Study Guide: Molecular Biology
advertisement

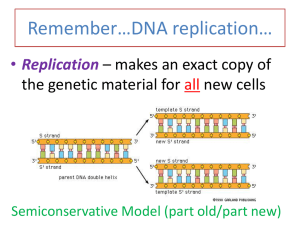
Study Guide: Molecular Biology Vocabulary: A and P site Aids Antibiotic Bacteriophage(Phages) Capsid Codons (anticodons) Conjugation DNA DNA and RNA polymerases DNA ligase Double Helix Emerging viruses Endospore F factor Genetic code HIV Introns and Exons Lysogenic cycle Lytic cycle Molecular Biology mRNA mRNA, tRNA, rRNA Mutagen Mutagenesis Mutation Nitrogenous bases Nucleotides Pathogen Pilus Plasmids and R plasmids Polynucleotide Prion Promoter and Terminator Prophage Provirus and Retrovirus Reading frame RNA RNA splicing Semiconservative model Spirillum Start and Stop codon Sugar-Phosphate backbone Toxin Transcription Transduction Transformation Translation Triplet code Viroid Viroids Virus 1. How could a single base substitution result in a shortened protein product? 2. Why doesn’t a bout of flu give us immunity to the flu in subsequent years? 3. Describe one way a virus can penetrate its genes without destroying its host cell. What is this type of reproductive cycle called? 4. Summarize the steps of viral replication. 5. Explain how HIV infects the immune system cells. 6. What convinced Hershey and Chase that DNA, rather than protein, is the genetic material of Phage T2? 7. Describe 3 modes of gene transfer between bacteria. 8. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA polynucleotides. 9. How does complementary base pairing make possible the replication of DNA? 10. What is the function of DNA polymerase in DNA replication? 11. Distinguish between transcription and translation. 12. What makes prions different from all other known infectious agents? Use your notes, labs, activities, video questions, and other practice to review for the test. Review textbook pages 181-205. Review the chapter summary on page 206 in textbook. Use review questions on p. 207 in textbook and then check answers in the back of your book. Review Mrs. Chaillou’s power points and notes posted on her documents and links pages on her website.