Woodland_Ecology
advertisement

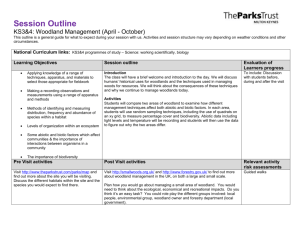
Woodland Ecology
Definitions
Habitat
Microhabitat
Ecosystem
Niche
Food Chains and Webs
A food chain shows how each living thing gets
its food
Plants are PRODUCERS –use sunlight to
produce food
Animals eat plants or other animals CONSUMERS
Animals eating plants are HERBIVORES
Animals eating other animals are
CARNIVORES
Carnivores that eat Herbivores are called
SECONDARY CONSUMERS
Carnivores eating other carnivores are
TERTIARY CONSUMERS
There are also DECOMPOSERS which feed
on dead and decaying matter
Interconnected food chains form a FOOD
WEB
TROPHIC LEVELS
In the chain energy is passed from one LEVEL
to the next
Only a small amount of the energy that is
received is passed on to next level
PYRAMIDS
Of numbers
Of biomass
A woodland chain
hazel tree food for wood mouse food for tawny owl
and nuts
Hazel trees grow well in open woodland and produce nuts.
Wood mice live on the woodland floor where they can find
nuts that have fallen off the trees and where they can hide in
the undergrowth from owls.
Tawny owls have exceptionally good hearing that helps them
to hear mice rustling in the undergrowth.
Here are examples of other food chains:
Dead plants centipede robin
Oak leaf caterpillar blue tit
Woodland structure
‘Layers’
Ground
Field
Shrub
Canopy – upper, lower
Examples of plants in each
‘layer’
http://www.countrysideinfo.co.uk/woodland_
manage/struct.htm
Colonisation
Succession
Catastrophic change
Veteran Trees
“Veteran Trees are trees which, because of
their great age, size or condition are of
exceptional value culturally, in the landscape
or for wildlife”
javascript:__doPostBack('ctl00$ContentPlace
Holder1$rpFiles$ctl01$hlLink','')
Plantations and man made
forests
Improving plantations
Different silvicultural systems
Restructuring – diversify age structure
Changing edge structure
More broadleaves
Diversify species
Less chemicals
Open ground , rides
Diversity of habitats.
Thinning
Use water, wetlands, rocks etc.. Riparian zones
Reduce grazing
Management for particular species or habitats
Integrated land use
UKWAS