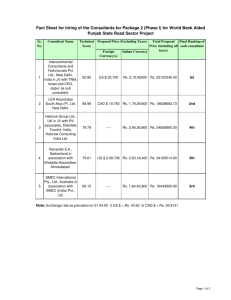
20CC Ltd
advertisement

Systems Thinking Overview TNT 2008 Sources from The Open University acknowledged © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants My Background • • • • • • • Fellow of Mech. Engg. & Management 40 years applying systems to business 13 years as independent consultant 25 years tutoring OU systems courses External examiner to Arab OU Lecturer on analytical techniques for MBA Course can be tailored in time & content © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Systems Thinking - Background • Formalised in ’60s by Peter Checkland • Need grew as society became increasingly “interconnected” • Opposite to “reductionism”, breaking things down into components, as most Work Study • Decreases the detail by “going up” to see the whole picture © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Systems Thinking - Utility • • • • Holistic view of human systems Systems that have a purpose Are complex and interconnected Results - intended, unintended & emergent properties – Try for them not to be a surprise © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Systems Thinking - Principles • Looks from a higher level to sense the issues • Uses many techniques to understand a problem • Adopts analytical management techniques to decide what to do • Embraces advanced management techniques for action and implementation © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Systems Thinking – A Toolbox • So the method helps progressively – To sense the context of the problem – To understand the issues – To decide upon options to solve – To act to an agreed plan • Systems Thinking has its own language • Integrates with advanced management concepts © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants The objective of the course hammered hammer hammerer © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Course Aims • Encourage an interest in systems thinking • Develop an awareness of systems – Their properties – Their interconnectedness • Enable student to start to think systemically – Or at least differently, openly • Create confidence to test on real problems © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Learning Outcomes • • • • • Understand where systems thinking is different Understand the meaning of systems terms Be alert to the perspectives of others Create 6 types of graphic analysis tool Understand how systems thinking can be useful • Create confidence in using some aspects • Provide links to other management concepts © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Course Modules • • • • • • • • Module 1 – Intros, Overview, ice breaker Module 2 – Stakeholder analysis Module 3 – Sensing & diagrams Module 4 – Systems maps Module 5 – Understanding & diagrams Module 6 – Modelling, Indicators & Deciding Module 7 – Acting & key management insights Module 8 – Reporting, wrap up, feedback © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Own Language - Key Concepts Worldview Perspectives Stakeholders Messes Difficulties Trap Holistic Systemic Reductionist Systematic System Purpose Boundary System of Interest Hierarchy Level Sub-system Indicators Control Complexity Interconnected Information © 20CC Ltd Emergence Unintended Consequences Modelling Environment Feedback 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants System • Connected components which do something – Systems must have an intended Purpose – May have emergent properties – not designed, but desirable – Or unintended consequences – not designed, but undesirable • They have a hierarchy – Levels – Sub-systems – Environment © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Setting a Boundary (Purpose) • Deciding a Boundary is key • Defines or isolates what is practical to consider • Determines focus of study • Determines the Environment, • So Limits and Defines the Study – inputs to the Terms of Reference © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Holistic • Systematic or Reductionist – Perfect for many problems – Step after step towards the solution – The “traditional” approach of engineers • Systems Thinking is about analysing complex problems in a holistic manner – Systemic, the total system – Look at all the issues and their implications – There will be many Inter-connections & Complexity © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Stakeholders & Perspectives • We recognise that we are not all the same • We attempt to maximise the consensus • Care can usually create an optimum solution • Stakeholders, no definition needed here – Analysis can often be quite simple yet powerful as a 2x2 matrix © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Boston Market Matrix KEY Easier PH W S S = Security F = Food MD = Medical devices P = Pharma C = Cosmetics H = Hospitals PH = HPA W = Water MD Ease of sale F P C Harder © 20CC Ltd Lower Risk to Reputation Higher 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Modelling & Indicators • Modelling performance of system/systems • Examples – Economies – Spread of infection – Insurance risks • Deciding on “true” indicators – Partial indicators • The change in value of