EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis
advertisement

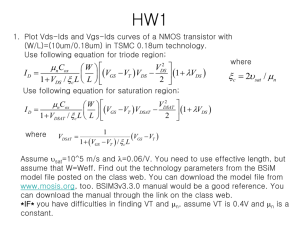
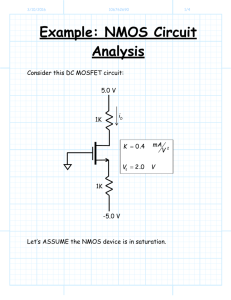
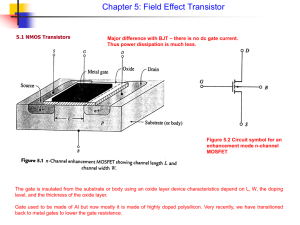
EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 3 MOS Transistor Device Characteristics Zhuo Feng 3.1 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Outline ■ Introduction ■ MOS Capacitor ■ NMOS I-V Characteristics ■ PMOS I-V Characteristics ■ Gate and Diffusion Capacitance ■ Nonideal Transistor Behavior ■ Process and Environmental Variations 3.2 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Introduction ■ ■ So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes a finite amount of current ► Depends on terminal voltages ► Derive current-voltage (I-V) relationships ■ Transistor gate, source, drain all have capacitance ► I = C (DV/Dt) -> Dt = (C/I) DV ► Capacitance and current determine speed ■ 3.3 Also explore what a “degraded level” really means Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis MOS Capacitor ■ Gate and body form MOS capacitor ■ Operating modes ► Accumulation polysilicon gate silicon dioxide insulator Vg < 0 + - ► Depletion p-type body ► Inversion (a) 0 < V g < Vt + - depletion region (b) V g > Vt + - (c) 3.4 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis inversion region depletion region Terminal Voltages ■ Mode of operation depends on Vg, Vd, Vs ► Vgs = Vg – Vs ► Vgd = Vg – Vd ► Vds = Vd – Vs = Vgs - Vgd ■ Source and drain are symmetric diffusion terminals ► By convention, source is terminal at lower voltage ► Hence Vds 0 ■ ■ NMOS body is grounded. First assume source is 0 too. Three regions of operation Vg ► Cutoff ► Linear ► Saturation Vgs Vs 3.5 + Vgd - + Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis - Vds + Vd NMOS Cutoff ■ No channel ■ Ids = 0 Vgs = 0 + - g s d n+ n+ p-type body b 3.6 + - Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Vgd NMOS Linear ■ ■ Channel forms Current flows from d to s Vgs > Vt ► e- from s to d ■ ■ g + - Ids increases with Vds Similar to linear resistor + - s d n+ n+ Vgd = Vgs Vds = 0 p-type body b Vgs > Vt g + s d n+ n+ p-type body b 3.7 + - Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Vgs > Vgd > Vt Ids 0 < Vds < Vgs-Vt NMOS Saturation ■ Channel pinches off ■ Ids independent of Vds ■ We say current saturates ■ Similar to current source Vgs > Vt + - g + - d Ids s n+ n+ p-type body b 3.8 Vgd < Vt Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Vds > Vgs-Vt I-V Characteristics ■ In Linear region, Ids depends on ► How much charge is in the channel? ► How fast is the charge moving? 3.9 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Channel Charge ■ MOS structure looks like parallel plate capacitor while operating in inversion ► Gate – oxide – channel ■ ■ ■ Qchannel = CV C = Cg = eoxWL/tox = CoxWL V = Vgc – Vt = (Vgs – Vds/2) – Vt polysilicon gate W tox L n+ n+ SiO2 gate oxide (good insulator, eox = 3.9) p-type body gate Vg + + Cg Vgd drain source Vgs channe Vs Vd l + n+ n+ Vds p-type body 3.10 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Cox = eox / tox Vgc=(Vgs+Vgd)/2 =Vgs-Vds /2 Carrier velocity ■ Charge is carried by e■ Carrier velocity v proportional to lateral E-field between source and drain ■ v = mE (m is called mobility) ■ E = Vds/L ■ Time for carrier to cross channel: ►t=L/v 3.11 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis NMOS Linear I-V ■ Now we know ► How much charge Qchannel is in the channel ► How much time t each carrier takes to cross Qchannel I ds t W mCox L V V Vds gs t 2 Vds Vgs Vt Vds 2 3.12 V ds Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis W = mCox L NMOS Saturation I-V ■ If Vgd < Vt, channel pinches off near drain ► When Vds > Vdsat = Vgs – Vt ■ Now drain voltage no longer increases current V I ds Vgs Vt dsat 2 3.13 V 2 gs Vt V dsat 2 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis NMOS I-V Summary ■ Shockley 1st order transistor models (long-channel) 0 V I ds Vgs Vt ds 2 2 Vgs Vt 2 3.14 Vgs Vt V V V ds ds dsat Vds Vdsat Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis cutoff linear saturation Example ■ We consider a 0.6 mm process ► From AMI Semiconductor ► tox = 100 Å 2.5 ► m = 350 cm2/V*s ■ Plot Ids vs. Vds ► Vgs = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ► Use