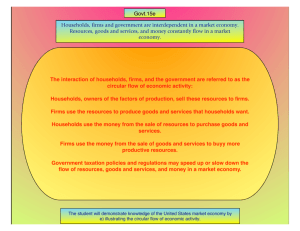
Economic Goals, Systems, Circular Flow Model (Chapter 2)
advertisement

Traditional Team 1 Team 2 Team 3 Team 4 Team 5 Team 6 Market Command Total 1. 2. 3. 4. Which system had the most incentive to work? Why? Which system had the least incentive to work? Why? Which system was the most inefficient by modern standards? Explain. Which system would you like to live in, why? Standards Mastery Sheet SSEF1a 1 2 3 4 5 37 + + + - + - SSEF1b 9 10 11 12 13 15 16 39 SSEF1c 6 8 SSEF1d 17 18 19 20 26 40 SSEF2a 23 24 25 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 SSEF2b 7 8 21 22 23 14 23 38 40 Total Correct Total Number Mastery Percentage 4 6 67 Economic System Economic System – method used by society to allocate/distribute the scarce resources, in order to provide for the wants and needs of the people Three Economic Questions 1. 2. 3. What goods and services should be produced? How should these goods and services be produced? For Whom to produce them for? Four Economic Systems 1. 2. 3. 4. Traditional economy – relies on habit, custom, or ritual to decided the 3 economic questions Market economy – economic decisions are made by buyers and sellers trading freely. Command Economies – in a centrally planned economy, the central government decides how to answer the three economic questions. Mixed Economies – most modern economies are mixed economies, marketbased economic systems in which government plays a role in the market. Bead Game Simulation Economic Freedom Economic Freedom - freedom to make choices free of the government • Individual – where to work, study, consume • Business – what, where and how to produce Economic Efficiency Economic Efficiency - making the most of scarce resources, using your resources wisely and productively •Technological innovations allow society to be more productive • Humans to robots Economic Security Economic Security - government will provide a safety net in times of economic downturns • Social Security, welfare, unemployment checks, etc. Economic Predictability Economic Predictability - knowing that goods and services will be consistently available • Gas, food, energy, etc. Economic Equity Economic Equity - Fairness, being paid according to your skill level, not being discriminated against • Lebron James is higher paid than a teacher • A teacher is higher paid than a cashier at Wal-mart Economic Growth Economic Growth – improving the economy from year to year, improving standard of living as measured by GDP. • Individual – better jobs, nicer homes, newer cars….better stuff! • Business – produce more, increase customers, open new factories, etc. Economic Innovation Economic innovation – improving upon existing technology in order to improve efficiency. • Walkman to the iPhone, Record Player to Digital Media Additional Goals Additional Goals – future goals for a society • Environmental protection, full employment, universal medical care, etc. Poster Requirements: 1. Title - Economic Goals and Societal Values 2. Summary Statement – “The Economic Goals and Societal Values provide a basic framework for each society and their attempts to provide for their people.” 3. Pictures of each goal represent each of the economic and social goals. • 1 if working alone • 2 if working with a partner • 3 if working with a group of 3 4. Label, describe and summarize each picture 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Economic Freedom Economic Efficiency Economic Security Economic Predictability Economic Equity Economic Growth Economic Innovation Additional Goals Economic Efficiency Picture Summary: This picture represents assembly line production at an automobile manufacturing plant. This shows how the division of labor and specialization can increase efficiency. Economic Goals and Societal Values Summary Statement: The Economic Goals and Societal Values provide a basic framework for each society and their attempts to provide for their people. Economic Predictability Economic Security Economic Efficiency Definition: picture represents an efficient use of resources through assembly line production Economic Innovation Economic Freedom Economic Growth Economic Equity Additional Goals Poster Requirements: 1. Title - Economic Goals and Societal Values 2. Summary Statement – Purpose of economic and Societal Values 3. At least 8 pictures to represent each of the Economic Goals and Social Values 4. Label, definition and picture description for each of the 8 Economic Goals and Societal Values Statements 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Last week I willingly enrolled in college courses at Coastal. I am so happy that I make my decisions about my future. My uncle lost his job, but thankfully he is able to receive unemployment checks. Wal-Mart recently upgraded all of their registers to touch screen monitors. General Motors replaced all of their human workers with robots in order to increase productivity. As a result of the