Unit 1_ Summary - Mater Academy Charter Middle/ High
advertisement

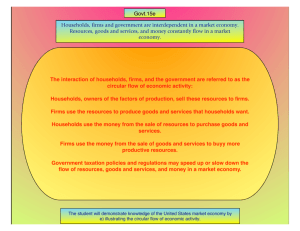
Principles of Macroeconomics / Dual Enrollment Class / Fall 2014 Unit 1” Introduction to Economics” Key Concepts and Terms / Summary Resources are limited, so people must make choices. Societies do not have enough productive resources to satisfy everyone’s wants and needs. Because you must choose among limited alternatives, the true cost of anything is what you must give up to get it (opportunity cost). Economists use economic models for both positive economics, which describes how the economy works (facts, evidences), and for normative economics (rules, goals), which prescribes how the economy should work. Microeconomics is the branch of economics that studies how people make decisions and how those decisions interact. Macroeconomics is concerned with the overall ups and downs of the economy, and focuses on economic aggregates such as the unemployment rate, gross domestic product (GDP), and inflation rate, that summarize data across many different markets. Four factors of production (or economic resources) can be classified as land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurs. They are inputs and must be present to produce goods and services. The production possibility frontier (or curve) illustrates different combinations of goods and services that can be produced in a fully employed economy, assuming that resources quantity, resources quality, and technology are fixed. To be efficient an economy must produce as much of each good as it can, given the production of other goods, according to a technological level and the among of factor of production (disposable resources) The production possibility curve or frontier (PPC/PPF)) represents the trade-off facing an economy that produces only 2 goods. It shows the maximum quantity of one good that can be produced for each possible quantity of the other good produced. The slope of the PPF tells the opportunity cost for increasing the production of item X in one unit An economy is efficient if there are no missed opportunities; it means that there is no way to make anyone better off without making at least one person worse off. The PPF is useful for illustrating the general economic concept of efficiency. Any point on the curve means that economy is not missing the opportunity to produce more of both goods. To be efficient an economy must produce as much of each good as it can, given the production of other goods, according to a technological level and the amount of factor of production (disposable resources). There are two basic sources of growth in the production possibility curve: an increase in resources and improved technology. An economic system represents the structure of methods and principles that a society uses to produce and distribute goods and services. The market system and the command system are two fundamental types of economic systems to address the economizing problem (scarcity). Every economic system has problems. Traditional economies have little potential for growth or change. Centrally planned economies asphyxiate innovation, do not adequately meet consumer needs, and limit freedom. Even free market economies, with all their advantages, have drawbacks (reasons for Government involvement). Each society faces basic questions about the production and consumption of goods and services. Five fundamental economic questions: o o o o o What goods and services will be produced? How will these goods and services be produced? Who will get (consume) these goods and services? How will the system accommodate change? How will the system promote the progress? Advantages of the Free Market / Market System : o Economic Efficiency: Because it is a self-regulating, a free market economy responds efficiently to any condition change. Producers produce only the goods and services that consumers want, in general at prices consumers are willing to pay. o Economic freedom. The market system has the highest degree of economic freedom of any system. As a concept, workers work where they want, firms produce what they want, and individuals consume what they want. o Economic growth come the competition. It encourages innovation. Businesses are looking for profit contributing new ideas and innovations. Disadvantages of centrally planned economies / Command System o The government owns all production factors. Since Government fixes wages, workers lack the motivation to work faster or produce more. o Traditionally, command economies sacrifice individual freedoms in order to follow collective goals. o Command economies do not tend to reward innovation. Everybody must follow an approved government plan. A Circular Flow model shows the interactions between households and firms in the free market. o A dynamic market economy creates continuous and repetitive flows of goods and services, resources, and money. o The circular flow diagram represents a complex, interrelated web of decision makers and economic activities involving businesses and householders (both are buyers and sellers). o The diagram groups private decision markets into Businesses (firms) and Households (people), participating in the resources market (factor of production market) and the products and services market. How does the RESOURCES MARKET work? o The resources market (upper part of the circular flow diagram) represents the place where resources or the services of resource suppliers are bought and sold. o In the resources market, HOUSEHODLS own all economic resources : Directly as workers or Entrepreneurs or Indirectly as ownership of business corporations o The funds that business pay for resources are COSTS to businesses but are FLOW of WAGE, RENTS, INTEREST, and PROFIT INCOME to the households O PRODUCTIVE RESOURCES FLOW from householders to businesses and MONEY FLOW FROM BUSINESSES TO HOUSEHOLDERS. How does the PRODUCT and SERVICE MARKET work? The product market is the place where goods and services produced by businesses are bought and sold. Businesses combine resources to produce and sell goods and services. Households (people) use the limited income they have received from the sale of resources to buy goods and services The monetary flow of consumer spending on goods and services yields sales revenues for businesses. Businesses compare COSTS and REVENUE to determine PROFIT, and to decide whether or not a particular good should continue to be produced. Specialization: people have different abilities, so, they are relatively good to do something. The society gains (more efficient) when each person contribute by using his/her “best abilities” to produce. This is because the division of labor permits people develops expertise (skills) in the task(s) that they concentrate on. A country has Absolute Advantage in the production of a good when it can produce that good using fewer resources per unit of output than another country. A country has Comparative Advantage in the production of a good when it can produce that good at a lower opportunity cost (a smaller loss in terms of the production of another good) than another country.