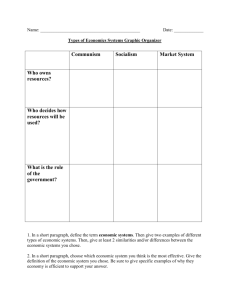
Economics Chapter 3 & 4 Vocabulary Review Vocabulary Word
advertisement
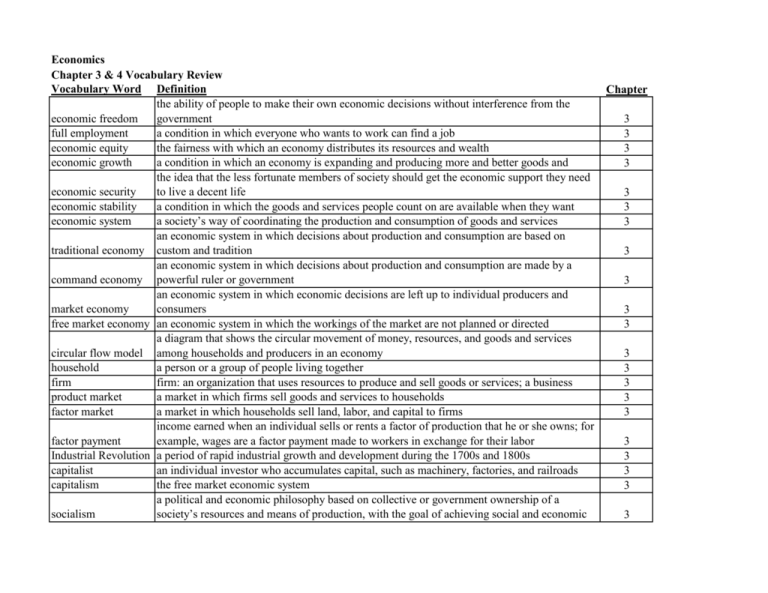
Economics Chapter 3 & 4 Vocabulary Review Vocabulary Word Definition the ability of people to make their own economic decisions without interference from the economic freedom government full employment a condition in which everyone who wants to work can find a job economic equity the fairness with which an economy distributes its resources and wealth economic growth a condition in which an economy is expanding and producing more and better goods and the idea that the less fortunate members of society should get the economic support they need economic security to live a decent life economic stability a condition in which the goods and services people count on are available when they want economic system a society’s way of coordinating the production and consumption of goods and services an economic system in which decisions about production and consumption are based on traditional economy custom and tradition an economic system in which decisions about production and consumption are made by a command economy powerful ruler or government an economic system in which economic decisions are left up to individual producers and market economy consumers free market economy an economic system in which the workings of the market are not planned or directed a diagram that shows the circular movement of money, resources, and goods and services circular flow model among households and producers in an economy household a person or a group of people living together firm firm: an organization that uses resources to produce and sell goods or services; a business product market a market in which firms sell goods and services to households factor market a market in which households sell land, labor, and capital to firms income earned when an individual sells or rents a factor of production that he or she owns; for factor payment example, wages are a factor payment made to workers in exchange for their labor Industrial Revolution a period of rapid industrial growth and development during the 1700s and 1800s capitalist an individual investor who accumulates capital, such as machinery, factories, and railroads capitalism the free market economic system a political and economic philosophy based on collective or government ownership of a socialism society’s resources and means of production, with the goal of achieving social and economic Chapter 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Vocabulary Word Definition Chapter a political and economic system in which all property and wealth is collectively owned by all communism members of society; the final stage of socialism in Marxist theory 3 the process by which economic decisions are made or influenced by central governments economic planning rather than by private individuals 3 an economic system in which both the government and individuals play important roles in mixed economy production and consumption; most modern economies are mixed economies 3 public works government-financed projects such as dams, highways, and bridges 3 a government payment to a household or firm for which the payer receives no good or service transfer payment in return; examples include Social Security checks and unemployment benefits 3 an economic system in which the means of production are mostly privately owned and free enterprise system operated for profit 3 the principle that government should not interfere with the workings of the economy; a French laissez-faire term meaning “let them do” 3 contract an agreement between a buyer and a seller 3 intellectual property: creations of the mind that have commercial value, such as inventions and property rights works of art 3 a legal protection that gives inventors the sole right to make, use, or sell their inventions for a patent fixed number of years 3 profit the money earned by a business after subtracting its operation costs 3 specialization the development of skills or knowledge in one aspect of a job or field of interest 4 division of labor the allocation of separate tasks to different people, based on the principle of specialization 4 voluntary exchange the act of willingly trading one item or service for another 4 the direct exchange of goods or services without the use of money; a typical feature of barter traditional economies 4 coincidence of wants a situation in which each of two individuals has something the other wants; the basis for barter 4 a generally accepted medium of exchange that can be traded for goods and services or used to money pay debts 4 economic the characteristic of a society in which people rely on others for most of the goods and services interdependence they want 4 trade barrier a government measure that limits international trade, such as a protective tariff or an import 4 Article I, Section 8 of the U.S. Constitution, which gives Congress the power to regulate Commerce Clause interstate trade 4 Vocabulary Word absolute advantage comparative advantage wealth mass production Definition the condition that exists when someone can produce a good or service using fewer resources than someone else the condition that exists when someone can produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than someone else the total value of all the things a person or a group of people owns large-scale manufacturing Chapter 4 4 4 4