CNS Examination
advertisement

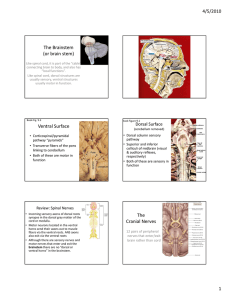
CNS Examination Done by Dr/ Abdullah Mohd. Jan MBBS,Intern Aspects of Examination 1. General Ex 2. The Cranial nerves 3. The upper limbs ( Motor + Sensory + coordenation ) 4. The lower limbs ( Motor + Sensory + coordenation) 5. The skull and spine for local disease 6. The carotid arteries for bruits General Examination • • • • Assessment of the higher centers Speech Neck stiffness Abnormal movements General Examination 1. Assessment of the higher centers o o o o Consciousness Orientation ( Person , Place , Time ). Memory Handedness 2. Speech o Flow of speech o o Comprehension Repetition 3. Neck stiffness looking for meningism ( meningitis ,SAH) Cranial Nerves Examination • you have to know how to examine all cranial nerves in detail but we will focus on the most important ones ( 3rd , 4th , 5th , 6th , 7th , 11th & 12th ) . Where CN Come From? • 3rd & 4th cranial nerves are located in the mid brain • 5th , 6th , 7th & 8th cranial nerves are located in the pons • 9th , 10th , 11th & 12th cranial nerves are located in the medulla oblongata CN III, IV, VI: Oculomotor, Trochlear, Abducent • • • • Inspection of pupil Light reflex Eye Movement & nystagmus Convergence & accomodation • Look at pupils: shape, relative size, • Ptosis. • Shine light in from the side to look for pupil's light reaction. • Assess both direct and consensual responses. • Assess afferent pupillary defect by moving light in arc from pupil to pupil. The pupils CN V :Trigeminal • Motor • Sensory • Reflex • Motor :pt opens mouth, clenches teeth )pterygoids). • Palpate temporal, masseter muscles as they clench . • Jaw jerk : – Dr's finger on tip of jaw . – Grip patellar hammer halfway up shaft and tap Dr's finger lightly. • Sensory Facial sensation by cotton on forehead, cheek & jaw. • Corneal reflex :patient looks up and away. • Touch cotton wool to other side. • Look for blink in both eyes, ask if can sense it. • Repeat other side [ tests V sensory, VII motor]. CN VII :Facial • Motor • Taste sensation CN VII :Facial • Inspect for facial droop or asymmetry . • Facial expression muscles :pt looks up and wrinkles forehead. • looking for wrinkling loss. • Pt shuts eyes tightly :compare each side . • Pt smile :compare nasolabial grooves . • Pt show teeth, puff out cheeks . • Taste sensation in the anterior 2/3 of the tongue. CN XI: Accessory • Inspection From behind, examine for trapezius atrophy, asymmetry. • Pt. shrugs shoulders (trapezius). • Pt. turns head against resistance: watch, palpate SCM on opposite side. CN XII: Hypoglossal • Inspect tongue in mouth for wasting, fasciculations. • Protrude tongue: unilateral deviates to affected side. Motor system • • • • • don’t forget to compare both limbs Inspection Palpation ( muscle bulk + tenderness ) Muscle tone Muscle power Reflexes Motor system 1. Upper limbs (compare) • Inspect for muscle wasting ( proximal & Distal ) – scars – deformity – fasciculation – skin pigmentation. • Drift test • Feel the muscle bulk ( proximally & Distally ) – muscle tenderness. • Tone ( normo – hypo – hypertonia ) by passive movement of wrist and elbow joints. • Power ( 0 – 5 ) by active movement at the shoulder , elbow , wrists and fingers. • Reflexes ( 0 - ++++ ) Biceps ( C5,C6 ) – Triceps ( C7,C8 ) – Brachioradialis ( C5,C6 ) • Coordination Finger to nose test Finger to finger test Dysdiadochokinesis Rebound test 2. Lower limbs • Inspect the gait of the patient • Expose both thighs and legs. • Inspect for muscle wasting – scars – deformity – posture -fasciculation – skin pigmentation . • Feel the muscle bulk and muscles for tenderness. • Tone ( normo – hypo – hypertonia ) by passive movement of the knee and ankle joints • Clonus more than 3 ankle and knee clonus • Power ( 0 – 5 ) by active movement at the hip , knee , ankle , and tarsal joints • Reflexes ( 0 - ++++ ) Knee jerk ( L3,L4 ) – Ankle jerk (S1,S2 ) – Plantar reflex ( L5, S1 , S2 ) • Coordination Heal to shin test Toe finger test Tapping test Foot Sensory system • Spinothalamic pathway Pain and Temperature ( usually temperature is not tested ) • Posterior column pathway Vibration and Proprioception Romberg Sign • Light touch with cotton wool Back • Inspect for deformity – scars – neurofibromas . • Palpate for tenderness over the vertebral bodies • Do the straight leg raising test Auscultation • Auscultate over the carotid arteries looking for bruits.