MGMT 490 Firm Strategic Analysis 2007
advertisement

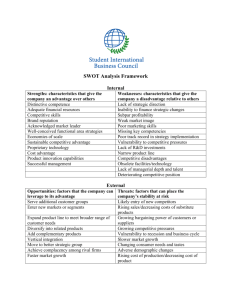
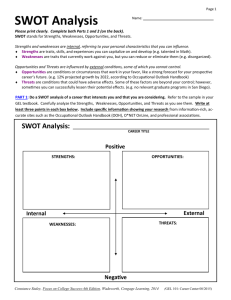
Firm Strategic Analysis (3-Step Process) Outline MGMT 490 Spring 2007 Dr. Dennis R. Briscoe I. Identification of Strategy (includes but not limited to SWOT) A. Firm Situation i. General macro environment ii. Industry and Competitive analysis 1. Dominant economic characteristics of the industry (e.g., size, rate of growth, stage in life cycle, nature of competition, georgraphic dispersion, degree of fragmentation) 2. Competitive analysis (Porter’s 5 Forces) [plus 6th force: complementors] 3. Driving Forces 4. Competitive Position of major companies/strategic groups 5. Competitor analysis 6. Key success factors 7. Opportunities and threats 8. Industry prospects and overall attractiveness iii. Firm analysis 1. Strategic performance indicators (e.g., revenues, profits, growth rate, market share) 2. Firm competitive advantage(s) and Distinctive Competencies (Strengths and Weaknessses) a. Internal resource strengths and competitive capabilities b. Internal weaknesses and resource deficiencies c. Efficiency, quality, innovativeness, customer responsiveness d. External threats to company’s well being 3. Competitive strength assessment (prices and costs competitive?) 4. Conclusions concerning competitive position 5. Barriers to developing and sustaining competitive advantage 6. Nature of industry firm competes in (e.g., fragmented or consolidated, stage of life cycle, technology-driven, global) 7. Major strategic issues the company must address B. Firm strategy: What is it? What has it been? What is its history (and how has it changed over time and why)? Intended or emergent? Strategy should be identified at all levels: corporate, business, and functional. Price versus differentiation; diversification; etc. II. Evaluation and Analysis A. How is firm doing? Financially and strategically? (This includes financial analysis, ratios, etc.) B. Is the strategy a good fit? C. Has the strategy been implemented well? III. Recommendations