1.2 to 1.4 Lesson Material
advertisement

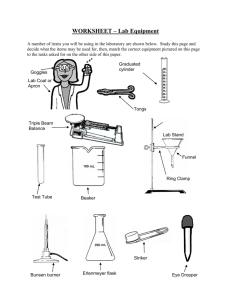
1.2 Let’s Play Safe 1.3 Drawing Scientist Tools 1.4 Using the Bunsen Burner Refer to page 5 of your notes • The science laboratory can be a dangerous place if you are not careful. • There are certain rules that must be followed for your own safety and for the safety of everyone else in the room. Refer to page 5 of your notes Refer to page 4 of your notes Activity Time (page 6) Look carefully at the drawing below and find all of the rules that are being broken in the science laboratory Pour substance down the sink •Mixing chemicals without the teachers’ permission Throwing rubbish / pouring chemicals into the washing basin Test tube pointing to own’s face and partner’s face Eating in the science lab. Playing and pushing in the lab Smelling chemicals without teachers’ permission Loose papers close to the Bunsen flame This will be done in the lab. Hazard Symbols Some of the chemicals that you use in the laboratory are potentially harmful. Hazard labels are used to label such chemicals to alert you to the type of hazards present. Refer to page 7 of your notes 1. All laboratory apparatus should be drawn in outline only and in their correct proportion. 2. Do NOT draw a 3-dimensional outlines for laboratory apparatus. 3. Draw sectional diagrams of the apparatus that your teacher shows you. 4. You may make use of the template of laboratory apparatus sold in the school bookstores or included in your mathematical set. Laboratory Apparatus Diagram Purpose For transferring For supporting liquids into a flask apparatus during experiments For separating an insoluble solid from a liquid with the help of a piece of filter paper Name thistle funnel filter funnel retort stand Laboratory Apparatus Diagram Purpose For separating an For supporting experimental set- apparatus during up from the heating outside environment For containing chemicals or collecting liquids Name bell jar beaker tripod stand Laboratory Apparatus Diagram Purpose For containing chemicals when preparing gases if the process requires no heating For containing or heating small amount of substances For measuring a volume of liquid to an accuracy of 0.5 cm3 Name flat-bottomed flask test tube Measuring Cylinder Laboratory Apparatus (pg7) Diagram Purpose For containing chemicals or collecting liquids For containing water when For preparation of gases collecting gases if the process requires heating Name conical flask water trough round-bottomed flask Laboratory Apparatus Diagram Purpose For evaporating a For collecting gases liquid from a solution For heating solids directly over a flame Name evaporating dish Crucible gas jar Let’s try(page 7) Name the apparatus C – H in the following figure. thistle funnel retort stand round-bottom flask gas jar tripod Water trough Refer to page 8 of your notes To raise the flame to a suitable height for burning The Bunsen Burner To control the amount of air entering the burner by opening or closing the airholes We will covering the Bunsen burner in the lab. To enable the gas to rush out from the gas supply and to draw in air To control the air entering the Bunsen Burner Gas Tap To control the flow of gas to the Bunsen Burner Refer to page 8 of your notes Types of flames almost colourless zone of complete combustion hottest part Hottest orange zone of incomplete combustion blue zone of partial combustion dark zone of unburnt gas Bunsen burner A non-luminous flame 1. occurs when the air-holes are open, allowing air into the burner 2. blue 3. burns steadily 4. hotter than the luminous flame 5. hottest part of the flame is just above the tip of the blue zone. A luminous flame 1. occurs when the air-holes are closed and very little air is allowed to mix with the gas 2. carbon particles are deposited on apparatus 3. orange 4. appears flickering and unsteady 5. not very hot Refer to page 9 of your notes STRIKEBACK 1. occurs when there is too much air entering air-hole 2. instead of burning at the top of the barrel, the gas burns at the jet 3. when a strike back occurs, turn off burner immediately jet http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AWnSSvdMp5g Refer to page 9 of your notes HEATING LIQUID IN A BEAKER 1. 2. 3. 4. put wire gauze on tripod stand put beaker of liquid on it light Bunsen burner and then push it under the tripod stand turn off burner when the liquid reaches required temperature Refer to page 9 of your notes HEATING LIQUID IN A TEST-TUBE 1. hold test-tube with test-tube holder 2. ensure that the mouth of the test-tube is pointing away from myself and others 3. slant test-tube at an angle of about 45o and heat it in the hottest part of a Bunsen flame 4. move the test-tube through flame 5. liquid to be heated should occupy no more than one-third test-tube Let’s try(page 7)