11会阴
advertisement

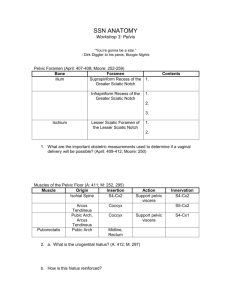
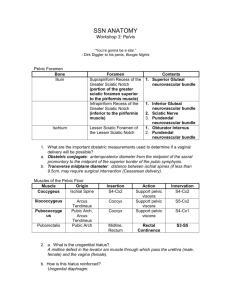
Section 3 The perineum Section 3 The perineum Urogenital triangle Anal triangle Male Section 3 The perineum Urogenital triangle Anal triangle Female Section 3 The perineum Female Obstetrical perineum Appendix II The Perineum (会阴) A. The Anal Region (triangle) [肛区 (肛三角)] B. The Urogenital Region (triangle) [尿生殖区 (尿生殖三角)] A. The Anal Region (Triangle) 1. Pelvic diaphragm (盆膈) 1) superior fascia of pelvic diaphragm (盆膈上筋膜) 2) levator ani (肛提肌) & coccygeus (尾骨肌) 3) inferior fascia of pelvic diaphragm (盆膈下筋膜) 2 Anal canal (肛管) 1. Internal structure 1) anal columns (肛柱) 2) anal valves (肛瓣) [fissure in ano 肛裂] 3) anal sinuses (肛窦) [anal fistula 肛瘘] 4) dentate (anocutaneous) line (齿状线) 5) anal pecten (肛梳) [pile (hemorrhoid) 痔] 6) white line (intersphincter sulcus) (白 线) 7) anus (肛门) [examination per anus 肛门 检查] A. The Anal Region A. The Anal Region 2. sphincter ani externus (肛门外括约肌) 皮下部 浅部 深部 2. Muscles 1) sphincter ani internus (肛门内括约肌) 2) sphincter ani externus (肛门外括约肌) a. subcutaneous part (皮下部) b. superficial part (浅部) c. deep part (深部) [fecal incontinence 大便失禁] 3. Ischioanal (ischiorectal) fossa (坐骨肛门窝) Ischioanal (ischiorectal) fossa (坐骨肛门窝) pudendal canal (阴部管) pudendal nerve & internal pudendal v., a., pudendal nerve (S2-4) → anal nn. → perineal nn. → dorsal n. of penis (clitoris) A. The Anal Region 3. Ischioanal (ischiorectal) fossa (坐骨肛门窝) pudendal canal (阴部管) pudendal nerve & internal pudendal v., a., [ischiorectal abscess 坐骨肛门窝脓肿] B. The Urogenital Region (triangle) 1. Superficial fascia of perineum (Colles) (会阴浅筋膜) The Urogenital Region 2. Superficial perineal space (会阴浅间隙) 1) superficial transverse muscle of perineum (会阴浅横肌) 2) bulbocavernous muscle (球海绵体肌) 3) ischiocavernous muscle (坐骨海绵体肌) The Urogenital Region 4) urogenital diaphragm (尿生殖膈) a. inferior fascia of urogenital diaphragm (尿生殖膈下筋膜) b. superior fascia of urogenital diaphragm (尿生殖膈上筋膜) The Urogenital Region c. deep perineal space (会阴深间隙) i. deep transverse muscle of perineum (会阴深横肌) ii. sphincter of urethra M: (尿道括约肌) urethrovaginal sphincter F: (尿道阴道括约肌) Section 3 The perineum pelvic diaphragm Urogenital diaphragm Section 3 The perineum Accessory gland • The greater vestibular (Bartholin’s) glands – On either side of vaginal orifice – Open into vestibule at orifice of vagina II. The external reproductive organs • • • • • • Mons pubis Greater lips of pudendum Lesser lips of pudendum Vaginal vestibule Clitoris Bulb of vestibule Hymen Section 3 The perineum The External Genital Organs (外 生殖器) A. THE SCROTUM (阴囊) B. THE PENIS (阴茎) The external reproductive organs Ⅰ) The scrotum • Pouch of thin skin lying below the root of the penis • Divided into two haves by septum of scrotum, contains testes and their ducts • Deep to skin is dartos coat , a connective tissue layer that contains many smooth muscle fibers which contracts in response to cold, pulling the testes closer to the body and wrinkling the skin The Scrotum (阴囊) cavity of tunica vaginalis (鞘膜腔) [hydrocele of tunica vaginalis 鞘膜积液] [varicocele 精索静脉曲张] Parietal peritoneum Transvers fascia Trasversus abdominis Obliquus internus abdominis Aponeurosis of obliquus externus abdominis External spermatic fascia Cremastter Internal spermatic fascia Tunica vaginalis of testis Ⅱ) The penis • Consists of the root, body and glans penis • Contains – Two cavernous body of penis – A cavernous body of urethra Skin-thin and loose – Prepuce of penis – Frenulum of prepuce The male urethra Three parts • Prostatic part Lies within the prostate and is the widest and most dilatable portion of urethra. • Membranous part Lies within the urogenital diaphragm surround by the sphincter of urethra. • Cavernous part Transverse the length of cavernous body of urethra. The Penis (阴茎) 2. Compositions (组成) 1) cavernous body of penis (阴茎海绵体) crus of penis (阴茎脚) 2) cavernous