Development and Human Rights
advertisement

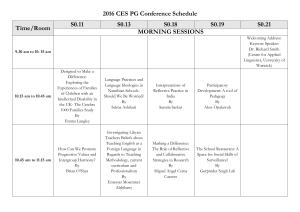
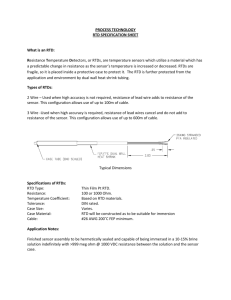
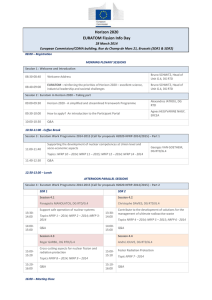
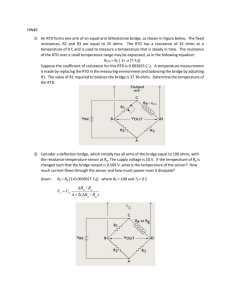
Reflections on Human Rights Today Amnesty International 30 May 2007 Development and Human Rights Dr Su-ming Khoo Dept of Political Science and Sociology NUI Galway s.khoo@nuigalway.ie www.nuigalway.ie/dern Synopsis Development and rights The Human Right To Development RTD is contested, but has core value Indivisibility - a historic obligation What RTD emphasises the human person, participation,non-discrimination, substantive processes, tools Further reading Development and rights Cold War divisions undermine UDHR The Empire of Liberty vs. the Empire of Justice HR in the West ideologically distanced from economic and social rights despite welfare state consensus “Economic Development” as a Cold War strategy Economism of development Seers (1969) the meaning of development Critique of economism (means and ends) Turn to humanism and ethics Development of WHAT? Countries? Peoples? Persons? Postcolonialism – self-determination, collective rights, international obligations (Bandung 1955, NIEO 1974) Sen (1993, 1999) Human functionings, capabilities, Freedoms Development – a tall order A process of economic growth, expanding output and employment Institutional transformation and technological progress of a country “…that steadily improves the well-being of all people” (E/CN.4/2004/WG.18/2) Definition of the human right to development a right to “a particular process of development in which all human rights and fundamental freedoms can be fully realized” Emphasises rights-based (non-discriminatory) access to goods/services corresponding to the realization of different rights First proposed by Keba M’Baye 1972, Working Group est. 1981 – influences African Charter 1986 UN Declaration on Right to Development Open ended WG + Ind. Expert 1998 Reaffirmed Vienna 1993, Millennium Declaration 2000 etc. The human right to development does NOT… Provide a legally binding obligation on the part of developed countries to provide development assistance OR Constitute a new human right that “trumps” other existing rights The human right to development DOES Take the global partnerships approach (MDG8) further and ground it in human rights Encourage us to critically evaluate globalization and understand its impact on human rights Underline the responsibility and accountability of governments, donors, recipients, IMF/WB/WTO RTD is contested 1 Developed countries disagree that they have a legal obligation to provide assistance Developing countries feel they have a right to development assistance due in part to legacy of colonialism/ neocolonialism Contesting development/ globalisation Decolonization ‘The concerns of decolonized states were translated into demands for greater recognition of economic, social and cultural rights, international recognition that colonialism and neocolonialism were gross violations of international human rights law, and the push to recognize development cooperation as an obligation owed by former colonial powers, rather than as an act of charity’ (Orford, 1991: 131) RTD is contested 2 Fear of RTD as “trumps”? Emphasis on communities, not individuals a dangerous “…delusion of well-meaning optimists” (Donnelly 1985:489) “…something of a mantra for states seeking to justify the privileging of economic development over human rights and to legitimize repressive or authoritarian policies” (Orford 2001: 132) Repressive “Asian developmentalism” (Ghai 1994) RTD emphasises interdependence and indivisibility RTD’s core focus The human person is the central subject of development and should be the active participant and beneficiary of the right to development The State is only an agent through which individual rights are asserted vis-à-vis the international community (Alston 1994:512) RTD as ends and process Other rights are ends, process is the means “the right of people to…improved realization of different human rights, as well as the right to the process itself” Requires resources – goods and services Duty bearers are primarily States, but also the international community I saw the angel in the marble and carved until I set him free. Michelangelo Sources Alston, P (1985) The Shortcomings of a Garfield the Cat Approach to the Right to Development California Western International Law Journal 510 Baxi, U ‘The Development of the Right to Development’ in J. Symonides Ed. Bedjaoui, M ‘The Right to Development’ Ghai, (1994) ‘Human rights and Governance: The Asia Debate’ 15 Australian Year Book of International Law 1 M’Baye, K. (1972) ‘Le droit au développement comme un droit de l’homme’ Revue des droit de l’homme 1972 503 Orford, Anne (2001) Globalization and the Right to Development in P. Alston (ed) People’s Rights OUP Piron, Laure-Hélène (2002) ‘The Right to Development: A review of the Current State of the Debate For DFID’ http://www.odi.org.uk/pppg/publications/papers_reports/dfid/issues/rights/right_to_dev.pdf