internet and technology, our economy has experienced significant expansion over the past 30 years. I can always expect Publix to have the food I like! Hopefully in the future we will have full employment. With every degree/skill I earn, I improve my ability to make money. Economic Goal 1. Economic Freedom 2. Economic Security 3. Economic Innovation (Efficiency) 4. Economic Efficiency (Innovation) 5. Economic Growth (Innovation) 6. Economic Predictability 7. Additional (Future) Goals (Equity) 8. Economic Equity (Growth) Imagine that you are walking into Walmart. List 3 items that you could purchase and the departments that you would find them in. The Free Market Market – buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods and services Market Economy – economic decisions are made by consumers and businesses based on buying and selling of goods and services All resources are privately owned Any income derived from selling resources goes exclusively to the owner The government has no role Role of the Consumer Consumer Sovereignty - in a free market, consumers determine the goods that are produced; this makes them "sovereign" over production in an economy. “Ruler” of the market; expressed through a dollar vote for products when we make purchases. “The customer is always right”. When consumers buy products, their “dollar vote” signals to producers what to make and how much. Specialization – the separation of tasks within a system; people focus on a specific purpose/task Division of Labor – Workers perform fewer tasks in order to operate more efficiently Specialization – the separation of tasks within a system; people focus on a specific purpose/task Division of Labor – Workers perform fewer tasks in order to operate more efficiently Specialization Examples Glynn Academy – teachers in different departments Each teacher can master their content Present it in the most efficient manner possible Social Studies Math Science English Specialization Examples Rancher Publix Worker Slaughter House Final Good (Output) Meat Cutter Consumer Good Specialization and Efficiency Productivity – average amount of output (good or service) per unit of input (labor, machine, etc.) Increased productivity means to do more with less Capital investments allow increased efficiency Specialization and Efficiency Productivity – average amount of output (good or service) per unit of input (labor, machine, etc.) Increased productivity means to do more with less Capital investments allow increased efficiency Productivity Mary looks over reports on four of her workers. Jack made 25 baskets in 5 hours. Walter made 36 baskets in 6 hours. Rudy made 40 baskets in 10 hours. Sam made 22 baskets in 4 hours. Jim made 50 baskets in 10 hours. Who has the greatest productivity? Jack 25/5 = 5 Baskets per hour Walter 36/6 = 6 Baskets per hour Rudy 40/10 = 4 Baskets per hour Sam 22/4 = 5.5 Baskets per hour Jim 50/10 = 5 Baskets per hour Walter has the greatest productivity Productivity Creates Wealth 3rd World Countries Developed Countries 29 Households and Firms Household – Person or group of people living in a residence Consumers - use the finished goods and services (outputs) to satisfy wants and needs Firm – business, organization that uses factors of production (inputs) to produce a product, which it then sells Suppliers – transform “inputs” (F.O.P.) into “outputs” (products) Product Markets Product Markets – Households and firms interact; producers sell their goods and services to consumers Households are buyers of goods and services Firms are sellers of goods and services (outputs) Factor Markets Factor Markets – the markets where productive resources (F.O.P)/Inputs are bought and sold Labor - Firms (businesses) hire workers and pay them salaries Land - Purchased/rented land Capital - Use money from households (savings, investment, etc) to purchase capital goods Circular Flow Model of Economic Activity – shows the flow of money and goods/services from and to businesses and households Consumer Spending Product Market Business Income/Revenue •Market for Goods and Services •Firms sell Households Buy Consumer Goods and Services Final Goods and Services Sold Households Firms (Business) • Buy and Consume Goods and Services •Own and sell the F.O.P • Produce and sell Goods and Services •Hire and use F.O.P. Land, Labor, Capital - provided by household Inputs for Production (F.O.P.) Factor Market Income to Households/Individuals Market for F.O.P •Households sell •Firms buy Payment for F.O.P. – Rent (Land) Wages (Labor), Interest (Capital), Profit (Entrepreneurs) Application Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. In the factor market, what do businesses provide households? Income/payment the F.O.P The flow of goods and services in the product market is represented by which firm and products on the model below? Starbucks/Coffee When you apply for a job at the local Starbucks which market are you in? Factor Which color arrows represent