ReviewEuropeRussia
advertisement

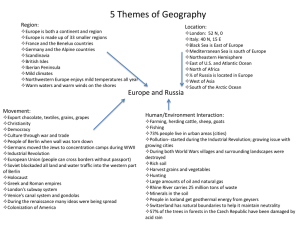
Europe and the Russian Zone A Quick Review Europe -- Definition There are many definitions of Europe. The textbook has one, the Coloring Book has one, and I have another. In general, I consider Europe to be those countries of western Eurasia that lie west of the Former Soviet Union. Europe: Peninsulas on a Peninsula Europe is NOT a separate continent. Rather, it is a peninsula of the Eurasian continent. Major Peninsulas of Europe: Scandinavian, Jutland, Iberian, Italian, and Balkan. Europe’s Northerly Orientation •Much of Europe lies north of 40°N, which bisects the Iberian Peninsula. - This means summer days AND winter nights are long. Scandinavia is land of the midnight sun Europe: Principle Mountains & Rivers Principal Mountain Ranges: • Pyrenees • Alps • Apennines • Carpathians Principal Rivers • Danube – longest river of non-Russian Europe • Rhine – most important commercial waterway of Europe Principle seas and lakes: what is the significance of each? Baltic Sea North Sea Mediterranean Sea Adriatic Sea Black Sea Subregions of Europe You have already learned the European countries for the map quiz, but to make it easier to remember them, it is easier to break them up into subregions. My subregions are a bit different than the text’s. Northern Europe Northern Europe includes the island of Iceland, Denmark (on the Jutland Peninsula and adjacent islands), Norway and Sweden (on the Scandinavian Peninsula), and Finland, which shares a long border with Russia. Western Europe Typically Western Europe includes the British Isles (United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland), the Benelux Countries (Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg), France, Germany, Switzerland and Austria. Eastern Europe South of the Baltic Sea lies Poland, the Czech Republic and Slovakia (once a single country known as Czechoslovakia), and Hungary. The Balkans Eight countries lie on the Balkan Peninsula between the Adriatic and Black Seas. Slovenia, Croatia (shaped like a C), BosniaHercegovina, Yugoslavia, and Macedonia once made up a single country called Yugoslavia. Tiny Albania faces the heel of Italy while Romania and Bulgaria face the Black Sea. Southern Europe Four countries lie predominantly in the south along the Mediterranean Sea. These are Portugal and Spain on the Iberian Peninsula, Italy, and Greece. Russia’s Northerly Orientation Notice how much of Russia lies north of the Arctic Circle. Again, summer days AND winter nights are long. The Arctic Ocean is ice covered for much of the winters leaving much of Russia effectively landlocked. Russia and Caucasus: Almost Landlocked Russia is almost a rectangle with few major peninsulas. Its largest peninsula is the Kamchatka Peninsula, located in Russia’s Far East. Russian Zone: Principle Mountains & Rivers Mountains: •Caucasus (landform?) •Urals (landform?) Principal Rivers • Volga – if you extend Europe all the way to the Ural Mountains, it is the longest river of Europe. It is certainly the most important river of Russia, but not the longest. • Notice the huge rivers that flow from south to north across Siberia. These are among the biggest rivers in the world. Baltic Sea Black Sea Caspian Sea Aral Sea Lake Baikal Arctic Ocean What is the significance of each? The Former Soviet Union The former Soviet Union consisted of fifteen republics. It is easier to learn them if you group them. Each group of countries constitutes a distinctive subregion. Baltic States Source: http://www.mythinglinks.org/euro~east~baltics.html The Baltic States – Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania – lie on the Baltic Sea. Remember that they are in alphabetical order from north to south. Kaliningrad, which lies west of Lithuania, is an exclave of Russia. European Republics These three republics lie between Europe to the west and Russia to the east, the Baltic States to the north and the Black Sea to the South. Note that Belarus and Moldova are landlocked. Caucasus Republics Source: http://chechen.8m.com/cgibin/i/maps/caucasus_zoom_map.gif These three republics lie between the Black Sea to the west and the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia to the north and Turkey and Iran to the South. Note that Armenia is landlocked, while Georgia fronts the Black Sea and Azerbaijan fronts