Chapter 10, Section 2
advertisement

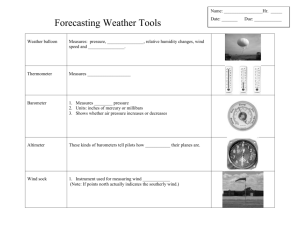
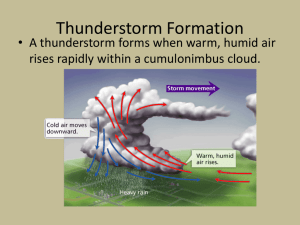
Chapter 24 Weather Standards 5a. Students know how differential heating of Earth results in circulation patterns in the atmosphere and oceans that globally distribute heat. 6a. Students know weather and climate involve the transfer of energy into and out of the atmosphere Objective 1 Describe cold and warm air masses and fronts. Objective 2 Describe hurricanes and tornadoes. Objective 3 Understand how to read a weather map. Objective 4 List tools meteorologists use and what they are for. Assessment Chapter Test Review Daily Bellwork, Science Starters, Standards Practice Vocabulary Create flashcards for the following words: o Air mass o Cold front o Warm front o Stationary front o Occluded front o thunderstorm o Hurricane o Tornado o Thermometer o Barometer o Anemoter o Radiosonde o radar Brainpop Weather! Air Masses • AIR MASS= large body of air throughout which temp. and moisture are similar • 4 types: Continental Maritime Tropical Polar Fronts • FRONTS= the boundary of an air mass when 2 air masses of different temps/moisture collide • COLD FRONT= when a cold air mass overtakes a warm air mass. If the warm air is moist, clouds will form and thunderstorms will result. • WARM FRONT= when a cold air mass leaves, a warm front moves in. Results in precipitation over a large area. • OCCLUDED FRONT=fast moving cold air mass lifts warm air off the ground Severe Weather Tornadoes • Rotating column of air with high winds • Forms when a thunderstorm meets high altitude horizontal winds Thunderstorms • Rain, thunder, lightning, strong winds • Lightning=cloud s discharging electricity. Noise is Thunder. Hurricanes • Develop over warm oceans • Most dangerous part of hurricane is STORM SURGE; rising sea level and large waves Brainpop! Tornadoes, Thunderstorms, Hurricanes! Weather Maps Isobars • Lines that connect points of equal atmospheric pressure Isotherms • Lines that connect points of equal temperature Weather Instruments/INTERACTIVE Fill in the chart… Name of Instrument What does it do? Other Thermometer 3 types: Barometer ----------------------------- Anenometer ------------------------- Radiosonde ---------------- Radar Doppler Radar What is the difference between Radar and Doppler Radar?