the flow of money; what color arrows represent the flow of inputs and outputs. Blue/Tan Daily Assignment - Circular Flow Model of Economic Activity Consumer Spending Business Income 1. _________________________ 1. _________________________ Product Market Goods Purchased Goods Offered 1. ___________________________ 1. ______________________________ 2. ___________________________ 2. _______________________________ Firm Household 1. ________________________ Firm 1. _____________________________ Firm 2. _____________________________ Input for Production Factor of Production Offered 1. ___________________________ 1. ___________________________ Weekly Income 1. __________________ Factor Market Payments for F.O.P 1. _________________ Daily Assignment - Circular Flow Model of Economic Activity Consumer Spending Business Income 1. _________________________ 1. _________________________ Product Market Goods Purchased Goods Offered 1. ___________________________ 1. ______________________________ 2. ___________________________ 2. _______________________________ Firm Household 1. ________________________ Firm 1. _____________________________ Firm 2. _____________________________ Input for Production Factor of Production Offered 1. ___________________________ 1. ___________________________ Weekly Income 1. __________________ Factor Market Payments for F.O.P 1. _________________ Circular Flow Model of Economic Activity Consumer Spending Business Income 9.49 1. _________________________ 1. _________________________ 9.49 Product Market Goods Purchased Goods Offered Tacos Burritos 2. ___________________________ Fajitas Fajitas 1. ___________________________ 1. ______________________________ 3.___________________________ Household Elisa 1. ________________________ Marcella 2. ________________________ Firm Cilantros Firm 1. _____________________________ Books a Million Firm 2. _____________________________ Input for Production Factor of Production Offered 1. Labor/Salesperson 1. ___________________________ 2. 3. Weekly Income 200 1. __________________ Factor Market Stockers _________________________ Coffee Sellers _________________________ Cashiers ________________________ Payments for F.O.P 3000- Lease 1. ________________ 2200 – Electric 2. ________________ 3. ________________ 400 - Water American Free Enterprise Economic Freedom Competition Private Property Rights Self-Interest Voluntary Exchange Profit Motive Description Description Description Description Description Description Example Example Example Example Example Example 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. Economic Freedom Description - Individuals’ right to choose your occupation and what to buy. Firms’ right to hire or produce. The right to conduct yourself with little government interference. Examples: 1. I had the freedom to become a teacher and a coach; I can buy whatever I want. 2. Firms range from automakers to fast food. Voluntary Exchange When individuals willingly engage in a transaction where both parties benefit. Allows people to decide what and when they want to buy and sell, rather than forcing them to buy and sell at particular times or specific prices Examples: When I get a haircut, I get a fresh look, Sportsclips gets my money When I buy gasoline, I get energy for my car, the firm gets my money Private Property Rights Description – Individuals and businesses have the right to buy and sell as much property as they want Property owners can prohibit others from using their property The fifth amendment protects us from the federal or state governments taking our property for their own use. Examples: Households and firms are encouraged to own property and enjoy the protection of the property Firms can own and operate their business with limited interference from the government Profit Motive The force that encourages people and organizations to improve their material well-being Examples Many people in our society are driven by the desire to make money, which ultimately benefits the market People in the U.S. are rewarded for innovations and efficiency via cash incentives Competition Competition – efforts among sellers/producers to attract consumers at various prices At the heart of market economic philosophy Examples: Mcdonalds vs. Burger King Walmart vs. Target Circular Flow Model of a Mixed Economy Consumer Spending/Investing Business Income/Revenue Product Market Goods and Services Sold Goods and Services Purchased: Households Expenditures Expenditures Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneur Income to Households/Individuals Firms Inputs for Production (F.O.P.) Factor Market Payment for F.O.P. – Wages, rent, capital goods Role of the Government in a Market Economy Government acts an informer, protector, provider, and regulator Government has the responsibility to protect property rights, contracts and other business activities Role of the Government in a Market Economy Government has the responsibility to