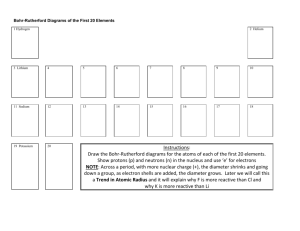
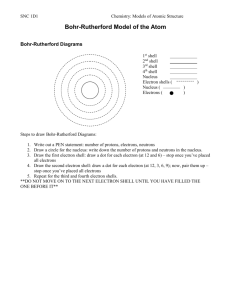
BOHR-RUTHERFORD DIAGRAMS
advertisement

BOHR-RUTHERFORD AND LEWIS DOT DIAGRAMS BOHR-RUTHERFORD DIAGRAMS A Bohr-Rutherford diagram is a simplified representation of an element. It is a simple visual way of expressing an element. BOHR-RUTHERFORD DIAGRAMS Bohr-Rutherford diagrams should be drawn using the following steps: Draw the nucleus with the proper number of protons (+1) and neutrons (0). Draw the first electron shell with the appropriate number of electrons (-1). BOHR-RUTHERFORD DIAGRAMS Draw the second valence shell (if applicable) with the appropriate number of electrons (-1). Continue to draw valence shells with electrons until you have the proper number of electrons for the element. Example: sulfur 1st shell 2; 2nd shell 8; 3rd shell 6 Magnesium (Mg) and Calcium (Ca) 1st shell 2; 2nd shell 8; 3rd shell 2 1st shell 2; 2nd shell 8; 3rd shell 8; 4th shell 2 Lewis Electron Dot Diagrams Invented by the American chemist, G.N. Lewis. 1. Write the chemical symbol 2. Write the appropriate number of dots in a clockwise manner Lewis Electron Dot Diagrams Lewis Electron Dot Diagrams You should notice that elements in the same group have IDENTICAL electron dot diagrams, except for the chemical symbol. Ex. Lithium (Li) and sodium (Na) are both in Group I, thus they only have one valence electron and therefore only one dot in their respective electron dot diagrams. Lewis Electron Dot Diagrams Ex. Fluorine (F) and chlorine (Cl) are both in Group VII, and have seven valence electrons, and therefore seven dots in their respective electron dot diagrams.