Key Indicators © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants The SUDA Methodology • There are many methodologies • This is one, sensible disciplined approach – Sensing the problem – Understanding the issues – Deciding on the options for action – Acting – taking action © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Link to Diagramming • Each type has an optimum use – Sort out your own ideas – Sensing – Suggest possible causes - Understanding – Suggest points of interest - Understanding – Determine impacts of actions - Deciding – Explain actions which may help – Acting © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Diagramming A key part of understanding & Communicating to the Steering Group © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Diagramming • The common types – Spray Diagram – Rich Picture – Systems Map – Influence Diagram – Multiple Cause Diagram – Sign Graph – Control Diagram © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Why use Diagrams • As an aid to study and note taking – Spray diagram • Convince others with emotion Rich Picture – with facts all the rest • Analyse how it works • Many diagram types – Convey information – facts & stimulate ideas • Fortunately T214 only uses 5 types • A picture is worth a 1,000 words © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Factors to Consider • Purpose of the diagram – to aid your own thinking – to inform or convince others • Assess the Influence or Effects of the factors involved • Estimate the effects of key factors © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Diagrams used for Sensing • Sensing the problem – Spray diagram – Rich picture – Systems map (this can also be used in the understanding phase to determine the structure of problems) © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Spray Diagram • Excellent for note taking – Use one per topic in initial studies – Then look for common themes – Re-draw showing connections to central topic • Not just a list, should convey some key relationships and the relative interests of stakeholders © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Spray Diagram • Similar to diagrams known as “Mind Maps” • Excellent for note taking – Use one per article/book when studying – Then look for common themes between the sample – Re-draw showing connections to central topic • Not just a list, should convey some key relationships and relative interests of key stakeholders or issues © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Spray Diagram of The Institution Regions Staff Events Assessment Process ILOs BFIM R. Managers Member Recruitment Member Services Promotion Proceedings The Institution Publications Admin Fees Non-members PE Public Perception Press Influence Public Government Marketing & PR © 20CC Ltd Fig. 1 Competing Institutions 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Spray Diagram Exercise • Consider examples passing around, mainly from students • Think of the topic “My Journey to this Tutorial” • Individually write a list of the stakeholders involved © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Rich Picture • Requires a little more feel for the topic • Does require an element of artistic talent – Do not get round this by excessive clip-art – Can convey emotion like art or photos • You know good RPs when you see them – They usually show a linking thread of ideas • Road from small (closed) shops to busy supermarkets • Pollution in river from industry to leisure areas • Studying at home with problems & distractions © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Rich Picture • A little more knowledge of the topic • Does require some artistic talent – Can convey emotion like good art or photos • You know good ones when you see them – They usually show a linking thread of ideas • Road from small (closed) shops to supermarkets • Pollution in river from industry outflow to fishermen • Studying at home with problems & distractions © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Studying at Home © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Rich Picture Exercise • Consider examples passing around, mainly from students • Consider all the SDs of “My Journey to this Tutorial” Now draw a Rich Picture in groups © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Systems Map • Show relationship between systems and components of systems • Must have a named boundary – may need to experiment with the boundary • • • • Want to see levels Some overlapping is acceptable Each sub-system must be named We have mentioned where conventions matter 20CC Ltd © 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants A Relevant Example © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Systems Map Exercise • Consider examples passing around, mainly from students • Think of the topic “Where I Live” • Individually write a list of the entities involved © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Systems Map of The Institution The Institution Governance TB Disc. M Recruit QMB Learned Soc C Outsource Co Regions Audit Admin Events TSB LASC Divns IT WP Finance FM TACs Grps Cater Room Book Development