17 Forebrain, diencephalon. Menimges of the brain
advertisement

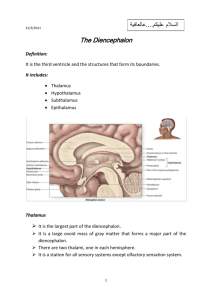
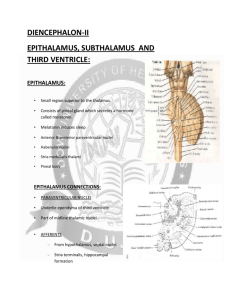
Forebrain, diencephalon. Meninges of the brain. Cerebro-spinal fluid. The diencephalon • The diencephalon is the region of the embryonic vertebrate neural tube that gives rise to posterior forebrain structures including the thalamus, hypothalamus, posterior portion of the pituitary gland, and pineal gland. • The hypothalamus performs numerous vital functions, most of which relate directly or indirectly to the regulation of visceral activities by way of other brain regions and the autonomic nervous system. THE DIENCEPHALON • EPITHALAMUS • THALAMUS • SUBTHALAMUS • HYPOTHALAMUS Diencephalon Hypothalamus Thalamus •Command for the •Chief relay centre for control of autonomic directing sensory messages functions such as heart Helps regulate awareness rate, blood pressure, •Relays commands going hunger, thirst. to the skeletal muscles •Role in emotions and from the motor cortex. motivation (e.g., thoughts about fear get translated into arousal through hypothalamus.) THE HYPOTHALAMUS • Lateral zone • No discrete nuclei • Regulation of food and water intake •Medial zone •Well defined nuclei •Chiasmatic region (anterior region) •hormone release• SO,PV) •Cardiovascular function (Ant.) •Circadian rhytms (SCH) •Body temperature (Preoptic nc.) • Tuberal region (middle reg.) • • VM – satiety center (lesion produces hyperphagia + obesity) Arcuate nc. - delivers peptides to the portal vessels • Mamillary region (posterior reg.) • • Posterior nc.- elevating of blood pressure, pupillary dilatation, body heat conservation Mammillary ncc. – memory formation (fornix) Vasopresin (Antidiuretic h.), Oxytocin (uterus,ejection of milk) Somatotropin, Prolactin, Folitropin, Lutropin, thyrotropin, ACTH Diencephalon3rd ventricle Surrounded by cerebrum Intermediate mass Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Mammillary body Thalamus Pineal body Epithalamus epithalamus Located at dorsal part of the diencephalons, it includes the pinieal body. It secretes melatonin which signals the nighttime stage of the sleep-wake cycle. pineal body — internal secretion gland habenular triangle— habenular nucleus habenular commissure thalamic medullary stria posterior commissure subthalamus subthalamic nucleus participate in the function of extracorticospinal tract