Carbohydrates – Complex (Polysaccharides)
advertisement

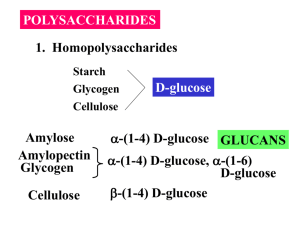
amylose Amylopectin or glycogen Polysaccharides Glycogen and Amylopectin Structures Glycogen and Amylopectin are a(1-4) chains with with a(1-6) branches Amylopectin Glycogen cellulose cellulose Carbohydrates – Complex (Polysaccharides) Cellulose fibers Cellulose = polysaccharide found in plant cell walls Macrofibril Microfibril Chains of cellulose chitin N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units in (b-->4) linkage Glycoprotein • Glycoproteins are proteins that contain oligosaccharide chains (glycans) covalently attached to their polypeptide side-chains. • The process of attaching the glycans is known as glycosalation. • The sugar groups attached to glycoprotein can assist in protein folding or improve a proteins’ stability. Functions of Glycoproteins Function Glycoprotein Structural Molecule Collagen Lubricant and Protective Agent Mucins Transport Molecule Transferrin, ceruloplasmin Immunologic Molecule Immunoglobins, histocompatibility antigens Enzyme Various, e.g alkaline phosphatase Cell Attachment-recognition site Proteins involved in cell to cellc ommunication Interact with specific carbohydrates Lectins, selectins (cell adhesion lectins), antibodies Functions of Glycoproteins Function Glycoprotein Receptor Various Proteins in hormone and drug action Affect folding of certain proteins Calnexin, Calreticulin Regulation of development Notch and its analogs, key proteins in development Hemostasis (and thrombosis) Specific glycoproteins on the surface membranes of platelets glycosaminoglycans of extracellular matrix lubricants in the synovial fluid of joints cartilage, tendons, ligaments a variety of horny structures formed of dead cells: horn, hair, hoofs, nails Proteoglycans: cell surface or extracellular matrix A typical tetrasaccharide linker (blue) connects a glycosamino-glycan—in this case chondroitin 4-sulfate (orange)—to a Ser residue (pink) in the core protein. The xylose residue at the reducing end of the linker is joined by its anomeric carbon to the hydroxyl of the Ser residue. Proteoglycan aggregate of the extracellular matrix One very long molecule of hyaluronan is associated noncovalently with about 100 molecules of the core protein aggrecan Interactions between cells and the extracellular matrix with binding sites for both integrin and the proteoglycan linkages in glycoproteins Ser/thr Bacterial lipopolysaccharides Lectins, found in all organisms, are proteins that bind carbohydrates with high specificity cell-cell recognition, signaling, adhesion processes, intracellular targeting, deterrent to insects lectin-ligand interactions in lymphocyte movement to the site of an infection Stronger interaction near the site of inflammation Helicobacter pylori Interaction between a bacterial surface lectin and an oligosaccharide of the gastric epithelium Recognition and adhesion at the cell surface