the Caspian. Central Asian Republics Source: http://www.usaid.gov/locations/europe_eurasia/car/im ages/ciacars1.jpg These five republics – Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan – lie between the Caspian Sea to the west and the China to the east, Russia to the north and Iran and Afghanistan to the South. Note that all but Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan are landlocked. K UK TT Here’s a little different view of the tectonic plates. What are the 3 types of tectonic plates. Describe the location of each that affect either Europe or the former Soviet region. What areas are the most tectonically active? What landform is best associated with plate boundaries? • • • • • • Alpine Remnant Mountains Isolated Volcanic Landform Landforms Laurasian Shield Rifted Shield Sedimentary Cover – North European Plain vs. Siberia What rock types, minerals and soils are associated with each? Note: These two maps do NOT use the same numbering schemes. What are the different landforms? Climates Western Europe has west coast mid-latitude climates. About 20°E (central Poland), you move into east coast mid-latitude climates. West-Coast Climates Mediterranean: - Where? - Temperature and precipitation patterns? - Agriculture? Marine West Coast: - Where? - Temperature and precipitation patterns? - Agriculture? Western Europe is relatively warmth despite its northerly location. Why? Western Europe is relatively warmth despite its northerly location. Why? North Atlantic Drift Lots of peninsulas mean more proximity to moderating influence of water. The Russia Zone does not enjoy these advantages. What will be the result of that? Why do the Mediterranean and Marine West Coast Climates Extend So Far Inland Compared to North America?? East-Coast Climates Humid Subtropical - Where? - Temperature and precipitation patterns? - Agriculture? Humid Continental - Where? -Temperature and precipitation patterns? - Agricutlure? Northern Climates Subarctic - Where? - Agriculture? Tundra - Where? - Agriculture? -Temperature and precipitation patterns? -Natural Vegetation? -Temperature and precipitation patterns? -Natural Vegetation? Undifferentiated Highland - Where? - Temperature and precipitation patterns? - Agriculture? Steppe - Where? - Temperature and precipitation patterns? - Agriculture? Russian Steppes Other Climates The North European Plain is an agriculturally productive, densely populated region, that has been a major thoroughfare through history. North European Plain vs. Siberia Siberia, though mineral-rich, is sparsely populated and very difficult to traverse. What’s the difference? What are the climates? What factors best explain birth rates? What factors best explain death rates? What is the main direction of voluntary immigration? Central Asia has a crude birth rate of 23 and a crude death rate of 8. What is its RNI? What is its doubling time? Russia has a crude birth rate of 10 and a crude death rate of 15. What is its RNI? What is its doubling time? What factors predict wealth? Europe has a per capita GDP of about $27,000. The richest 10% of the population controls about 25.2% of the wealth. The poorest controls about 3%. What is the per capita GDP of the poorest 90%? What factors predict arithmetic population density? Belarus has about 10 million people living in 200,000 square kilometers. 30% of the land is arable. What is its arithmetic population density? What is its physiological population density? What do most of the people of Europe do for a living? What do people of the Russia zone do for a living? What is the spatial link between language and religion in Europe? What is the Slavic Coreland? What forms the boundaries of the Coreland? What religion and language family dominate the Coreland? Describe the distribution of languages and religions outside the Coreland? Major Events: Medieval Agricultural Revolution Introduction of Paper Bubonic Plague Printing Press Columbian Exchange Protestant Reformation Century of Religious Wars Industrial Revolution European Union Slavs, Vikings Byzantine Influence Mongols/Tatars Growth of Russian Empire Czarist Russia Enslavement of Serfs Opportunities/Threats of European Plain Russo-Japanese War, WWI Rise of Soviet Union Drawing Borders WWII & Cold War Successes/Failures Role of Oil Collapse of Soviet Union Balkanization & Ethnic Cleansing Ossetians Rise of Militant Islam