Economic Activities PowerPoint
advertisement

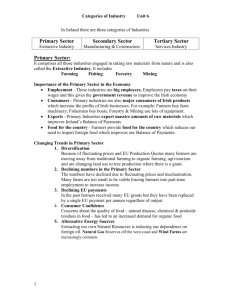
Economic Activities Prepared by Rachel Farrell The Sectors of the Economy Primary Sector – Extractive Industry Secondary Sector – Construction & Manufacturing Tertiary Sector – Service Sector Primary Sector Also known as extractive insdustry. Turns natural resources into raw materials for use in secondary sector. e.g. agriculture, forestry, fishing, mining. Agriculture Produces meat, milk, cereals & horticultural output. 1/3 of the largest firms in Ireland use agricultural output such as milk & beef in their products. Problems with agriculture Climate: Bad weather distroys crops. Output: Overproduction leads to low prices - milk quotas and single farm payments restrict the amount of milk & beef that can be produced in order to keep farm incomes higher. Disease: Foot & Mouth, BSE, Salmonella, Bird Flu………… Forestry Forests in Ireland mostly owned by Coillte (one million acres) They are involved in tree plantation & timber processing …… Problems: Forestry drains nearby soils of vital nutrients. Land used in forestry cannot be used for animal rearing. Fishing BIM is the Irish Fisheries Board. They promote the fishing industry. Fish is caught and sold fresh, processed or frozen. Salmon farming is on the increase. Problems: Overfishing – depletion of fish eg. Cod EU quotas – limits put on fishing Competition from large European fleets. Mining Tara mines – zinc & lead (exported) Monaghan – gypsum (plasterboard) BNM – peat (generates electricity, fuel, peat moss……) Problems: World demand for zinc is falling. Closures of some mines. Mining damages the environment. Secondary Sector The manufacturing & construction sector of the economy. It turns raw materials into finished products. 3 Main Groups 1. Transnationals (TNC’s) 2. Agri-business 3. Indigenous Firms Transnationals (TNC) Large business with headquarters in one country and branches in many others. May move operations from one country to another in response to market conditions. IDA offers incentives to foreign TNC’s to set up here. e.g. INTEL, IBM, Coca Cola, Nestle, Unilever………. Unilever Agri-business Turns produce from agriculture into food products, e.g. Glanbia plc. Opportunities: Access to new markets of Eastern Europe. Produce GM free, organic, clean food. New product ideas, yogurt drinks ….. Challenges: Competition from other countries. Powerful multiple stores dictating prices & credit terms. Indigenous Firms Set up in Ireland by Irish people. Helped by Enterprise Ireland & County Enterprise Boards. Advantages: Loyal to the country. They foster an enterprise culture. Profits remain in Ireland and reinvested in new businesses. Challenges : Competition May depend on TNC’s. To ensure success the secondary Sector needs to: Produce high quality goods. Export, find new markets. Invest in capital & R & D. Avail of advice & grants from Enterprise Ireland (indigenous) IDA (TNC’s). Adopt World Class Manufacturing (WCM) (TQM, Empowerment & Quality Control). Tertiary Sector Service Sector. Provides support services for the extractive & manufacturing sectors and to consumers. e.g. finance, insurance, medical, beauty, recreation……… It is the last to develop, but eventually becomes largest employer. Why is the tertiary sector the fastest growing sector? Economic development = increased wealth. Increased wealth = increased demand for services. Expansion of Public Sector = more jobs in health education …. Expansion of business = need for support services. International trade in services such as IT & finance. The 4 stages in the development of the economy, Decline in agriculture as technology improves. Growth in construction & manufacturing. People move to non rural areas to live. Growth in service sector to support the growth in manufacturing & construction. Globalisation of services facilitated by developments in ICT. Contribution of the three sectors of the economy Primary Sector Provides raw materials for secondary sector. Provides approximately 10% employment, tax etc.. Pump a lot of money into the Irish economy by purchasing machinery and consumables for their business. Export a lot of produce. Secondary Sector Consume Irish raw materials e.g. Ribena. Provides appproximately 25% employment, tax.. Export a lot of their produce. Encourages the development of indigenous firms. Tertiary Sector Provides support services for the primary & secondary sectors. Employs approximately 65% of work force, tax.. IFSC attracts half of the worlds top 50 banks & half the worlds top 20 insurance co.’s. Invisible exports such as call centres provide Ireland with more wealth. Important trends & issues in the main industries in Ireland. Primary Quotas, organic food, provision of sustainable energy to reduce dependence on oil, more forests. Secondary: IT TNC’s coming to Ireland, Manufacturing TNC’s leaving Ireland (FOTL), major infrastructural improvements, slowdown in construction. Tertiary Huge increase in services supplied. Invisible exports such as call centres, software development, finance….. Foreign banks and insurance companies locating in International Financial Services Centre in order to have access to EU market. 4 Factors of Production Land Labour Capital Enterprise Land All things supplied by nature. Natural resources used in production. e.g. fields, water, natural gas, oil, coal, minerals, trees…….. The payment/reward for land is rent. Labour The human element in the production process. e.g. employees, builders, carpenters, factory workers….. The reward for labour is wages. Capital All man-made things that help produce goods. Money is invested to buy things such as buildings, machinery… The reward for capital investment is interest. Enterprise Entrepreneur taking the initiative and risk to set up a new business. e.g. Ramona Nicholas, Richard Branson… The reward for enterprise is profit. The risk of enterprise is loss.