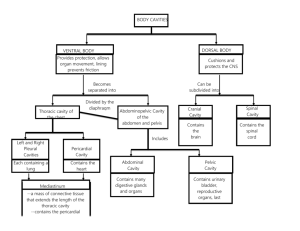
Body Organization and Terminology LAB
advertisement

Body Organization and Terminology Background The major features of the human body include certain cavities, a set of membranes associated with these cavities, and a group of organ systems composed of related organs. In order to communicate effectively with each other about the body, scientists have devised names to describe these body features. They also have developed terms to represent the relative positions of body parts, imaginary planes passing through these parts, and body regions. Materials Needed Textbook Human torso model Purpose of the Exercise Review the organizational pattern of the human body, review its organ systems and the organs included in each system, and become acquainted with the terms used to describe the relative position of body parts, body sections, and body regions. Procedure A – Body Cavities and Membranes 1. Label figures 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3. 2. Locate the following features on the human torso model: dorsal cavity, cranial cavity, spinal cavity, ventral cavity, thoracic cavity, mediastinum, pleural cavity, pericardial cavity, diaphragm, abdominopelvic cavity, abdominal cavity, pelvic cavity. 3. Complete Parts A and B of the laboratory report. Procedure B – Relative Positions, Planes, Sections, and Regions 1. Label figures 2.4 and 2.5. 2. Complete Parts C and D of the laboratory report. Figure 2.1 Label the major body cavities. Figure 2.2 Label the major body cavities and organs in this anterior view. Figure 2.3 Label the thoracic membranes and cavities in (a) and the abdominopelvic membranes and cavity in (b) as shown in these superior views of transverse sections. Figure 2.4 Label the planes represented in this illustration. Figure 2.5 Label (a) the regions and (b) the quadrants of the abdominopelvic area. Part A Match the body cavities in column B with the organs contained in the cavities in column A. Place the letter of your choice in the space provided. Column A ___ 1. Liver Column B a. Cranial cavity ___ 2. Lungs b. Spinal cavity ___ 3. Spleen c. Thoracic cavity ___ 4. Stomach d. Abdominal cavity ___ 5. Brain e. Pelvic cavity ___ 6. Gallbladder ___ 7. Urinary bladder ___ 8. Spinal cord ___ 9. Rectum ___10. Heart ___11. Esophagus ___12. Trachea Part B Complete the following: 1. The membrane on the surface of the lung is called the ____________________. 2. The membrane on the surface of the heart is called the ___________________. 3. The membrane that lines the wall of the abdominopelvic cavity is called the _____________________. 4. The membrane on the surface of the stomach is called the _________________. 5. The thin, watery fluid located between the pleural membranes is called ________________________. 6. Epicardium is another name for ________________________. 7. The region of the thoracic cavity between the two lungs is called the _________________________. 8. The muscular structure that separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities is called the _________________________. Part C Indicate whether each of the following sentences makes correct or incorrect usage of the word in boldface type (assume that the body is in the anatomical position). If the sentence is incorrect, supply a term that will make it correct in the space provided. 1. The mouth is superior to the nose. _____________ 2. The stomach is inferior to the diaphragm. _____________ 3. The trachea is anterior to the spinal cord. _____________ 4. The larynx is posterior to the esophagus. _____________ 5. The heart is medial to the lungs. _____________ 6. The kidneys are inferior to the adrenal glands. _____________ 7. The hand is proximal to the elbow. _____________ 8. The knee is proximal to the ankle. _____________ 9. Blood in deep blood vessels gives color to the skin. _____________ 10. A peripheral nerve passes from the spinal cord into the limbs. _____________ 11. The spleen and gallbladder are ipsilateral. _____________ 12. The dermis is the superficial layer of the skin. _____________ Part D Identify each of the planes and sections represented in figure 2.6. 1. __________________ _______ 4. _____ ____________________ 2. __________________ _______ 5. ________ 3. ________________ _________ 6. ____________ _________________ _____________ Posterior Anterior Critical Thinking Application State the quadrant of the abdominopelvic cavity where the pain or sound would be located for each of the six common conditions listed. In some cases, there may be more than one correct answer and pain is sometimes referred to another region. This phenomenon, called referred pain, occurs when pain is interpreted as originating from some area other than the parts being stimulated. 1. Stomach ulcer _______________ 2. Appendicitis _______________ 3. Bowel sounds _______________ 4. Gallbladder attack _______________ 5. Kidney stone in left ureter _______________ 6. Ruptured spleen _______________