Millionaire Brain surgeon
advertisement

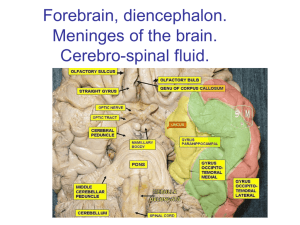
Created by Terri Street for OKTechMasters © 2000 Adapted by Penni Johnson, Human Anatomy & Physiology, Alpharetta High School, 2008 $ 1,000,000 $ 500,000 $ 250,000 $ 125,000 $ 64,000 $ 32,000 $ 16,000 $ 8,000 $ 4,000 $ 2,000 $ 1,000 $ 500 $ 250 $ 100 $100 A. B. C. D. $100 A. B. C. D. Back to Board The site of regulation of water balance and body temperature. A. Pons B. Hypothalmus C. Cerebellum D. Frontal lobe The site of regulation of water balance and body temperature. A. Pons B. Hypothalmus The site of regulation of water balance and body temperature is the Hypothalmus. Back to Board Responsible for the regulation of posture, balance and coordination. Takes over learned motor skills. A. Occipital lobe B. Cerebral aqueduct C. Cerebellum D. Hypothalmus Responsible for the regulation of posture, balance and coordination. Takes over learned motor skills. C. Cerebellum D. Hypothamus The cerebellum is responsible for the regulation of posture, balance and coordination. It takes over learned motor skills. Back to Board Contains autonomic centers, which regulate blood pressure and respiratory rhythm, as well as coughing and sneezing centers. A. Pons B. Medulla oblongata C. Motor cortex D. Neurotransmitters Contains autonomic centers, which regulate blood pressure and respiratory rhythm, as well as coughing and sneezing centers. B. Medulla oblongata C. Motor cortex The medulla oblongata contains autonomic centers, which regulate blood pressure and respiratory rhythm, as well as coughing and sneezing centers. Back to Board Large fiber tract connecting the cerebral hemispheres. A. Temporal lobe B. Cerebral cortex C. axons D. Corpus callosum Large fiber tract connecting the cerebral hemispheres. C. axons D. Corpus callosum The large fiber tract connecting the cerebral hemispheres is the corpus callosum. Back to Board Forms the cerebrospinal fluid. A. Spinal cord B. Brain stem C. Choroid plexus D. Thalamus Forms the cerebrospinal fluid. A. Spinal cord C. Choroid plexus The Choroid plexus forms the cerebrospinal fluid. Back to Board Part of the limbic system; contains centers for many drives (rage, pleasure, hunger, sex, etc.) A. Hypothalamus B. Diencephalon C. Ventricles D. schwann cells Part of the limbic system; contains centers for many drives (rage, pleasure, hunger, sex, etc.) A. Hypothalamus B. Diencephalon The Hypothalamus is the part of the limbic system that contains centers for many drives (rage, pleasure, hunger, sex, etc.) Back to Board The outermost meningeal layer. A. Visera B. Dura C. Arachnoid D. Pia The middle meningeal layer; has a cobweb like structure. A. Visera B. Dura The outermost meningeal layer is the Dura matter. Back to Board Known as the inter brain; it is located deep within the brain and composed of the thalamus, hypothalamus and epithalamus. A. Pyramidal tract B. Diencephalon C. Cerebral cortex D. Brain stem Known as the inter brain; it is located deep within the brain and composed of the thalamus, hypothalamus and epithalamus. A. Pyramidal tract B. Diencephalon Known as the inter brain; the Diencephalon is located deep within the brain and composed of the thalamus, hypothalamus and epithalamus. Back to Board The pineal gland is located in the: A. Mesencephalon B. Epithalamus C. Forebrain D. Corpus callosum The pineal gland is located in the: B. Epithalamus C. Forebrain The pineal glad is located in the epithalamus. Back to Board Regulates essential survival functions and composed of Pons and Medulla oblongata. Maintains life without conscience thought. A. Brain stem B. Choroid plexus C. Diencephalon D. Cerebellum Regulates essential survival functions and composed of Pons and Medulla oblongata. Maintains life without conscience thought. A. Brain stem D. Cerebellum The Brain stem regulates essential survival functions and is composed of Pons and Medulla oblongata. Maintains life without conscience thought. Back to Board The motor cortex located on the right half of the cerebrum controls: A. heart rate B. blood pressure C. Walking D. The left side of the body The motor cortex located on the right half of the cerebrum controls: C. Walking D. The left half of the body The right half of the motor cortex located on the cerebrum controls the left half of the body. Back to Board What muscles do the midbrain control? A. Move and coordinate the eyes B. Muscles of the digestive system C. Smooth muscles D. Voluntary muscle movements What muscles do the midbrain control? A. Move and coordinate the eyes D. Voluntary muscle movements The muscles that move and coordinate the eyes are the muscles the midbrain control? Back to Board Secretes melatonin and regulates the sleep wake cycle. A. Pineal gland B. Wernicke’s area C. Broca’s area D. Hypothalamus Secretes melatonin and regulates the sleep wake cycle. A. Pineal gland B. Wernicke’s area The pineal gland secrete melatonin and regulates the sleep wake cycle. Back to Board What is found in & around the brain & spinal cord; forms a cushion that protects the nervous tissue from blows and other trauma? A. Cerebral spinal fluid B. Blood brain barrier C. Meneges D. Arachnoid space What is found in & around the brain & spinal cord; forms a cushion that protects the nervous tissue from blows and other trauma? A. Cerebral spinal fluid B. Blood brain barrier Cerebral spinal fluid is found in & around the brain & spinal cord; it forms a cushion that protects the nervous tissue from blows and other trauma? Sorry, that is incorrect! Ask a friend! Remove two answers Consult the module! I hope you enjoyed playing.