Blood Composition-formed elements 2
advertisement

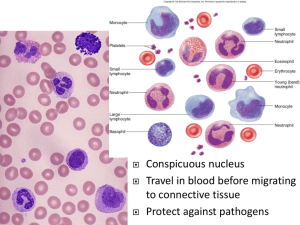
Blood Composition Formed Elements Erythrocytes • • • • • Transports oxygen to cells and tissues Anucleate ~7 µm Few organelles Hemoglobin – Iron rich protein – Binds with oxygen Erythrocyte Characteristics • Small, flexible, bi-concave discs – Center is depressed to increase surface area – Cell must be flexible to fold to cross capillaries • Amount of oxygen carried directly related to hemoglobin concentrations – ~250 million hgb molecules per cell! Hemoglobin • Made up of 4 connected protein chains • Responsible for the red color of blood • Forms the heme molecule – Important • Carries oxygen, returns carbon dioxide • Helps maintain structure of cell Leukocytes • Contain nuclei & organelles • Body’s “Army” – Defends/protects body – WBC’s move to fight infection • Can leave blood stream-diapedesis • Positive chemotaxis – Damaged cells give off chemicals to alert body – Activates WBC’s – Body will produce more of that type WBC Leukocytes • Two major groups – Granulocytes • Cytoplasm contains visible granular inclusions • Lobed nuclei – Agranulocytes • Cytoplasm does not have visible granules • Spherical nuclei – Oval – Kidney shaped Granulocytes • Neutrophils –Most numerous WBC –Multi-lobed nucleus –Fine granules –Phagocytic cell • FUNGI • BACTERIA Granulocytes • Eosinophils – Bluish red nuclei – Nucleus is usually bi-lobed – Coarse, red granules – Increase due to • Allergies • Parasites Granulocytes • Basophils – Rare WBC – Nucleus “u” or “s” shaped – Granules stain dark blue/purple – Helps mediate inflammatory response • Contains histamine – Makes blood vessels leaky to allow WBC to get to inflammation site • Contains heparin – Anti-coagulant Agranulocytes • Lymphocytes – Small (slightly bigger than a RBC) – Dark staining nucleus – Second most numerous WBC – Tend to reside in lymph tissues – Important in antibody production – Increase in response to VIRUSES Agranulocytes • Monocytes – Largest WBC – “U” or kidney shaped nucleus – Convert into macrophages in tissues – Seen in chronic infections Platelets • Not a true cell – Fragments of megakaryocytes – Dark staining pieces – Critical to clotting process • Bind together to stop bleeding Complete Blood Counts • Measures – The number of RBC’s – The number of WBC’s – The number of platelets – Hgb – Hematocrit • Can include – Morphology of RBC’s – Size of RBC’s Typical CBC results • RBC count (varies): – Male: 4.7 to 6.1 million cells/µL – Female: 4.2 to 5.4 million cells/µL • WBC count: 4,500 to 10,000 cells/µL • Hematocrit (varies): – Male: 40.7 to 50.3 % – Female: 36.1 to 44.3 % • Hemoglobin (varies): – Male: 13.8 to 17.2 gm/dL – Female: 12.1 to 15.1 gm/dL Typical CBC results • • • • • Segmented neutrophils: (50–70%) Lymphocytes: (15–45%) Monocytes: (0–10%) Eosinophils: (0–6%) Basophils: (0–2%)