Groundwater Flashcards
advertisement
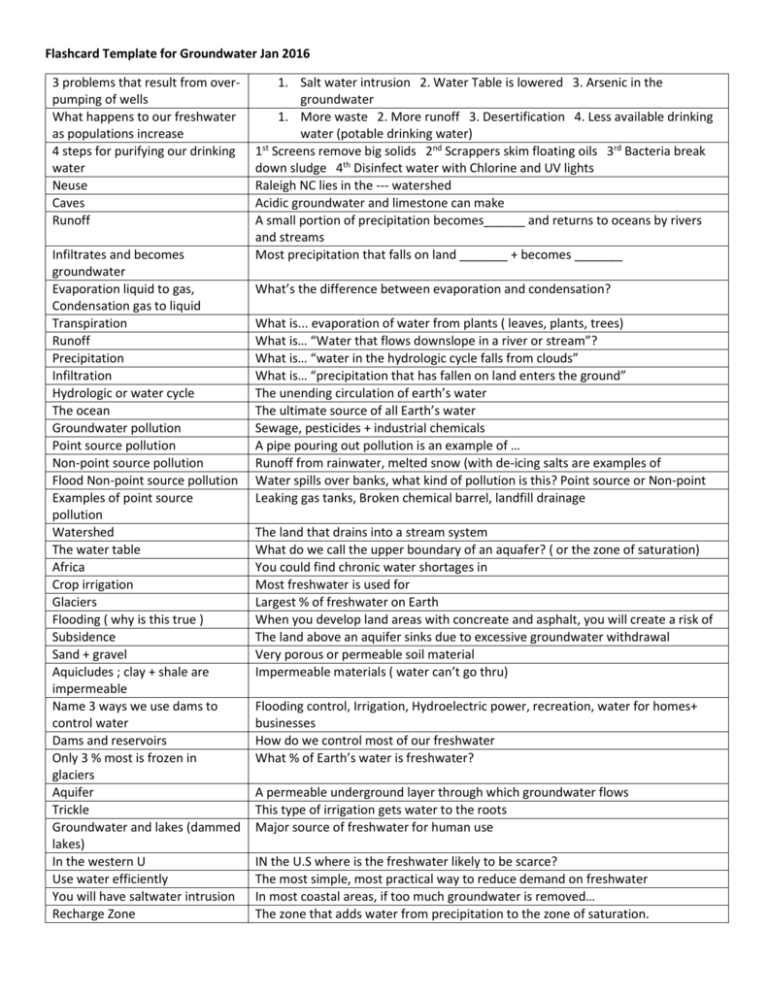
Flashcard Template for Groundwater Jan 2016 3 problems that result from overpumping of wells What happens to our freshwater as populations increase 4 steps for purifying our drinking water Neuse Caves Runoff Infiltrates and becomes groundwater Evaporation liquid to gas, Condensation gas to liquid Transpiration Runoff Precipitation Infiltration Hydrologic or water cycle The ocean Groundwater pollution Point source pollution Non-point source pollution Flood Non-point source pollution Examples of point source pollution Watershed The water table Africa Crop irrigation Glaciers Flooding ( why is this true ) Subsidence Sand + gravel Aquicludes ; clay + shale are impermeable Name 3 ways we use dams to control water Dams and reservoirs Only 3 % most is frozen in glaciers Aquifer Trickle Groundwater and lakes (dammed lakes) In the western U Use water efficiently You will have saltwater intrusion Recharge Zone 1. Salt water intrusion 2. Water Table is lowered 3. Arsenic in the groundwater 1. More waste 2. More runoff 3. Desertification 4. Less available drinking water (potable drinking water) st 1 Screens remove big solids 2nd Scrappers skim floating oils 3rd Bacteria break down sludge 4th Disinfect water with Chlorine and UV lights Raleigh NC lies in the --- watershed Acidic groundwater and limestone can make A small portion of precipitation becomes______ and returns to oceans by rivers and streams Most precipitation that falls on land _______ + becomes _______ What’s the difference between evaporation and condensation? What is... evaporation of water from plants ( leaves, plants, trees) What is… “Water that flows downslope in a river or stream”? What is… “water in the hydrologic cycle falls from clouds” What is… “precipitation that has fallen on land enters the ground” The unending circulation of earth’s water The ultimate source of all Earth’s water Sewage, pesticides + industrial chemicals A pipe pouring out pollution is an example of … Runoff from rainwater, melted snow (with de-icing salts are examples of Water spills over banks, what kind of pollution is this? Point source or Non-point Leaking gas tanks, Broken chemical barrel, landfill drainage The land that drains into a stream system What do we call the upper boundary of an aquafer? ( or the zone of saturation) You could find chronic water shortages in Most freshwater is used for Largest % of freshwater on Earth When you develop land areas with concreate and asphalt, you will create a risk of The land above an aquifer sinks due to excessive groundwater withdrawal Very porous or permeable soil material Impermeable materials ( water can’t go thru) Flooding control, Irrigation, Hydroelectric power, recreation, water for homes+ businesses How do we control most of our freshwater What % of Earth’s water is freshwater? A permeable underground layer through which groundwater flows This type of irrigation gets water to the roots Major source of freshwater for human use IN the U.S where is the freshwater likely to be scarce? The most simple, most practical way to reduce demand on freshwater In most coastal areas, if too much groundwater is removed… The zone that adds water from precipitation to the zone of saturation.