W/L = 4/2 l 2 Ids (mA) ► Vt = 0.7 V Vgs = 5 1.5 Vgs = 4 1 Vgs = 3 0.5 0 0 Vgs = 2 Vgs = 1 1 2 3 Vds 3.9 8.85 1014 W W W 2 mCox 350 120 m A / V L 8 L 100 10 L 3.15 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis 4 5 PMOS I-V ■ All dopings and voltages are inverted for PMOS ■ Mobility mp is determined by holes ► Typically 2-3x lower than that of electrons mn ► 120 cm2/V*s in AMI 0.6 mm process ■ Thus PMOS must be wider to provide same current ► In this class, assume mn / mp = 2 ► *** plot I-V here 3.16 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Capacitance ■ ■ Any two conductors separated by an insulator have capacitance Gate to channel capacitor is very important ► Creates channel charge necessary for operation ■ Source and drain have capacitance to body ► Across reverse-biased diodes ► Called diffusion capacitance because it is associated with source/drain diffusion 3.17 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Gate Capacitance ■ Approximate channel as connected to source ■ Cgs = eoxWL/tox = CoxWL = CpermicronW (minimum L) ■ Cpermicron is typically about 2 fF/mm polysilicon gate W tox n+ L n+ SiO2 gate oxide (good insulator, eox = 3.9e0) p-type body 3.18 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Diffusion Capacitance ■ Csb, Cdb ■ Undesirable, called parasitic capacitance ■ Capacitance depends on area and perimeter ► Use small diffusion nodes ► Comparable to Cg for contacted diff ► ½ Cg for uncontacted ► Varies with process 3.19 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Ideal vs. Simulated nMOS I-V Plot ■ 65 nm IBM process, VDD = 1.0 V Ids (mA) Simulated Vgs = 1.0 Ideal 1200 Velocity saturation & Mobility degradation: Ion lower than ideal model predicts 1000 Ion = 747 mA @ Channel length modulation: V = V = V gs ds DD Saturation current increases with Vds Vgs = 1.0 800 Vgs = 0.8 600 Velocity saturation & Mobility degradation: Saturation current increases less than quadratically with Vgs 400 Vgs = 0.8 Vgs = 0.6 200 Vgs = 0.6 Vgs = 0.4 0 Vds 0 3.20 0.2 0.4 0.6 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis 0.8 1 ON and OFF Current ■ Ion = Ids @ Vgs = Vds = VDD ► Saturation Ids (mA) 1000 Ion = 747 mA @ Vgs = Vds = VDD 800 Vgs = 1.0 600 Vgs = 0.8 400 Vgs = 0.6 200 ■ Ioff = Ids @ Vgs = 0, Vds = VDD Vgs = 0.4 0 Vds 0 0.2 ► Cutoff 3.21 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 Electric Fields Effects ■ Vertical electric field: Evert = Vgs / tox ► Attracts carriers into channel ► Long channel: Qchannel Evert ■ Lateral electric field: Elat = Vds / L ► Accelerates carriers from drain to source ► Long channel: v = mElat 3.22 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Mobility Degradation ■ High Evert effectively reduces mobility ► Collisions with oxide interface 3.23 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Velocity Saturation ■ At high Elat, carrier velocity rolls off ► Carriers scatter off atoms in silicon lattice ► Velocity reaches vsat ▼ Electrons: 107 cm/s ▼ Holes: 8 x 106 cm/s ► Better model 3.24 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Vel Sat I-V Effects ■ Ideal transistor ON current increases with VDD2 2 W Vgs Vt Vgs Vt L 2 2 2 I ds mCox ■ Velocity-saturated ON current increases with VDD I ds CoxW Vgs Vt vmax ■ Real transistors are partially velocity saturated ► Approximate with a-power law model ► Ids VDDa ► 1 < a < 2 determined empirically (≈ 1.3 for 65 nm) 3.25 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis a-Power Model 0 V I ds I dsat ds Vdsat I dsat 3.26 Vgs Vt cutoff Vds Vdsat linear Vds Vdsat saturation I dsat Pc V 2 gs Vt a Vdsat Pv Vgs Vt a /2 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Channel Length Modulation ■ Reverse-biased p-n junctions form a depletion region ► Region between n and p with no carriers ► Width of depletion Ld region grows with reverse bias ► Leff = L – Ld ■ Shorter Leff gives more current ► Ids increases with Vds ► Even in saturation GND Source VDD Gate VDD Drain Depletion Region Width: Ld n + 3.27 L Leff p GND Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis n + bulk Si Channel Length Modulation I ds V 2 gs Vt 1 lVds 2 ■ l = channel length modulation coefficient ► not feature size ► Empirically fit to I-V characteristics 3.28 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Threshold