protect property rights, honor contracts, protect against discrimination, monopolies or unfair business practices Role of the Government as Informer Role of the Government as Informer: Make sure that producers provide consumers with accurate information Consumers use govt. info. to protect themselves from dangerous products and fraudulent claims. Role of Government as Regulator Role of government as a protector: Federal government acts to preserve competition, regulates airlines, communications, banking, etc. Though they do not control it, they impose various restrictions on the private market Gas stations, must dispose of used motor oil properly Zoning laws, prevent homeowners from running businesses out of their homes Negative Effects of Regulation Government regulation can have negative effects on businesses and consumers Negative effects: 1. Government rules can increase the cost of business 2. Stifled competition can lead to high prices 3. Increase of governmental spending can lead to higher taxes Government as a Provider Public sector- the part of the economy that involves the goods provided by the government Private sector- the part of the economy that involves the goods provided by private firms Public Goods and Services Public Good/Service - A shared good or service for which it would be impractical to make consumers pay individually and to exclude nonpayers. Education, military, National Park, Snow Removal, Fireman Redistribution of Income When the government takes from one group and reallocates to another group Welfare, Social Security, Unemployment, Food Stamps, etc. Market Failure The market, on its own, does not distribute resources efficiently, choices made by individuals determine what goods get made, how, and how much Free riders, monopoly, roads and bridges in a sparsely populated area, etc. Negative Externalities Negative Externality – negative effects experienced by people that had no part in the consumption of a good or service Cigarette smoker, chemical waste dumping, foreclosures and property values, etc. Negative Externalities Negative Externality – negative effects experienced by people that had no part in the consumption of a good or service Positive Externalities Goods/services that generate benefits to many people, not just those who pay for the goods Education, better technology, medicine, etc. Free-Rider Problem A free rider is someone who would not choose to pay for a certain good or service, but who would get the benefits of it anyway if it were provided as a public good Application Question Write an example of a negative and positive externality. What kind of government regulation could be used to eliminate your negative externality? Command Economies Command – central authority owns and operates the Factors of Production Centrally Planned Economy – central government answers the three economic questions; WHAT to produce, HOW to produce, and FOR WHOM to produce Oppose private property, free market pricing, economic freedom Socialism and Communism Karl Marx – German social philosopher that studied economic systems in Europe Communist Manifesto – written by Marx and Frederick Engels became basis for modern-day command economies Thought capitalism would fail because it put too much wealth in the hands of few and left everyone else poor Believed in a “no-class” system, where all share in wealth/power Socialism – distribution of wealth and F.O.P. equally amongst society Communism – political and economic system with centralized economic decision-making Authoritarian Government – exact strict obedience from their citizens; do not allow individual freedom Chapter 2 Section 2 – Daily Assignment Economic Profile Adam Smith pgs. 33 1. 2. 3. What was Adam Smith’s ethnic and professional background? •Scottish, Philosopher, Professor What was the name of the book that he published; when was it published? •Wealth of Nations What did Smith identify in the book? •Land, labor and capital as the factors of production that generate wealth 4. What did he assert about specialization and division of labor? •Productivity increases through specialization 5. What did he believe about the role of government in the economy? •Government must leave individuals as free as possible to pursue their interests 6. Define the French term Laissez Faire; why did Smith believe in Laissez-Faire economics? •Individuals try to pursue their own self-interest will benefit all of society 7. What is meant by his metaphor of the Invisible Hand? • Let them do as they please 8. How do both consumers and businesses benefit from this philosophy? •Consumers buy what they want, producers supply for profit Chapter 2 Section 3 – Daily Assignment Questions “The Former Soviet Union” pgs. 36-38 How did the Soviet Union arise? 2. Where did Soviet planners allocate the factors of production? 3. How did the Soviet Union control agriculture? 4. What three industries did Soviet Planners favor? 5. How did the Soviet Union view entrepreneurial endeavors? 