federal courts
advertisement

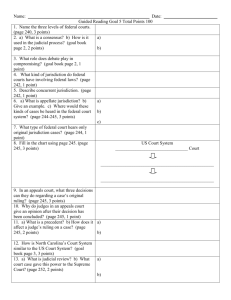
American Tort Law Carolyn McAllaster Clinical Professor of Law Duke University School of Law Class One Federal Courts and Civil Procedure U.S. Government Organization Hierarchy of binding precedents U.S. Constitution Federal Laws State Laws Common Law Local Ordinances Horizontal Federalism Dual system of state and federal jurisdiction Federal System U.S. District Courts (trial courts) US Courts of Appeals US Supreme Court 50 state court systems United States Courts of Appeals Personal Jurisdiction Over property Where property is located (in rem) If a debt dispute, where property that is security for debt is located (quasi in rem) Over a party If party is located in jurisdiction, or Has certain minimum contacts with the forum (International Shoe Co. v. Washington, 326 U.S. 310 (1945) Federal Court Jurisdiction Federal Question Jurisdiction Cases “arising under the Constitution, the laws of the U.S., and treaties Diversity Jurisdiction Citizens of different states Amount in controversy is at least $75,000 Federal Rules of Civil Procedure Govern all civil lawsuits in federal courts (all court trials except criminal and admiralty trials.) Essentially the same in all the Federal Courts; State Court rules are modeled after the federal rules; Pre-trial Procedure Starting the Lawsuit Party meets with his/her attorney After investigation, attorney files Complaint Short & plain statement of jurisdiction Short & plain statement of the facts Demand for relief Clerk issues Summons (order to respond to complaint or lose the lawsuit by default) Pre-trial Procedure Defendant’s Response Defendant has 20 days to respond to Complaint after service; Response can be either: Motion to Dismiss Answer Motions to Dismiss Grounds for Motion to Dismiss Lack of subject matter jurisdiction Lack of personal jurisdiction Improper venue Insufficiency of process Insufficiency of service of process Failure to state a legal claim Failure to include a necessary party. Defendant’s Answer Contents of Answer Admit, deny or state lack of knowledge of allegations in the Complaint; Raise affirmative defenses to lawsuit; Counter-claims against plaintiff Cross-claims against 3rd party Discovery Process through which the parties exchange information on “any matter, not privileged, which is relevant to the subject matter involved in the pending action.” (FRCP 26(b)) Privileged information is excluded: communications between certain categories of professionals. Discovery, continued Lawyers gather discovery information, not the judge; Idea is full disclosure of information each side has to promote: Truth-finding Fairness Earlier settlement efficiency Discovery Required initial disclosures: Name and contact information about any person likely to know about the claim or defenses; Copy or description of all documents to be used in case; Materials related to how damages are calculated Forms of Discovery: Depositions Deposition: sworn testimony of a party or witness Court reporter is present who “takes down” the testimony. Lawyers ask questions Transcript can be used at trial To impeach witnesses As testimony of unavailable witnesses Forms of Discovery Interrogatories Interrogatories: written questions sent to a party to be answered in writing under oath; Lawyer usually drafts responses within 30 day time limit Limit: 25 questions including subparts Forms of Discovery Request to Produce Request for Production of Documents: Used to request inspection and copies of documents or for inspection of land; Must specify a reasonable time, place, and manner of making the inspection and copies; Response due within 30 days Forms of Discovery Requests for Admission/ Order for Physical or Mental Examination Requests for Admission: Written requests to opposing party to admit facts that are undisputed. Can deny admission, but failure to respond results in admission Order for Physical or Mental Examination Used for party only when physical or mental health is an issue in the lawsuit. Summary Judgment Judge decides case without full trial when there is “no genuine issue as to any material fact and…the moving party is entitled to judgment as a matter of law.” The Trial Jury selection (voir dire) Plaintiff’s opening statement Plaintiff’s evidence Direct and cross examination of witnesses Defendant’s motion for directed verdict Defendant’s opening statement Defendant’s evidence Closing Arguments Verdict (based on instruction about the law from the judge.) Post-trial Post-trial Motions To set aside verdict For a new trial Appeal of verdict to higher court Appellate Court affirms, reverses, or reverses and remands