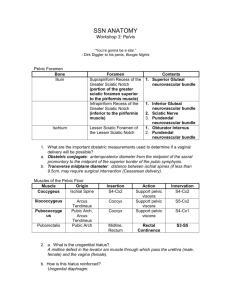
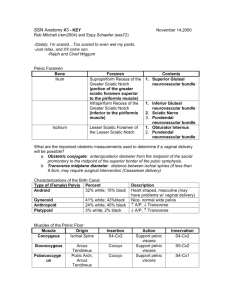
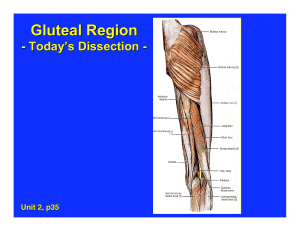
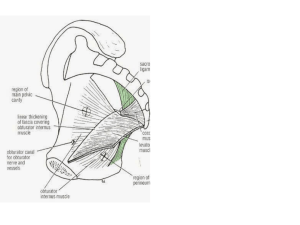
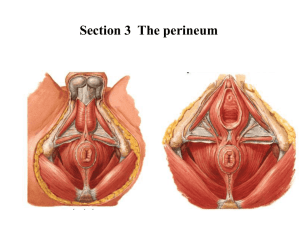
Region 19: Perineum Perineum --diamond shaped space occupying the pelvic outlet *superior boundary: pelvic diaphragm *inferior boundary: skin --arbitrarily divided by an imaginary line b/w the ischial tuberosisites into: --urogenital triangle (anteriorly) *layers superficial to deep 1. skin 2. superficial fascia: superficial fatty layer/Camper’s fascia and a membranous layer/Colles’ fascia continusous with scarpa’s fascia and dartos fascia 3. fascia of the muscles of the urogenital diaphragm is the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm or perineal membrane (Gallaudet’s fascia) 4. structures of the urogenital diaphragm (UG diaphragm) itself 5. superior fascia of the UG diaphragm is deepest layer *two spaces are b/w these layers of fascia from the superficial to deep fascia 1. superficial perineal space: lies b/w membranous and perineal mem. *Contents: crura and bulb of penis/clitoris, ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus mm, superifical transverse perineal m, branches of perineal vessesls and nerves, greater vestibular/ Bartholin’s gland 2. deep perineal space: actual urogential diaphragm, sandwiched b/w inferior fascia of UG diaphragm and superior fascia of UG diaphragm *Contents: bulbourethral/Cowper’s gland (males) --anal triangle (posteriorly) External Genitalia --Male: penis *paired dorsal corpora cavernosa penis *single ventral corpus spongiosum penis: expands distally into glans penis marked by the external urethral orifice, covered by prepuce/foreskin --Female: pudendal cleft having all the parts below collectively being called the vulva/pudendum a. mons pubis b. labia majora: homologue of scrotum c. labia minora: smaller, hairless swellings or folds bounding vestibule where the vagina and urethra open d. clitoris: homologue of penis Superificial perineal space in urogenital triangle --Male: superficial perineal space *two crura of corpora cavernosa penis: these erectile bodies attch to ischiopubic rami towards the ischial tuberosity *bulb of penis: enlarged proximal part of the corpus spongiosum (also has parts called body and glans) *muscles of the superficial perineal space a. bulbospongiosus muscle: envelopes the bulb of the penis b. ischiocavernosus muscles: cover the crura of the penis *nerves and vessels of the superficial perineal space a. perineal a. and n. --Female: superficial perineal space *crura of the cavernous bodies of the clitoris: covered by homologous ischiocavernosus mm. *two unfused masses of erectile tissue, the bulbs of the vestibule (homologous with bulb of penis), each bulb covered by bulbospongiosus m. *greater vestibular/Bartholin’s glands: homolgues to male’s bulbourethral glands but found in the sueprifical perineal space --Structures in superifical space in both males and females *innervated by branches of pudendal nerve (S2,3,4) from sacral plexus *supplied by branches of the internal pudendal a. Anal Triangle --Anal canal and anus a. as rectum passes through the pelvic diaphragm and levator ani at a 90o angle, the tube becomes the anal canal b. the lining of the anal canal chanes from mucosa to skin: true mucosa ends at the anal valves --external sphincter ani muscle *inn: by inferior rectal brances of the pudendal nerve --ischoanalischiorectal fossa *fat filled space surrounding the anal canal and inferior to the pelvic diaphragm *has an anterior recess that extends superiorly to the urogenital diaphragm Nerves and Vessels --derived from internal pudendal vessels and pudendal nerve --enter perineum via the lesser sciatic foramen --travel through the ischiorectal fossa in a fibrous canal, the pudendal/Alcock’s canal formed in the facia of the obturator internus muscle --internal pudendal vessels and pudendal nerve continue anteriorly to the posterior border of the urogenital diaphragm where they divide into branches to the superficial and deep perineal spaces