review flashcards
advertisement

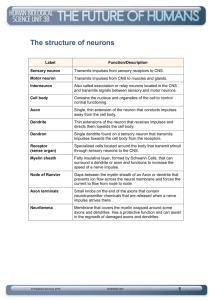
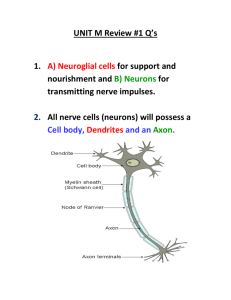
What are the different parts of a neuron? • • • • • Dendrites Cell body Axon Axon terminal Myelin sheath What is a neurotransmitter? • Substance released at axon terminals • Stimulates muscle contraction • Stimulates nerve impulse What is your central nervous system? • Brain • Spinal Cord What is the function of your Autonomic Nervous System? • Inovluntary Response • Emotional (Fight/Flight): – Increased adrenaline – Increase sweat – Pupil dilation – Increased heart and respiratory rate • Natural – Digestion – Excretion What is a neuron like at resting potential? • Inside less positive Less K+ ions • Outside more positive More Na+ ions What is the spinal cord? • Middle man between body and brain • Contains motor pathways • Contains sensory pathways What are unipolar neurons? • Cell body away from dendrites • Sends sensory / afferent messages to CNS What are multipolar neurons? • Cell body directly off of dendrites • Sends motor/efferent messages from CNS to body What do you use Broca’s Area for? • Speech production • Complicated speech What does your occipital lobe do? • Vision • Combines images to form complete picture What does your temporal lobe do? • Visual + Auditory Memory What is your cerebellum for? • Coordinates muscle movement • Makes movement smooth What are your thalamus and hypothalamus used for? • Maintaining fluid-ion levels • Maintaining salt levels Describe the pathway for an involuntary, natural response: • • • • • Sensory CNS Motor Autonomic Parasympathetic Describe the pathway for an involuntary, emotional response: • • • • • Sensory CNS Motor Autonomic Sympathetic Describe the pathway for a voluntary response: • • • • Sensory CNS Motor Somatic What are the events in a nerve impulse? • • • • • Neurotransmitter Opening of Na+ channels Na+ flows into neuron Opening of K+ channels K+ flows out of neuron What are junctions? • Space between… • 2 neurons • 1 neuron + 1 muscle (effector organ) What are different ways to describe a nerve impulse? • • • • Electrical current Flow of charged particles Movement of ions Movement of sodium in, and potassium out What are neurons? • Nerve cells • The dendrites receive incoming messages • The cell body integrates incoming messages • The axon sends messages out • The axon terminal is the end of outgoing messages What happens with your iris when you go from a dark bright room? • Iris contracts • Decreases amount of light entering eye What happens to your iris when you go from a bright dark room? • Iris relaxes • Increases amount of light entering eye What is myopia? • Nearsightedness • Bulging or Enlarged Cornea • Light overfocused How do you fix myopia? • Lens which is thinner in the middle • Spreads out light rays What is hyperopia? • Farsightedness • Flattened cornea • Light underfocused How can you fix hyperopia? • Lens that is thicker in the middle • Will condense light rays What is the sclera? • Outermost, white tissue of eye What is the choroid? • Made of dark pigments • Keeps light inside eye What is the pupil? • Hole in the iris • Lets light into the eye What is the iris? • Colored ring around pupil • Contracts + Relaxes to control amount of light entering eye What is the optic nerve? • Connected between Retina + Brain • Relays visual impulses What’s another word for afferent? • sensory What’s another word for efferent? • motor What are some involuntary organs? • • • • • Intestines Stomach Heart Glands Kidneys What are some voluntary organs? • Skeletal muscle List out the tissues of the eye: • Outermost = Sclera • Choroid • Innermost = Retina What could cause sound waves to not get to your cochlea? • Damage to hammer, anvil and stirrup • Damage to ear drum (tympanic membrane) What does the basilar membrane respond to? • Changes in pitch What does your otolithic membrane respond to? • Changes in static equilibrium • Head upright or not What does your endolymph fluid + cap respond to? • Changes in dynamic equilibrium • Head twisting and turning? What is conduction deafness? • Temporary • Damage to tympanic membrane, hammeranvil-stirrup What is sensorineural deafness? • • • • Permanent damage Damage to receptor hairs Damage to cochlea Caused by disease, virus, genetics Describe the process of smelling: • Smell = organic molecules • Organic molecules dissolve in nose mucus • Molecules bind to olfactory receptor hairs Where do you taste something sweet? • Very front tip of tongue • Taste monosaccharides (sugars) Where do you taste something sour? • Back Sides of tongue • Taste acidic, hydrogen ions in food Where do you taste something salty? • Front sides of tongue • Taste metallic ions in food Where do you taste something bitter? • Very back of tongue • Taste alkaline or nitrogenous compounds in food Which receptors pick up on changes in temperature? • thermoreceptors Which receptors pick up on pain? • nociceptors Which receptors pick up on deep vibrations? • paccinian KNOW THIS DIAGRAM! KNOW THIS DIAGRAM! KNOW THIS DIAGRAM! KNOW THIS DIAGRAM!