Public Services M Services MB Pubs CPD Lib BF Bks ILOs Proc PE BC Govt.Register © 20CC Ltd Fig. 2 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Example Problems • The “practitioner” course allows groups to work on current topical examples • They witness varying perspectives • The observe new insights © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Diagrams for Understanding • Understanding the problem – Systems map – Influence diagram – Multiple cause diagram – Sign graph – Modelling techniques and flow diagrams © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Influence Diagram on Potential Members Local Events Members National Events Government Service Prestige National Press Profit Qualified Non Members PR Fig. 3 © 20CC Ltd Public 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants MC Diagram of Delivery National TACs (c.30) Grps/WPs (c.15) Local Local Events No.1 Room National Events Centres (23) Regions (16) Other Room Members Served Local Room Branches Areas Panels Electronic Poss. Profit ? More No.1 Rm Hire Non-members Served Fig. 4 © 20CC Ltd Small Costs 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Techniques for Deciding • Sign Graphs or Control Diagrams • Multiple Criteria analysis (MCA) • Strength Weakness Opportunity & Threat (SWOT) • Social, Technical, Economic & Political (STEP) • 4 Ws & an H What, How, Why, When & Where? • Modelling © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Modelling • Selection of techniques • Spreadsheets – Pre-formatted – “Self built” • Prediction of changed performance • Essential to decide/agree indicators – Qualitative – Quantitative © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Frequently Referenced Authors • • • • • Handy 4 cultures Hofstede’s culture categories Bates pathologies Pfeffer Sterner and many others © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Frequently Referenced Concepts • • • • Top down, bottom up Emergent & Managed Change Problem Articulating Skills Simplifying Strategies – Selective attention, Assuming continuity over time, Local focus, Typifying, Averaging • Colonisation, Collaboration • Interpenetration, boundary people, interlocking elites © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Comment on Modules • Modules 1 – 6 can be expanded to 2 days • Client specific project preparation can be added to a third day • Arab OU tutor training of 18 hours of material • A more in depth follow-up is possible © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Course Delivery • This course is tailored in time & content • Objective: – Management overview – Practitioner team – An OU qualification 2 - 4 hours 2 – 3 days 2 – 3 years • Group size 4 - 12 © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Course Deliveries • Many years to OU students – 16 hours pa • Arab OU tutors – 24 hours • Various commercial clients © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Influence Diagram • A influences B, not B certainly follows A – Not a flow diagram • Can map onto a Systems Map, but go to individual entities not (sub) systems • Should show – a boundary although you can start without one – arrows show the direction of influence – have a key to the strength of influence 20CC • When analysing them it is usually best to Ltd © 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Influence Diagram - Hints • • • • • • • • • • • © 20CC Ltd Basically Systems Maps with lines of influence added Like SMs, snapshots of the system of interest Use to highlight key influences between components Be selective - show important influences only Use space and relative distance to indicate nature of relationship Arrows are used to indicate direction of influence Never double headed arrows - use two arrows Nearly always arrows of influence from one entity to another Use arrows of different thickness to denote different strengths of influence Provide a key Keep crossed lines to a minimum - redraw to avoid 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Drawing a ID • Start with topic of key interest in centre of space • Add the major relevant influences • Add the “next layer” of contributory causes and their links • Aim for between 7 and 15 “entities” • Revise and iterate, but keep your discarded versions • Experiment with the appropriate Boundary • Review the purpose • It is a part of the ART of communication 20CC Ltd © 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Influence Diagram Exercise • Consider examples passing around, mainly from students • Think of the topic “The choice of method of getting Children to School” • Individually write a list of the factors involved Now draw an Influence Diagram in groups © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Cause and Effect (1) Cause • • • • Do “That” again Trip to the Pictures One for the Road Do not follow WebZone Effect (Ultimate) • • • • No Sweets No GCSE! No Driving Licence No T205 pass Examples indicate, that there may be many links in the chain © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Cause & Effect (2) • A single cause can have one Effect • A single Cause can have multiple Effects • Number of single Causes