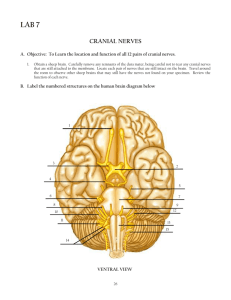
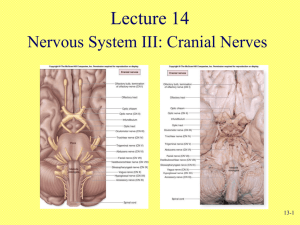
Neurology - 2 - Porterville College
advertisement

Neurology - 2 Part 2 Intellectual Function • Calculations – Count backwards from 100 – Spell backwards • Integrative capacity – How are a cat and a wolf alike? • Judgment – Interpret a well known proverb • A bird in the hand is worth more than two in the bush. • The early bird catches the worm Intellectual Function • Judgment – You arrive home without a house key, what alternatives do you have? • Short term memory test? – 3 words – Repeat in 5 minutes – Amnesia • Loss of memory Thought Content • Are the thoughts…? – – – – – Spontaneous Natural Clear Relevant Coherent Thought Content • Fixed ideas • Preoccupations Hallucinations • False perceptions (sensory) • Does not have an external stimuli • Patients see, hear, taste things that are not really there Illusions • Has a real external stimuli, but the patient misinterprets the stimuli Delusions • False beliefs Emotional Status • • • • Affect/ Mood Consistent Appropriate Facial expressions, body language Perception • Agnosia – The inability to interpret or recognize objects • Visual – Occipital • Auditory – Temporal • Tactile – Parietal lobe Motor Ability • Ask to perform a small task • Understanding + motor strength • Movement smooth, coordinated • Involuntary movements • Gait Language Ability • Spoken and written • Aphasia – Expressive • Motor aphasia • Broca’s aphasia – Receptive • Sensory aphasia • Wernicke’s aphasia – Global Language ability • Dysphasia / aphasia • Dysphagia / aphagia • Dysarthria – Imperfect articulation of speech Terminology • • • • • • – – – – – – Anosmia I - Inability to smell Anisocoria J - Inequality of pupil size Agnosia F - Inability to determine meaning or significance of sensory stimulus Apraxia G - Inability to performed learned movements, defect in motor planning Analgesia M - Loss of pain sensation Anesthesia A - Absence of sensation Terminology • Astereognosis – H - Inability to recognize form of object by touch • Ataxia – L - Lack of coordination of movement • Diplopia – C - Double vision • Dysarthria – K - Lack of coordination in articulating speech • Dyskinesia – E - Impairment of power of voluntary movement, resulting in fragmentary on incomplete movements Terminology • Dysphagia – B - Difficulty swallowing • Homonymous hemianopsia – N - Loss of vision in one side of visual field • Ophthalmoplegia – P - Paralysis of eye muscles • Opisthotonus – D - Extreme arching of back with retraction of head • Paraplegia – O - Paralysis of lower extremities Small group Questions • • • • • • • • What does battle’s sign indicate What does raccoon eyes indicate What is rhinorrhea and how do you know they have it? What is Otorrhea and what does it indicate? Described decorticated and Decerebrated posturing and what they each indicate What are the three areas of orientation How do you test judgment? Short term memory Differentiate be hallucinations, delusions and illusions. Cranial Nerves • 12 pairs • PNS • You must know: – – – – – – The name The number The order The function S/M How to assess Cranial Nerves • • • • Number -1 Name: Olfactory Sensory Function – Sense of smell • Assessment – Identify familiar odor Cranial Nerves • • • • Number -2 Name: Optic Sensory Function – Visual Acuity • Assessment – Snellen eye chart Cranial Nerves • • • • Number -3 Name: Oculomotor Motor Function – Muscles that move the eye, lid, papillary constriction, lens accommodation • Assessment – Test for ocular rotation, nystagmus, Papillary reflexes, check for ptosis • Nystagmus: – Involuntary osculation of the eyeball • Ptosis – Drooping eyelid • Papillary reflexes – Pupil changing in size when exposed to light Cranial Nerves • • • • Number -4 Name: Trochlear Motor Function – Muscles the move the eye, lid, papillary constriction, lens accommodation • Assessment – Test for ocular rotation, nystagmus, Papillary reflexes, check for ptosis Cranial Nerves • • • • Number -5 Name: Trigeminal Sensory & Motor Function – Facial sensation, corneal reflex, mastication • Assessment – Distinguish between sharp and dull on face – Check blink reflex – Have patient clinch and move jaw from side to side, feel jaw strength Cranial Nerves • • • • Number -6 Name: Abducens Motor Function – Muscles the move the eye, lid, papillary constriction, lens accommodation • Assessment – Test for ocular rotation, nystagmus, Papillary reflexes, check for ptosis Cranial Nerves • • • • Number - 7 Name: Facial Sensory & Motor Function – Facial expression and muscle movement – Salivation and tearing – Taste • Assessment – Observe for symmetry while pt performs facial movement – Stick out tongue – Distinguish between sugar and salt Cranial Nerves • • • • Number -8 Name: Acoustic Sensory Function – Hearing & equilibrium • Assessment – Simple hearing test Cranial Nerves • Number -9 • Name: Glossopharyngeal • Sensory & Motor • Function – Taste – Sensation in pharynx and tongue – Pharyngeal muscles • Assessment – Ability to discriminate btw sugar and salt Cranial Nerves • • • • Number -10 Name: Vagus Sensory & Motor Function – Muscle of pharynx, larynx, thoracic and abdominal viscera – Parasympathetic innervations • Assessment – Gag response – Have person say “Ah….” – Symmetrical rise of uvular and soft palate – Assess swallowing Cranial Nerves • • • • Number -11 Name: Accessory Motor Function – Shoulder movement • Assessment – Strength of muscle, shrug Cranial Nerves • • • • Number -12 Name: Hypoglossal Motor Function – Tongue movement • Assessment – Check tongue strength and movement Sample quiz questions What cranial nerve is responsible for hearing and equilibrium? A. Vagus B. Acoustic C. Glossopharyngeal D. Accessory Sample Quiz Questions What Cranial nerve is responsible for tongue movement? A. 6 B. 8 C. 10 D. 12 E. None of the above Sample Quiz Questions How do you test for cranial nerve number 3? A. Snellen eye chart B. Hearing test C. Have them follow your pen with their eyes as you move it about D. Have them stick out their tongue Sample Quiz Questions When you check for nystagmus, what cranial nerve are you assessing? A. Olfactory B. Optic C. Abducens D. All of the above E. None of the above Sample Quiz Questions When you check someone's shoulder strength, what cranial nerve are you assessing? A. 6 B. 8 C. 10 D. 12 E. None of the above Learning Tip On Old Olympus Towing Top a Finn and German Viewed A Hawk