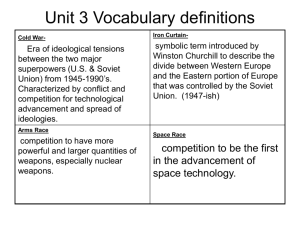
Origins of the Cold War
advertisement

Origins of the Cold War (1945-48) • After North Korean strike, South Korean leader threatens 'retaliation' • By the CNN Wire Staff • Seoul, South Korea (CNN) -- Hours after North Korea's deadly artillery attacks Tuesday, South Korea's president said "enormous retaliation" is needed to stop Pyongyang's incitement, but international diplomats urgently appealed for restraint. "The provocation this time can be regarded as an invasion of South Korean territory," President Lee Myung-bak said at the headquarters of the Joint Chiefs of Staff here, according to South Korea's Yonhap news agency. The incident -- in which two South Korean marines died -- is "the first direct artillery attack on South Korean territory since the Korean War ended in an armistice" in 1953, Yonhap reported. • • • The United States has about 28,500 troops deployed in South Korea. A U.S. defense official said more than 50 U.S. Navy vessels are in the area, including a carrier strike group led by the USS George Washington. • Any other Cold War Legacies/Issues Today? • Cuba • NATO • Nuclear missiles – Weapons of Mass Destruction • Nuclear missile defense • Afghanistan • Africa • Anti-communism/socialism – US • Space Program • US military bases • Underdevelopment in Eastern Europe • What are the Origins of the Cold War? • Before WWII • During WWII • After WWII • Before – Russian Revolution – Conflicting Ideologies Marxism vs Capitalism – Russian Civil War Spanish Civil War – Rise of Fascism/Germany – Munich agreements – Nazi Soviet Pact • During the War – Atmosphere of distrust • • • • • • • • • • • Nazi-Soviet collaboration Poland – Katyn Massacre Spheres of Influence Second Front Tehran Yalta Potsdam Russian casualties Soviet occupation forces Soviet puppet governments US nuclear monopoly – Bombing of Japan Political Division of Europe • Political vacuum in central Europe (due to German collapse) • Pro-western and Soviet spheres of influence • Each sphere would adopt the political institutions, economic systems and foreign policies of its liberators/conquerors • Western half of continent adopted parliamentary style governance, capitalist economic structures, and Anglo-American foreign policies • Eastern half of continent adopted Soviet political and economic models and supported the Kremlin in foreign policies (under the eyes of the Soviet occupation armies) What led to Division? • • • • Suppression in the Eastern Bloc The determination of the Soviet Union to establish a protective ring of subservient client states in Eastern Europe (from the Black Sea to the Baltic) Although non-communist political parties were allowed in Eastern Europe for a time, by 194748 this was no longer allowed All democratic and non-socialist parties were purged on orders by Stalin In 1948, Czechoslovakia’s coalition government was dissolved and became the last state to become fully communist in Eastern Europe Why suppression? • The Soviet Union will seek this protective ring, in order to avoid another eastern invasion of its territory (like in 1914 and 1941) • What was the U.S. response? Churchill’s “Iron Curtain” Speech • March 5, 1946 • Fulton, Missouri • From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an Iron Curtain has descended across the continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia, all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere • Sent a warning to Americans who many in the government were looking to keep out of international affairs • Wartime Propaganda U.S. Response - Containment • George Kennan – “Long Telegram” • Director of the Policy Planning Staff of the State Department – Deputy Chief US Mission in Moscow 1944-7 • USSR still lives in antagonistic "capitalist encirclement" with which in the long run there can be no permanent peaceful coexistence. • It was in the national interest of the US to contain any such expansion by strengthening the political, social, and economic institutions of countries subject to such expansionist pressures • • • • Truman Doctrine - With the void of German power, the USA feared a Soviet expansionist policy that stretched from the Sea of Japan to Western Europe - The Anglo-American alliance feared that the Soviet Union would be in better position for world domination than even Germany itself - Policy of containment was created to contain Soviet expansion to Eastern Europe - Stalin’s effort to establish a security zone in Eastern Europe was seen as a drive for continental hegemony and world domination • "the policy of the United States to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or by outside pressures." Truman reasoned, because these "totalitarian regimes" coerced "free peoples," they represented a threat to international peace and the national security of the United States. Military Situation in Europe • • • • 1945 – USA had 1.2 million 1947 – USA had 1.4 million 1945 – USSR had 20+ million 1947 – USSR had 4 million • Why would this make the American’s European Allies uneasy? Why such a difference? • US forces were brought home from Europe and demobilized , since it would have been impossible to explain that such large forces would be needed to oppose the forces of a wartime ally • As well, the US monopoly on nuclear weapons would counter balance such large conventional (non-nuclear) forces The Marshall Plan • US Secretary of State George C. Marshall • Proposed a plan to of economic aid to Europe to solve its postwar financial collapse • Authorized by the US Congress as the European Recovery Act • Between 1948-52, $13.2 billion was given to western European nations Effects of Marshall Plan • By 1952, European industrial production had risen 35% above pre 1939 levels • By 1952, European agricultural production had risen 10% above pre 1939 levels • The US dollar became the world’s principal currency • While USA quadrupled its exports to Europe, it still only amounted to 10% of its overall GNP (90% of its wealth was created in the domestic market) Soviet Reaction to Marshall Plan • Marshall invited all the nations in Europe, including the Soviet Union to participate in this program • The Soviet delegation walked out of the discussion and forbade its satellite states from participating • This was because of two American demands for economic aid: • 1) Access to internal budgets of states that accept the loans and aid • 2) Washington maintained that much of the aid money be spent on American exports • Thus, these terms were unacceptable to the USSR, since they renounced capitalism and did not want the USA to have any access to their economic statements (security threat) Division of Germany • By 1947, the divisions in Europe now spread to Germany • In all three zones of western occupation (USA, UK and France), Marshall Plan aid was used to revive the German economy • A common West German currency was established • The Soviets viewed this with suspicion, and talks of a “reunification” were put on hold “indefinitely” Decolonization • While the European powers expected to retain their colonies in 1945, several colonial people’s now had other ideas • Due to Japan’s rapid defeat of the UK, France and the Dutch in WWII, the idea of European invincibility was now broken • These actions for independence ranged from civil disobedience (British India) to outright war (French Indochina, Dutch Indonesia) Civil Disobedience Revolutionary Struggle