6. What was the quote used by Soviet consumers as a joke? 7. Why were Soviet Consumers’ left unsatisfied? Page 39 – Russia in Crisis 1. How did many Russians initially respond to the Communist collapse? 2. What happened over the next decade? 3. How did Russia deal with corruption? 4. What were some characteristics of Russia’s financial problems? 5. What evidence can be seen that success is in sight? 1. Scenario 1 You have two cows. You trade one to your neighbour for a bull. You only produce what you need to survive. Scenario 2 You have two cows. The State takes both and gives you just enough milk to live Scenario 3 You have two cows. You sell one and buy a bull. Your herd multiplies, and your wealth grows. You sell your herd and retire on the income. 1. 2. 3. 4. What economic system matches each scenario? Which scenario do you think is the most ideal and why? Which scenario do you think sounds the most like the United States? Why? What countries do you know of that could fall into scenario 2. Tradition Command Market What to Produce? Whatever is necessary for the tribe to survive. Whatever the government tells them to produce. Whatever is in demand by the consumers. How to Produce it? Based on tradition, habit and custom; the way its always been done. Based on the government. The most efficient method possible; technological innovations. For Whom to Produce? The tribe Whoever the government tells them to produce it for. Consumers that are willing to purchase. Examples Tradition 1. Central African Mbuti 1. North Korea 2. Australian Aborigines 2. Cuba 3. Inuits of Canada 3. China 4. Former Soviet Union 1. Change economic direction in a short time Health and public services are available at little or no cost (regardless of income) Advantages 1. Everyone knows their role in society/economy 2. 2. 1. Disadvantages Command Economic questions are answered based on tradition Discourages new ideas 1. Not designed to meet wants of consumers work hard Lack of progress, lower standard of living 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. United States Canada Japan South Korea Singapore Germany France Great Britain Western Europe 1. Adjust to change over time 2. Individual economic freedom 3. Limited government interference 4. Decision-making is decentralized 5. Variety of goods and services 6. High degree of consumer satisfaction 2. Does not give incentive to 2. Market 3. Large decision-making bureaucracy 4. Lack of economic flexibility Lack of economic freedom, 5. profit motive 1. Does not provide basic needs for everyone 2. Lack of public goods by private markets 3. High degree of uncertainty, job loss, competition 4. Market failures (monopoly) 1. What traditions are mentioned regarding American society? •Thanksgiving, bouquet toss, shaking hands 2. List some additional traditions that you have in your family. • Open one present on Christmas Eve 3. How did the Inuit exemplify a traditional economic system? •Share the spoils of the hunt 4. How did the State Planning Commission determine the direction of the Soviet economy? • Determined the needs based on governmental decisions 5. What shortcut did Soviet workers take in order to fill their quotas; what did it lead to? • Made their products heavier 6. How did the State Planning Commission respond to a shortage of male workers? • Made the women go to work 7. Describe what a “dollar vote” indicates. • Spending money to show firms what to produce 8. Describe how the market adjusted from the 1970s gas shortage, to the 1980s. • People bought less gas-guzzling cars and bought more fuel-efficient ones 9. What examples are provided of the various goods and services provided in a market economy? • Internet, electric dog collars, Cable TV 10.How do both the majority and minority end up satisfied in a market economy? • Both can get what they want 11.What are the three conditions that must be met to ensure that market economies do not fail? • Competition, Flexibility, Access to information Modern Economies Free Enterprise – competition in the marketplace is allowed to flourish with no interference from government Modified Free Enterprise (mixed economy) – businesses are free to compete with some government regulation/intervention Centrally Planned Free Market Mexico North Korea France Hong Kong Iran South Africa Cuba United Kingdom Canada China Poland Japan United States Singapore Laissez Faire in a Modern Economy Laissez Faire – no government intervention in the economy Some government intervention is necessary in the economy; some needs are difficult to answer in the marketplace National defense, roads and highways, education, etc… Government acts a protector, regulator and overseer of economy Government Money Taxes from both households and businesses Income tax, state income tax, social security, Medicare/Medicaid, unemployment insurance, etc. Government in the Factor Market Government purchases land, labor, and capital from