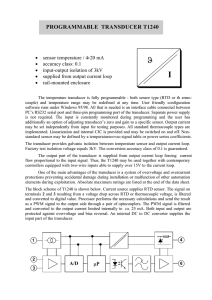
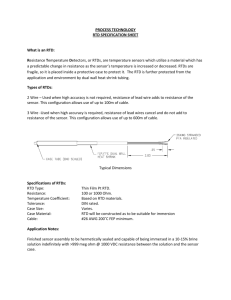
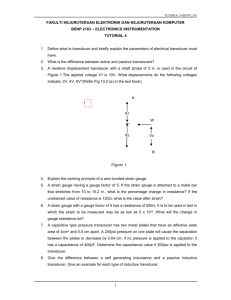
HW#2 An RTD forms one arm of an equal
advertisement

HW#2 1) An RTD forms one arm of an equal-arm Wheatstone bridge, as shown in Figure below. The fixed resistances, R2 and R3 are equal to 25 ohms. The RTD has a resistance of 25 ohms at a temperature of 0 C and is used to measure a temperature that is steady in time. The resistance of the RTD over a small temperature range may be expressed, as in the following equation: RRTD = R0 [ 1+ (T-T0)] Suppose the coefficient of resistance for this RTD is 0.003925 C-1. A temperature measurement is made by replacing the RTD in the measuring environment and balancing the bridge by adjusting R1. The value of R1 required to balance the bridge is 37.36 ohms. Determine the temperature of the RTD. 2) Consider a deflection bridge, which initially has all arms of the bridge equal to 100 ohms, with the resistance temperature sensor at Rg. The supply voltage is 10 V. If the temperature of Rg is changed such that the bridge output is 0.569 V, what is the temperature of the sensor? How much current flows through the sensor and how much power must it dissipate? Given: Rg = R0 [1+0.00395(T-T0)] where R0 = 100 and T0 = 0 C Vo Vin Rg / Rg 4 2(Rg / Rg ) 3) An engineer finds a desirable potentiometric bellows gauge with a stated change of 0 to 700 kPa in a catalog. It uses a sliding contact potentiometer having a terminal resistance of 50 – 10k. The supply voltage is 5V. Plot a Pin-Eo graph and determine (a) the static sensitivity of the transducer (b) Pin if Eo =2.5 V. 4) A piezoelectric pressure transducer as shown in figure is used to measure the absolute pressure of air in a tank by generating analogue signals, and it is to be calibrated by measuring both the pressure and the electric current simultaneously for various settings. If the relationship between the pressure and the corresponding current is given by P = 12.00 I – 48 where P = pressure of air [kPa], I = current [mA], Draw the calibration curve of the transducer and Determine (a) the static sensitivity of the transducer (b) the zero offset of the transducer (c) the static sensitivity of the manometer (d) the current, I if h = 50 cm