Stoffstromanalyse
advertisement

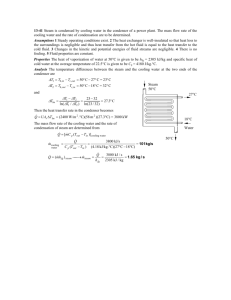
Slides 4- Energy analysis ENERGY ANALYSIS 4 – Energy analysis Slides Structure of a company's energy system Supply Conversion Distribution Consumption Heat recovery Disposal Slides 4 – Energy analysis Energy efficiency Typical areas of improvement Cooling/refrigeration Heating Compressed air Insulation Heat recovery Separation processes Lighting ... Slides 4 – Energy analysis Efficient energy use Not only a question of best technology! Slides 4 – Energy analysis Energy management Organization Analysis and Planning Set up an organizational unit, identify responsibilities and determine the budget Inventory and description of the energy situation search for energy saving options Control Control of the energy plants, work out energy indicators Consulting Energy reports, internal consulting and market analysis Implementation Implementation of energy saving options maintenance of energy plants Slides 4 – Energy analysis Documentation of load curves Documentation of curves for A year A week A day Analysis of load curves Winter – summer ratio Combined use of heat and power Switched off or reduced operation at weekends Days with high energy demand Bottlenecks Energy demand after production Slides 4 – Energy analysis Annual energy consumption Collection and documentation for all energy carriers Quantity Cost Reference quantities Definition of indicators Analysis and interpretation Distribution of quantities Distribution of costs Variation of indicators Comparison of indicators with other companies or publications Slides 4 – Energy analysis Analysis of consumers Heat Electric power Avoid partial load and use adequate machines Separate control of plants Adapt power (e. g. fans) Adequate temperatures Optimize lights (cleaning, No internal sources of heat modern lighting, analyse and humidity in cooled areas demand) Use shades for heat protection Clean and service (air filter, Frequency-controlled fans nozzles, etc.) Use heat cascades Compressor location and ... pressure Peak load management Thermostatic valves Slides 4 – Energy analysis Heat losses detected with an infrared camera 4 – Energy analysis Slides Specific energy consumption 150 Example: Energy consumption of a brewery 125 Indicator: MJ/hl 100 Measure: 90 91 92 93 94 June 1992 Installation of a vapour recompression plant Slides 4 – Energy analysis Energy, work and power Work is the transmission of energy. The unit of work and energy is JOULE. The speed at which work is performed is power [J/s = W]. 4 – Energy analysis Slides Heat capacity To heat up a body with a mass of m by DT, the following amount of heat is required: Q = c m DT The specific heat capacity c of the material depends on the temperature. Specific heat capacity The specific heat capacity is the amount of energy required to heat up 1 kg of material by 1 °C. Gold Unit: [c] = 1 J.kg-1.K-1 Iron Oxygen Benzene Water Slides 4 – Energy analysis The performance of 1 kWh Lifts 1 ton of steel by 367 m! Accelerates a car (1 ton) to approx. 60 km/h (without losses 305 km/h)! Heats up 1 000 l of water by 0.86 °C! Source: Karl Lummerstorfer, Energie Institut Linz Slides 4 – Energy analysis Efficiency in a steam system Part of the steam system Steam boiler Efficiency (70-) 82 – 90% Steam transportation 75 – 90% Heat exchange 85 – 98% Slides 4 – Energy analysis Steam system Reduce leaks. Improve operation of steam traps. Increase condensate recovery. Increase flash steam recovery. Use lower steam pressure if possible. Use direct steam for heating if possible. 4 – Energy analysis Slides Cooling process Efficiency = Qcond. / P ~ Tcond. / (Tcond. – Tevap.) Consequences: Q: Heat P: Power T: Temperature The lower the temperature difference the better: Check the necessary cooling temperature Allow the temperature in the condenser to be as low as possible (e.g. water cooling) Maintain the heat exchanger (especially evaporator) ... The higher the cooling temperature the better Others: Remove water from ground Avoid high temperature of the incoming product ... 4 – Energy analysis Slides Cooling process P Qu = Qo + P M Compressor Qo Evaporator Qu Condenser To Tu Collector Low pressure High pressure Efficiency = Qo / P = To / (Tu – To) Slides 4 – Energy analysis Cooling and freezing Raising the cooling temperature by 1 °C saves approx. 4% of electric energy. Choose the adequate temperature: frozen meat at -20 °C, cooling at 0 °C to 4 °C. Clean the condenser regularly and provide sufficient cool air supply. Use the capacity of the storage rooms, collect goods, switch off unused cooling units. Keep storage rooms closed to avoid entrance of humidity and warm air. Defrost cooling rooms. Slides 4 – Energy analysis Cooling – 2 Insulation Recommendations for PU-foam insulation: Insulation thickness 0 to -8 °C 0 to -15 °C below -15 °C 80mm 110mm 150mm Evaporator: Optimize defrosting Compressor Close to evaporator Central location makes servicing and use of heat easier Condenser: Outside of building, sun-protected Clean regularly Use R134 a, R22 or ammonia 4 – Energy analysis Slides Drying process •Fresh air drying Q1 •Fresh air drying with heat recovery 8 •Circulating air drying with/without heat recovery Q4 Q3 Ti •Heat recovery with condensation of humidity (heat pumps, thermo-compression) Td Q2 QT Typical options for improvement: Q1 = Insulation of drier Q2 = Pre-drying, pre-concentration of the product Q3 = Control of temperature and humidity Q4 = Heat recovery, humidity control of flue gas, good housekeeping To Slides Compressed air Shut down compressor, drier and the network Reduce the pressure level (as far as possible) Avoid leakages Lower the temperature of incoming air Avoid compressed air for cleaning Carry out maintenance Use electrically-driven equipment Foster heat recovery Source: Karl Lummerstorfer, Energie Institut Linz 4 – Energy analysis Slides Lighting Turn off when not needed Use timer or motion detector Use daylight as much as possible Service and clean Clean windows, ensure efficient design of rooms Use energy saving bulbs 4 – Energy analysis Slides 4 – Energy analysis Heat recovery cooling units – 1 Air-cooled condenser Water-cooled condenser Evaporator Compressor Slides 4 – Energy analysis Heat recovery cooling units – 2 Slides 4 – Energy analysis ECOPROFIT-company: Brewery Annual production: > 1 million hl, ISO 14000 Saving of water, energy and chemicals due to CP options: Cold filtering/sterilization New filling line Heat/power co-generation Vapour compression ... 4 – Energy analysis Slides Specific heat consumption of a brewery 50.00 in kWh/hl 40.00 30.00 20.00 10.00 0.00 spec. heat 1993 1994 ´95 ´96 ´97 ´98 ´99 2000 2001 2002 38.60 40.67 47.30 42.62 41.42 37.56 34.19 29.91 27.58 24.47 4 – Energy analysis Slides Multistage evaporation 1. evaporator 2. evaporator 1. vapour 3. evaporator 2. vapour condenser 3. vapour vacuum pump feed steam 1. concentrate steam condensate Source: Ignatowitz 1994 final concentrate 2. concentrate 1. vapour condensate 2. vapour condensate 3. vapour condensate Slides 4 – Energy analysis Evaporation with vapour compression evaporator vapour preheated feed pre-heater steam (start-up) compressor vapour- condensate feed solution Source: Ignatowitz 1994 concentrate