households United States gov’t pays 2.8 million employees $9.7 billion for labor Government in the Product Market Government purchases goods and services from firms (businesses) Office supplies, telephones, computers, etc. Economic Goals Market Command Tradition Economic Freedom Yes - People can produce what they want, how they want to and for whom No - Many aspects of economic activity are tightly controlled by the government No - Extremely limited, a person’s role in society is based on custom, heritage and tradition Economic Efficiency Yes – specialization, wise use of resources leads to profit No – Many resources go unused, Cuba 50% of fertile land is not utilized Yes/No – Tribal living does not waste resources/lack modern standards of efficiency and growth Economic Security No – a pure market economy prescribes to laissez faire. (mixed economies have some safeguards) Yes - employment and government sponsored programs are assured Some – your job and provisions are guaranteed by your tribe Economic Predictability Yes – most market No – command economies economies have high levels struggle to meet the needs of resource predictability of the consumer No – in most cases unpredictable, because resources can become scarce Economic Equity Yes – fairly paid based on your skills No – based on customary means of production not fair pay for acquired skills Economic Growth Yes - a fast rate due to competition and profit motive Economic Innovation Yes – innovation and technology leads to profit No – private incentive, profit motive do not exist Slow - lack of growth because of a lack of efficiency and profit motive Limited – lack of innovation because of a lack of profit motive No - lack of growth due to a lack of productivity and innovation No – lack of modern innovations Chapter 2 – VIS Terms 1. Traditional Economy 15. Socialism 2. Command Economy 16. Communism 3. Market Economy 17. Authoritarian 4. Market 18. Laissez-Faire 5. Free Market 6. Specialization 7. Division of Labor 8. Household 9. Consumer 10. Firm 11. Supplier 12. Product Market 13. Factor Market 14. Centrally Planned Economy Junk!!! Using the Chart Below, identify each groups Economic Goals and Societal Values and the picture they used to represent each goal. Group Number Economic Goal Picture 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Name Date (1-30) Class Period Chapter 2 Test ID: A, B, C Junk!!! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Economic Systems D.A. Video Questions - North Korea Circular Flow (Elisa and Marcella) Comparing Economic Systems Reflection Questions and Chart Free Enterprise Flow Chart Study Guide Chapter 2 CW Puzzle Terms Ch. 2 Daily Tens (9) Essential Questions (3) Notes Test Standard Sheet (include original test answers + corrections) Junk!!! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Economic System What to produce, How to produce them, Who to produce them for Economic: efficiency, freedom, security, predictability, equity, growth, innovation, additional goals Tradition, custom, ritual, habit Central planners dictate the what, how, for whom Buying and selling of households and firms Market Market economy Capitalism Households and Firms Input is something used to produce and output, which is a final good or service Product Factor Adam Smith, Wealth of Nations 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. Be limited in its role in the economy, “Let them do as they please”. Invisible Hand See Circular Flow a) Product b) when it changed hands from the household to the firm c) Factor, labor d) Grills, hostesses, cashiers e) Factor Karl Marx, Communist Manifesto That it would fail because it put too much money in the hands of the rich and not in the hands of the poor Communism, Socialism Authoritarian Economic Freedom Property Rights Profit Motive Voluntary Exchange Competition 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Name Date (9-4) Class Period ID: A, B or C Test Economics Systems 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. Economic Freedom Property Rights Profit Motive Voluntary Exchange Competition Extra Credit 1. Give an example of a positive and negative incentive. 2. Explain why the United States is not a true “pure market/free enterprise” system. Extra Credit 1. Which type of economic system do you think is the best method for allocating scarce resources? Explain why. 2. Other than the goal that you identified on your test, write the one that you think is the next most important. Explain why. Economic Goal and Societal Values 1. Economic Efficiency 2. Economic Freedom 3. Economic Security and Predictability 4. Economic Equity 5. Economic Growth and Innovation 6. Additional Goals Summary Making the most of scarce resources Freedom from government intervention in the production and distribution of goods/services Knowing that goods and services will be available, payments made on time, government will provide a safety net in times of economic downturns