Study Notes - Johns Hopkins Medicine
advertisement

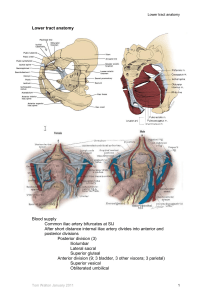
NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman’s lecture, fill in the topics. Anatomy above the arcuate line Skin Camper’s fascia Scarpa’s fascia External oblique aponeurosis Internal oblique aponeurosis Rectus muscle Internal oblique aponeurosis Transversus abdominis muscle Transversalis fascia peritoneum below the arcuate line Skin Camper’s fascia Scarpa’s fascia External oblique aponeurosis Internal oblique aponeurosis Rectus muscle Transversus abdominis muscle Transversalis fascia peritoneum Anterior Abdominal Wall landmarks Median umbilical foldsMedial umbilical folds – Lateral umbilical folds– Bones of pelvis Sacrum Coccyx Innominate bones Pubis Ischium Ilium Sacrotuberous – ischial tuberosity Æsacrum Sacrospinous – ischil spine Æ sacrum Anterior longitudinal ligament (ASC) Anal coccygeal ligament Pectineal ligament = Cooper’s ligament - along pectin pubis (Burch retropubic urethropexy) Pelvimetry Inlet true conjugate - AP diameter from superior margin pubic symphysis to sacral promontory (11cm) Obstetric conjugate – AP diameter that runs from back of pubic symphysis to sacral promontory (10cm), smallest conjugate. Diagonal conjugate – AP diameter from inferior margin of pubic symphysis to sacral promontory (11.5cm) Oblique diameter – from sacroiliac joint to contralateral iliopubic eminence (<13cm) Transverse diameter – widest distance across the pelvic brim (13.5cm) Midplane Outlet Pelvic shapes Gynecoid – Android – Anthropoid – Platypelloid – interspinous diameter - (10cm), smallest diameter, very important obstetrically. Site of deep transverse arrest. <9.5cm and there is a 50% chance of intervention during childbirth Transverse diameter – intertuberoud diameter - distance between ischial tuberosities (11.5cm) AP diameter – inferior aspect of pubic symphysis to tip of coccyx (10cm) Pubic arch Pelvic Vasculature External iliac Inferior epigastric artery (under fascia) Deep circumflex artery Æfemoral artery (passes through inguinal ligament) Internal iliac/hypogastric Anterior Obliterated umbilical Æ superior vesical Uterine Ævaginal Middle rectal (hemorrhoidal) Obturator Inferior gluteal Internal pudendal Æ inferior rectal Posterior Iliolumbar Lateral sacral Superior gluteal Collateral Circulation after hypogastric artery ligation Anterior div Systemic middle rectal (hypogastric) superior rectal (IMA) inferior rectal (hypogastric) Middle sacral Lumbar Hypogastric artery ligation Right angle clamp 2.5 - 3.0 cm distal to bifurcation of common iliac artery lateral Æ medial to void vein double ligate with 1-0 silk, don’t divide repeat on contralateral side Course of Pudendal artery and nerve Behind ischial spine Out greater sciatic In lesser sciatic Through alcock 3 branches of pudendal artery Inferior rectal Perineal Clitoral Posterior div lateral sacral iliolumbar Blood supply to the ureter Renal Ovarian Aorta Iliac/hypogastric Superior vesical Inferior vesical artery Blood supply to colon/rectum SMA - proximal 1/3 colon IMA (L2-3) - distal 1/3 transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum --left colic --sigmoidal --superior rectal (IMA) Middle rectal (hypogastric) Inferior rectal (pudendal) Nerves of pelvis Iliohypogastric (L1) Ilioinguinal (L2) Genitofemoral (L1-2) Lateral femoral cutaneous (L2-3) Femoral (L2-4, post) Obturator (L2-4) Sciatic (L4-5, S1-3 through greater sciatic foramen) Common perineal nerve (branch of sciatic) Muscles of the pelvic girdle Iliacus – flexes hip Psoas major – flexes body at hip and waist Piriformis – lateral rotator of hip Obturator externus and internus – lateral rotater of hip Levator ani (puborectalis, pubococcygeus, iliococcygeus) Coccygeus Superior hypogstric plexus = presacral nerve Hypogastric nerge Inferior hypogastric Pudendal Nerve Block Surgical Spaces Prevesical (space of Retzius) Vesicovaginal and vesicocervical Paravesical Rectovaginal Pararectal Retrorectal Presacral Perineum Anterior triangle Posterior triangle Compressor urethrae Urethrae sphincter Pelvic diaphragm Levator ani Puborectalis (90 degree anorectal angle)) Pubococcycges Iliococcygeus Coccygeus Function of pelvis diaphragm Close genital hiatos Create levator plate Anal Continence Mechanism Delancey level of support 1 - uterosacral, cardinal ligaments, support uterus and vaginal apex 2 - lateral attachements of endopelvic fascia and vagina to arcus tendineus fascia pelvis, support bladder, vagina and rectum 3 – perineal membrana and perineal body, support urethrovesical junction and perineum Uterosacral ligament suspensión Rectovaginal fascia attachments “boat in dry dock”