Intro to Macro
advertisement

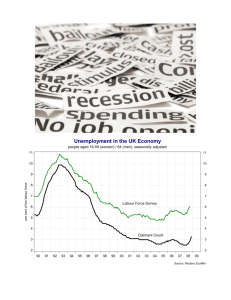
Module 2 Jan 2015 The alternation between economics downturns and upturns in the macroeconomy Depression-A deep and prolonged downturn Recession-A shallower and shorter downturn; period in which output and employment are falling. Expansions-Periods in which output and employment are rising. AKA as Recoveries Employment is the total number of people working for pay Unemployment is the total number of people who are actively looking for work Labor force is the total employed and unemployed (Please note – people who do not work and are not actively seeking employment are not part of the labor force.) The unemployment rate – the % of the labor force who are unemployed is a good indicator of what conditions are like in the job market Output – the quantity of goods and services produced Aggregate output – the economy’s total production of goods and services for a given time period Inflation – the rising overall price level, the price of a can of soda when I was 10 was .25, now I pay .75 Deflation – the falling overall price level, the price of gas last summer was over 4.00, yesterday I paid 2.35 Price Stability – when the aggregate price level is changing only slowwwwwly. We can afford many conveniences today as compared to the past because of economic growth, or the increase in the maximum amount of goods and services an economy can produce. Models are simplified versions of reality used to study economics “Other things equal” assumption – means that all other factors remain unchanged and economists can focus on one change at a time Define depression and recession and explain the difference between the two concepts. During the expansion phase of a business cycle, which of the following is likely to increase? ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ A. the unemployment rate B. The price level C. economic growth rates D. the labor force E. wages Imagine a firm that manufactures textiles (pants and shirts). List the four categories of resources, and for each category, give an example of a specific resource that the firm might use to manufacture textiles. Describe some of the opportunity costs of the following choices: ◦ A. attend college instead of taking a job ◦ B. watch a movie instead of studying for an exam ◦ C. ride the bus instead of driving your car Use the concept of opportunity cost to explain the following: ◦ A. There are more parks in suburban areas than urban areas ◦ B. More people choose to pack their own lunch when the economy is slow and wages are down