Fairness, being paid according to your skill level, not being discriminated against Example Manufacturer knowing the best way to use resources wisely (Assembly Line) Working where you want, spending money the way that you want, owning a business, etc. Security – Unemployment Checks, Social Security, Stimulus Money Predictability – gas at gas pumps, food at store Lawyers earn more than nurses, computer programmers more than truck drivers Economic growth refers to improving standard of living and GDP. Innovation, improving existing technology. Agricultural age to industrial age to information age. Innovations in computers, communication. Future goal for society. Environmental protection, full employment, universal medical care. Circular Flow Model of Economic Activity Consumer Spending/Investing Business Income/Revenue Product Market Goods and Services Purchased: Caramel Frappuccino Goods and Services Sold Firms Households Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneurs Inputs for Production (F.O.P.) Factor Market Income to Households/Individuals Payment for F.O.P. – Wages, rent, capital goods Essential Question #1 +2 How do each of the economic systems answer the three economic questions? 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. Tradition – based on habit, ritual, custom Market - based on buyers and sellers Command – based on central planners/government Mixed – market based with some government regulation How does the Circular Flow model show a market economy? 2. Flow of money from households to firms (product market), firms to households (factor market). • Flow of final goods and services (outputs) to households (product market), and factors of production (inputs) to the firm (factor market). 3. What do the economic and social goals help us to understand? • • Explain how each society provide goods and services for their people in light of scarce resources. Essential Question #1 1. How do each of the economic systems answer the three economic questions? 1. 2. 3. Tradition – based on habit, ritual, custom Market - based on buyers and sellers Command – based on central planners/government Essential Question # 3 3. What do the economic and social goals help us to understand? • Explain how each society provide goods and services for their people in light of scarce resources. Vince Lombardi “What it Takes To Be Number 1” "Winning is not a sometime thing; it's an all the time thing. You don't win once in a while; you don't do things right once in a while; you do them right all the time. Winning is a habit. Unfortunately, so is losing. There is no room for second place. There is only one place in my game, and that's first place. I have finished second twice in my time at Green Bay, and I don't ever want to finish second again. There is a second place bowl game, but it is a game for losers played by losers. It is and always has been an American zeal to be first in anything we do, and to win, and to win, and to win. Every time a football player goes to play his trade he's got to play from the ground up-from the soles of his feet right up to his head. Every inch of him has to play. Some guys play with their heads. That's O.K. You've got to be smart to be number one in any business. But more importantly, you've got to play with your heart, with every fiber of your body. If you're lucky enough to find a guy with a lot of head and a lot of heart, he's never going to come off the field second. Vince Lombardi “What it Takes To Be Number 1” Running a football team is no different than running any other kind of organization-an army, a political party or a business. The principles are the same. The object is to win-to beat the other guy. Maybe that sounds hard or cruel. I don't think it is. It is a reality of life that men are competitive and the most competitive games draw the most competitive men. That's why they are there-to compete. To know the rules and objectives when they get in the game. The object is to win fairly, squarely, by the rules-but to win. And in truth, I've never known a man worth his salt who in the long run, deep down in his heart, didn't appreciate the grind, the discipline. There is something in good men that really yearns for discipline and the harsh reality of head to head combat. I don't say these things because I believe in the "brute" nature of man or that men must be brutalized to be combative. I believe in God, and I believe in human decency. But I firmly believe that any man's finest hour, the greatest fulfillment of all that he holds dear, is that moment when he has worked his heart out in a good cause and lies exhausted on the field of battle - victorious." ...Vince Lombardi 1. 2. 3. 4. Do you agree with Vincent Lombardi’s assertion that people are born with the desire to compete why or why not? What areas do you see competition in the economy of the United States ? How is competition beneficial to our economy/society? How is it harmful to our economy/society?