What Is Strategy?
advertisement

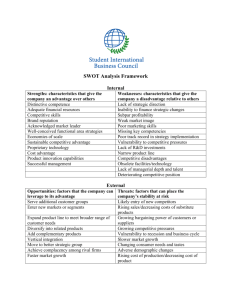
What Is Strategy? • Distinguishing strategy from tactics: – Strategy is the overall plan for deploying resources to establish a favorable position. – Tactic is a scheme for a specific maneuver. • Characteristics of strategic decisions: – Important. – Involve a significant commitment of resources. – Not easily reversible. Common Elements in Successful Strategy Successful Strategy EFFECTIVE IMPLEMENTATION Long-term, simple and agreed objectives Profound understanding of the competitive environment Objective appraisal of resources Sources of Superior Profitability INDUSTRY ATTRACTIVENESS RATE OF PROFIT ABOVE THE COMPETITIVE LEVEL Which industries should we be in? CORPORATE STRATEGY How do we make money? COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE How should we compete? BUSINESS STRATEGY Resources As the Basis for Superior Profitability Barriers to Entry Industry Attractiveness Rate of Profit in Excess of the Competitive Level Monopoly Patents Brands Retaliatory capability Market share Vertical Power Firm size Financial resources Cost Advantage Process technology Plant size Low-cost inputs Differentiation Advantage Brands Product technology Marketing capabilities Competitive Advantage The Value Chain: The Mckinsey Business System TECHNOLOGY PRODUCT DESIGN MANUFACTURING MARKETING DISTRIBUTION SERVICE The Porter Value Chain SUPPORT ACTIVITIES FIRM INFRASTRUCTURE HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT PROCUREMENT INBOUND LOGISTICS OPERATIONS OUTBOUND MARKETING LOGISTICS & SALES PRIMARY ACTIVITIES SERVICE The Rent-earning Potential of Resources and Capabilities THE EXTENT OF THE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE ESTABLISHED THE PROFIT EARNING POTENTIAL OF A RESOURCE OR CAPABILITY Scarcity Relevance Durability SUSTAINABILITY OF THE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE Mobility Replicability Property rights APPROPRIABILITY Relative bargaining power Embeddedness of resources The Framework for Analyzing Resources and Capabilities 4. Select a strategy 3. Appraise the rent-earning potential of resources/ capabilities 2. Identify capabilities 1. Identify the firm’s resources. Appraise strengths and weaknesses STRATEGY POTENTIAL FOR SUSTAINABLE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE CAPABILITIES RESOURCES 5. Identify resource gaps that need to be filled. SWOT Analysis • Acronym derived from Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. – Used for analyzing industry environments and firms’ internal strengths and weaknesses. • Performed in a 2-step process: – Managers thoroughly evaluate their firm’s internal strengths and weaknesses and its environmental (external) opportunities and threats. – Managers use the evaluation developed in the first step to place the firm in one of the quadrants of the SWOT matrix shown in Exhibit 5. Exhibit 5: SWOT Analysis Numerous Environmental Opportunities Critical Internal Weaknesses Overcome Weakness Restructure Grow Diversify Major Environmental Threats Substantial Internal Strengths SWOT Analysis (Cont.) • Advantages of SWOT analysis – Easy to use. – Can be helpful framework for getting managers to think constructively about their firms’ external environments and internal strengths and weaknesses. • Drawbacks of SWOT analysis – Subjective. – Biased by managers’ perceptions of their firms’ strengths and weaknesses SWOT Analysis (Cont.) • For example, managers of strong firms will likely view environmental phenomena as opportunities, while their counterparts in weak companies will likely view them as threats. – The use of SWOT analysis is likely to yield few clear-cut recommendations. The Emergence of Competitive Advantage How does competitive advantage emerge? External sources of change e.g.: •Changing customer demand •Changing prices •Technological change Resource heterogeneity among firms means differential impact Some firms faster and more effective in exploiting change Internal sources of change Some firms have greater creative and innovative capability Sustaining Competitive Advantage Against Imitation REQUIREMENTS FOR IMITATION Identification Incentives for imitation ISOLATING MECHANISMS - Obscure superior performance - Deterrence--signal aggressive intentions to imitators - Pre-emption--exploit all available investment opportunities Diagnosis - Rely upon multiple sources of competitive advantage to create “causal ambiguity” Resource acquisition - Base competitive advantage upon resources and capabilities that are immobile and difficult to replicate Sources of Competitive Advantage COST ADVANTAGE COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE DIFFERENTIATION ADVANTAGE