produce the same Effect © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Multiple Cause Diagram • A causes B • Should show – a boundary and – the direction of cause • When using them it is often best to focus on concentrations of effects © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Good example © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Drawing a MC Diagram • Start with topic of key interest in centre of space • Add the major relevant causes • Add the “next layer” of contributory causes and their links • Aim for between 7 and 15 “entities” • Revise and iterate, but keep your discarded versions • Experiment with the appropriate Boundary • Review the purpose • It is a part of the ART of communication 20CC Ltd © 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants MC Diagram Exercise - Scout Hut • Draw a MCD of the ‘messy problem’ ‘the scout group isn’t meeting’ based on the following types of event: – – – – – – – – – – – – © 20CC Ltd Holes in fencing The scout hut is in disrepair No-one with financial skill Damage done by young people No fundraising Budget is unrealistic Other people do not respect the property Not enough money Damage done by vandals Young people do not respect the property Property is not secure Young people are not involved in the upkeep 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Key Features of MC Diagrams • Most interesting outcomes – RESULTS • Main factors effecting THE INTERESTING RESULTS – How are they measured • Qualitatively on the diagram • Quantitatively via a Sign Graph • Search for more links • Search for feedback loops © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Comparison between IDs & MCs INFLUENCE DIAGRAMS • • • • • • • • • Influences that have an effect on a situation, a broad view at an instant Represents main structural features and relationships of a situation Useful for exploring interrelationships Title Words labelling components in blobs of different sizes Arrows – representing different degrees of influence by thicknesses, dotted Key needed Arrows may be labelled System boundary distinguishing the system of interest from the environment © 20CC Ltd MULTIPLE CAUSE DIAGRAMS • • • • • • • • • Causes, leading to events or types of event, sequential, not a snapshot Represents causal relationships between states and events Useful for exploring why something goes wrong, or keeps re-occurring Title States or situations in phrases Arrows, single-headed, one thickness, all meaning ‘leads to, causes’ No key needed Arrows may be labelled System boundary is recommended, but I believe essential 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Considering The Boundary (Purpose) • Think about the whole – holistic • Think about how it all works - systemic • Define or isolate that part which is practical to consider • So defines and limits your Study • Or the Terms of Reference for a consultant © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Sign Graph • Basically a MCD, but with a + or – sign added to each cause • Is the effect at one end, in the same direction at the other? • Can be more, less, in/decrease, higher, lower, etc. – More car parking creates more car journeys • Label with +ve if the same effect – Decrease in train fares, increases passenger journeys • Label with –ve if the opposite effect • Check the loops for –ve signs only – If ODD number, negative feedback, generally good – If EVEN number, positive feedback, generally bad © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Feedback • Positive Feedback – Amplifies variance – Can be unstable and dangerous • Negative feedback – Reduces variance – Is stable and SAFER • A long time lag © 20CC Ltd – Can amplify variance, before corrective action is taken 20CC Ltd – Is potentially dangerous Independent Consultants Control Diagram • Closed Loop – Ignore Open Loop, it only exists in theory • A system has – – – – – © 20CC Ltd Input Transformation Process Measured Output Comparison of the Output with desired Goal Actuator to adjust Input 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Control Diagram or Model Input(s) “Black Box” Transformation Process Output(s) Feedback Loop © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Control Diagram or Model Input(s) Actuator “Black Box” Transformation Process Output(s) Feedback Goal © 20CC Ltd Comparator 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Summary of Factors to Consider • Purpose of the diagram – to aid your own thinking – to inform or convince others • Assess the Influence or Effects of the factors involved • Estimate the Size of the effects of the factor • Use what you have learned in the rest of your TMA © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants And Finally • Do practice doing the diagrams correctly to the conventions • Can be more flexible on these conventions, once it is clear they have been mastered – Diagrams are tools – Their value is their utility for you and/or your audience © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants Any Questions? Now or later to consult@20cc.co.uk 020 8680 3511 or 0788 799 2427 © 20CC Ltd 20CC Ltd Independent Consultants