body of urethra (尿道海绵体) glans f penis ( 阴茎头) bulb of urethra (尿道球) The Penis (阴茎) [redundant prepuce 包皮过长] [phimosis 包皮狭窄] [paraphimosis 包皮嵌顿] [circumcision 包皮环切术] [smegma 包皮垢] [carcinoma of penis 阴茎癌] 2) neck of penis (阴茎颈) 3) body of penis (阴茎体) 4) root of penis (阴茎根) The Bulbourethral Gland (尿道球腺) The bulbourethral gland (尿道球腺) The urethral mucous glands (尿道粘膜腺) Function (功能): produce a mucous secretion sometime (up to several minutes) before ejaculation (射精前分泌) The Male Urethra(男尿道) A. Division (分部) 1. Prostatic part (前列腺部) 1) urethral ridge (尿道嵴) 2) seminal colliculus (精阜) 3) prostatic utricle (前列腺小 囊) 2. Membranous part (膜部) 3. Cavernous part (海绵体部) 1) bulb of urethra (尿道球) 2) navicular fossa (舟状窝) The Male Urethra(男尿道) B. Strictures (狭窄) 1. Internal urethral orifice (尿道内口) 2. Membranous portion (膜部) 3. External orifice (尿道外口) The Male Urethra(男尿道) C. Curvatures (弯曲) 1. Subpubic curvature (耻骨下曲) 2. Prepubic curvature (耻骨前 [urethrostenosis 尿道狭窄] The gluteal region and back of thigh and leg Cutaneous nerves Superior cluneal n. Medial cluneal n. Inferior cluneal n. suprapiriform foramen infrapiriform foramen Structures passing suprapiriform foramen • Superior gluteal n., a., v. from lateral to medial side Structures passing infrapiriform foramen • Sciatic n., posterior femoral cutaneous n., inferior gluteal n., a.,v., internal pudendal v., a., and pudendal n. from lateral to medial side Pudendal nerve, internal pudendal artery • These structures enter the gluteal region through the infrapiriform foramen. • They then curve forwards to enter the perineum through the lesser sciatic foramen. ★Sciatic nerve • Course: It arises from the sacral plexus and passes through infrapiriform foramen into the gluteal region, deep to gluteus maximus, passing midway between the greater trochanter of femur and ischial tuberosity to back of thigh, the nerve lies deep to the long head of biceps on the posterior surface of adductor magnus. The sciatic nerve usually ends half-way down the back of the thigh by dividing into the common peroneal and tibial nerves. • Distribution: semitendinosus, semimembranosus and biceps femoris and has articular branches to hip and knee joints Relationship of sciatic n. to the piriformis Boundaries of the popliteal fossa • Diamond-shaped • Upper lateral boundary: Biceps femoris • Upper medial boundary: semimembranosus and semitendinosus • Two lower boundaries are the heads of gastrocnemius • Posterior wall: deep fascia • Anterior wall: popliteal surface of the femur, the posterior capsule of the knee joint, and the fascia covering poplitells Contents of the popliteal fossa • Tibial and common peroneal nerves and their branches • Popliteal vein and its tributaries • Popliteal artery and its branches • Popliteal lympn nodes • Fatty tissue Popliteal artery • It begins at the adductor tendinous opening in. Here it is continuous with the femoral artery. It ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle where it divides into anterior and posterior tibial arteries. • Branches: 1. Superior, inferior, and middle genicular arteries 2. Muscular branches Popliteal vein • This is formed by the junction of the anterior and posterior tibial veins near the lower border of the popliteus muscle. Popliteal lymph nodes • There may be one or two nodes just under the deep fascia, close to the popliteal fossa vessels. • They drain the deep tissues of the leg and foot and the knee joint. They also receive superficial lymph vessels from the lateral side of the foot, the heel, and the back of the calf. These drain along the line of the small saphenous vein. The back of the leg • Find the small saphenous vein • Find the Sural nerve and Peroneal communicating nerve Find out • Gastrocnemius • Soleus • Plantaris • Tibial nerve • Popliteal artery and branches (Peroneal artery ) • Popliteus • Flexor hallucis longus • Flexor digitorum longus • Tibialis posterior