Voltage Effects ■ Vt is Vgs for which the channel starts to invert ■ Ideal models assumed Vt is constant ■ Really depends (weakly) on almost everything else: ► Body voltage: Body Effect ► Drain voltage: Drain-Induced Barrier Lowering ► Channel length: Short Channel Effect 3.29 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Body Effect ■ Body is a fourth transistor terminal ■ Vsb affects the charge required to invert the channel ► Increasing Vs or decreasing Vb increases Vt Vt Vt 0 g fs Vsb fs ■ fs = surface potential at threshold fs 2vT ln NA ni ► Depends on doping level NA ► And intrinsic carrier concentration ni ■ g = body effect coefficient g 3.30 tox e ox 2qe si N A 2qe si N A Cox Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Short Channel Effect ■ In small transistors, source/drain depletion regions extend into the channel ► Impacts the amount of charge required to invert the channel ► And thus makes Vt a function of channel length ■ Short channel effect: Vt increases with L ► Some processes exhibit a reverse short channel effect in which Vt decreases with L 3.31 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Leakage ■ What about current in cutoff? ■ Simulated results ■ What differs? ► Current doesn’t go to 0 in cutoff 3.32 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Leakage Sources ■ Subthreshold conduction ► Transistors can’t abruptly turn ON or OFF ► Dominant source in contemporary transistors ■ Gate leakage ► Tunneling through ultrathin gate dielectric ■ Junction leakage ► Reverse-biased PN junction diode current 3.33 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Subthreshold Leakage ■ Subthreshold leakage exponential with Vgs Vgs Vt 0 Vds kg Vsb Vds nvT vT I ds I ds 0 e 1 e ■ n is process dependent ► typically 1.3-1.7 ■ Rewrite relative to Ioff on log scale ■ S ≈ 100 mV/decade @ room temperature 34 3.34 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Gate Leakage ■ Carriers tunnel thorough very thin gate oxides ■ Exponentially sensitive to tox and VDD ► A and B are tech constants ► Greater for electrons ▼ So nMOS gates leak more ■ Negligible for older processes (tox > 20 Å) ■ Critically important at 65 nm and below (tox ≈ 10.5 Å) 3.35 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis From [Song01] Junction Leakage ■ Reverse-biased p-n junctions have some leakage VvD T I D I S e 1 ► Ordinary diode leakage ► Band-to-band tunneling (BTBT) ► Gate-induced drain leakage (GIDL) ■ Is depends on doping levels ► And area and perimeter of diffusion regions ► Typically < 1 fA/mm2 (negligible) p+ n+ n+ p+ p+ n well p substrate 3.36 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis n+ Temperature Sensitivity ■ Increasing temperature ► Reduces mobility ► Reduces Vt ■ ION decreases with temperature ■ IOFF increases with temperature I ds increasing temperature Vgs 3.37 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis So What? ■ So what if transistors are not ideal? ► They still behave like switches. ■ But these effects matter for… ► Supply voltage choice ► Logical effort ► Quiescent power consumption ► Pass transistors ► Temperature of operation 3.38 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Parameter Variation ■ Transistors have uncertainty in parameters ► Process: Leff, Vt, tox of nMOS and pMOS ► Vary around typical (T) values ► Leff: short ► Vt: low fast ■ Fast (F) FF SF ■ Slow (S): opposite ■ Not all parameters are independent pMOS ► tox: thin TT for nMOS and pMOS FS slow SS slow 3.39 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis nMOS fast Environmental Variation ■ VDD and T also vary in time and space ■ Fast: ► VDD: high ► T: 3.40 low Corner Voltage Temperature F 1.98 0C T 1.8 70 C S 1.62 125 C Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Process Corners ■ Process corners describe worst case variations ► If a design works in all corners, it will probably work for any variation. ■ Describe corner with four letters (T, F, S) ► nMOS speed ► pMOS speed ► Voltage ► Temperature 3.41 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Important Corners ■ Some critical simulation corners include Purpose nMOS pMOS VDD Temp Cycle time S S S S Power F F F F Subthreshold leakage F F F S 3.42 Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis