Corruption - Christian Connections for International Health
advertisement

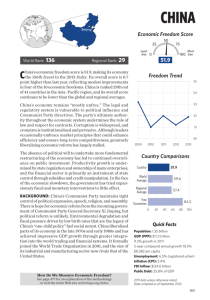
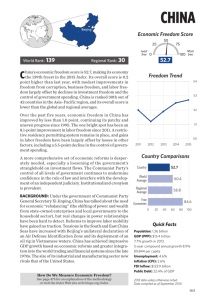
Definition Integrity comes from the Latin word integrare which is to make whole. In mathematics “integer” is a whole number and not a fraction. WHAT IS WHOLENESS. What you Say What you are in What you Do Public What you are in Private All of these needs to fit together Saying Doing Public Private Family versus truth- Root of corruption-I A father and a husband is like a God World values survey 54 countries 64 societies Covering 80 per cent of the world Attitudes to family, gender, work, neighbor tolerance, democracy etc. Family values & corruption Scale of familism (World Values survey code book 1994 & World Bank statistics) o Powerful father, docile mother, no divorce, joint family, control over children o o Correlates well with the CPI.(Regression analysis) o Tribalism- Africa and India- The greater the tribal loyalty greater the corruption. The man who knew too much Edward Banfield 1916-99 Social scientist Edward Banfield- “ Amoral familism”- The Moral Basis of a backward society In 1958, Ed, with the assistance of his wife, Laura, explained why a backward area in southern Italy was poor. The reason was not government neglect or poor education but culture. In this area of Italy, the Banfields said in The Moral Basis of a Backward Society, people would not cooperate outside the boundaries of their immediate families Family values and corruption o Lawrence Harrison- Extended family –antidevelopment (Underdevelopment is a state of mind-page 7) Plato's Republic chapter 5: On matrimony and philosophy “Children should be institutionalized” –Republic Chapter 5 Plato- This is the only way to have a corrupt free society Max Weber o Weber- Family Loyalty and market are antithetical -The religion of China- page 237. Corruption Perceptions Index 2004 Corruption Perceptions Index 2004 This table was compiled at the University of Passau on behalf of Transparency International. For information on data and methodology, please consult the frequently asked questions and the framework document. Country Rank Country 2004 CPI Score* Confidence Range** Surveys Used*** 1 Finland 9,7 9.5 - 9.8 9 2 New Zealand 9,6 9.4 - 9.6 9 3 Denmark 9,5 9.3 - 9.7 10 Iceland 9,5 9.4 - 9.7 8 5 Singapore 9,3 9.2 - 9.4 13 6 Sweden 9,2 9.1 - 9.3 11 7 Switzerland 9,1 8.9 - 9.2 10 8 Norway 8,9 8.6 - 9.1 9 9 Australia 8,8 8.4 - 9.1 15 10 Netherlands 8,7 8.5 - 8.9 10 11 United Kingdom 8,6 8.4 - 8.8 12 12 Canada 8,5 8.1 - 8.9 12 13 Austria 8,4 8.1 - 8.8 10 Luxembourg 8,4 8.0 - 8.9 7 15 Germany 8,2 8.0 - 8.5 11 16 Hong Kong 8,0 7.1 - 8.5 13 Country Rank Country 2004 CPI Score* Confidence Range** Surveys Used*** 17 Belgium 7,5 7.1 - 8.0 10 Ireland 7,5 7.2 - 7.9 10 USA 7,5 6.9 - 8.0 14 20 Chile 7,4 7.0 - 7.8 11 21 Barbados 7,3 6.6 - 7. 6 3 22 France 7,1 6.6 - 7.6 12 Spain 7,1 6.7 - 7.4 11 24 Japan 6,9 6.2 - 7.4 15 25 Malta 6,8 5.3 - 8.2 4 26 Israel 6,4 5.6 - 7.1 10 27 Portugal 6,3 5.8 - 6.8 9 28 Uruguay 6,2 5.9 - 6.7 6 29 Oman 6,1 5.1 - 6.8 5 Emirates 6,1 5.1 - 7.1 5 Botswana 6,0 5.3 - 6.8 7 United Arab 31 Country Rank 31 34 35 36 37 38 39 41 42 44 47 48 49 Country Estonia Slovenia Bahrain Taiwan Cyprus Jordan Qatar Malaysia Tunisia Costa Rica Hungary Italy Kuwait Lithuania South Africa South Korea Seychelles Greece 2004 CPI Score* 6,0 6,0 5,8 5,6 5,4 5,3 5,2 5,0 5,0 4,9 4,8 4,8 4,6 4,6 4,6 4,5 4,4 4,3 Confidence Range** 5.6 - 6.7 5.6 - 6.6 5.5 - 6.2 5.2 - 6.1 5.0 - 5.8 4.6 - 5.9 4.6 - 5.6 4.5 - 5.6 4.5 - 5.6 4.2 - 5.8 4.6 - 5.0 4.4 - 5.1 3.8 - 5.3 4.0 - 5.4 4.2 - 5.0 4.0 - 4.9 3.7 - 5.0 4.0 - 4.8 Surveys Used*** 12 12 5 15 4 9 4 15 7 8 12 10 5 9 11 14 3 9 Country Rank 49 51 54 57 59 60 62 64 Country Suriname Czech Republic El Salvador Trinidad and Tobago Bulgaria Mauritius 4,1 Namibia Latvia Slovakia Brazil Belize Colombia 3,8 Cuba Panama Ghana Mexico Thailand 2004 CPI Score* Confidence Range** Surveys Used*** 4,3 4,2 4,2 4,2 2.1 - 5.8 3.7 - 4.9 3.3 - 5.1 3.6 - 5.2 3 11 7 6 4,1 3.7 - 4.6 10 3.2 - 4.8 4,1 4,0 4,0 3,9 3,8 5 3.5 - 4.6 3.8 - 4.3 3.6 - 4.5 3.7 - 4.1 3.4 - 4.1 3.4 - 4.1 3,7 3,7 3,6 3,6 3,6 7 8 11 11 3 10 2.2 - 4.7 3.4 - 4.2 3.1 - 4.1 3.3 - 3.8 3.3 - 3.9 4 7 7 11 14 Country Rank 67 71 74 77 82 Country Croatia Peru Poland Sri Lanka China Saudi Arabia Syria Belarus Gabon Jamaica Benin Egypt Mali Morocco Turkey Armenia Bosnia and Herzegovina 2004 CPI Score* 3,5 3,5 3,5 3,5 3,4 3,4 3,4 3,3 3,3 3,3 3,2 3,2 3,2 3,2 3,2 3,1 3,1 Confidence Range** 3.3 - 3.8 3.3 - 3.7 3.1 - 3.9 3.1 - 3.9 3.0 - 3.8 2.7 - 4.0 2.8 - 4.1 1.9 - 4.8 2.1 - 3.7 2.8 - 3.7 2.0 - 4.3 2.7 - 3.8 2.2 - 4.2 2.9 - 3.5 2.8 - 3.7 2.4 - 3.7 2.7 - 3.5 Surveys Used*** 9 8 13 8 16 5 5 5 3 6 3 8 5 7 13 5 7 Country Rank 82 85 87 90 97 Country Madagascar Mongolia Senegal Dominican Republic Iran Romania Gambia India Malawi Mozambique Nepal Russia Tanzania Algeria Lebanon Macedonia 2004 CPI Score* Confidence Range** Surveys Used*** 3,1 3,0 3,0 2,9 1.8 - 4.4 2.6 - 3.2 2.5 - 3.5 2.4 - 3.3 4 3 6 6 2,9 2,9 2,8 2,8 2,8 2,8 2,8 2,8 2,8 2,7 2,7 2,7 2.2 - 3.4 2.5 - 3.4 2.2 - 3.4 2.6 - 3.0 2.2 - 3.7 2.4 - 3.1 1.6 - 3.4 2.5 - 3.1 2.4 - 3.2 2.3 - 3.0 2.1 - 3.2 2.3 - 3.2 5 12 5 15 5 7 3 15 7 6 5 7 Country Rank Used*** 97 102 108 112 Country Nicaragua Serbia and Montenegro Eritrea Papua New Guinea Philippines Uganda Vietnam Zambia Albania Argentina Libya Palestinian Authority Ecuador Yemen 2004 CPI Score* Confidence Range** Surveys 2,7 2,7 2.5 - 3.0 2.3 - 3.0 7 7 2,6 2,6 1.6 - 3.4 1.9 - 3.4 3 4 2,6 2,6 2,6 2,6 2,5 2,5 2,5 2,5 2.4 - 2.9 2.1 - 3.1 2.3 - 2.9 2.3 - 2.9 2.0 - 3.0 2.2 - 2.8 1.9 - 3.0 2.0 - 2.7 14 7 11 6 4 11 4 3 2,4 2,4 2.3 - 2.5 1.9 - 2.9 7 5 The fatal evolution Family/Truth Relationship/Truth Roots of corruption-2 Power distance is a cultural index derived by sociologist Geert Hofstede. • It measures how much a culture has respect for authority. Power distance it's acceptable for a supervisor to display his authority superiors rarely give their subordinates important work if something goes wrong, the subordinates are usually blamed for not doing their proper job/role managers rarely interact or socialize with workers teachers are treated respectfully local politics are prone to totalitarianism class distinctions are emphasized parents are more highly respected and corporal punishment is more common revolutions are, or were, common Power Distance • The Arab nations, Latin America, Russia, and nearly all of Asia (especially India and China) are high in power distance. • Most of Europe, Canada, Australia and Israel are low in power distance. • Japan and Mediterranean-Europe fall in the middle range. What is important.. Values OR Power Countries with more power distance have more corruption Once upon a time all the known gods & goddesses had no….values • All the known gods & goddesses had power ascribed to them but no value. Roman pantheon APPOLLO – God of sun, plague, light Caesar Augustus called himself the son of Appollo Appollo – god of sun, plague, light Bacchus god of wine & agriculture Ceres – godesses of growing plants & cereals (for worship in famine) (Tying lighted brands to the tails of foxes) CUPID – god of erotic love pranks (Son of Venus) Gold headed arrows Lead for hatred Diana – goddess of chastity/hunting Freemasons worship her. Fortuna goddess of luck. Shakespeare makes & reference to lady fortune Janus – god of gates door beginnings & end Jupiter war lightening Jove very powerful god Greek Pantheon Hades – god of the underworld Hermes god of commerce interpreting with foreign traders oratory Hermeneuticsscience of interpretation Ares-god of warsame as mars Athena Battle strategy weaving Aphrodite goddess of love & beauty Temple prostitutes ARTEMIS/Diana fertility goddess childbirth Ephesians Power gods versus Value God When you worship power gods the culture has high power distance and becomes corrupted The Judeo-Christian God is the only God I know who is primarily a value God. Shame versus guilt Guilt happens in cultures which have low power distance. These produce less corruption. Shame happens when exposed (in cultures with high power distance). Related to higher corruption levels. Guilt- acts from within. Shame acts from without. Philippians 2.5-8 Let this mind be in you, which was also in Christ Jesus: Who, being in the form of God, thought it not robbery to be equal with God: But made himself of no reputation, and took upon him the form of a servant, and was made in the likeness of men: And being found in fashion as a man, he humbled himself, and became obedient unto death, even the death of the cross. Justice/Power Jesus changed the paradigm POWER Value Transparency Related to “Social capital”- the more trusted friends the more openness needed. Trusted friends SENSE OF COMMUNITY IMPACT ON HEALTH/ ECONOMICS ACCORDING TO FRANCIS FUKUYOMA. Author of book on Trust THE ORTHODOX INDIAN CONTEXT LOW TRUST SOCIETIES LESS WEALTH CREATION LESS SPONTANEOUS SOLITARY WORSHIP SOCIALIBILITY FAMILY BUSINESS ONLY LESS SOCIAL CAPITAL JUDEO CHRISTIAN CONTEXT HIGH TRUST SOCIETIES MORE SPONTANEOUS SOCIALIBILITY COMMUNITY WORSHIP MORE SOCIAL CAPITAL MORE WEALTH CREATION MULTINATIONAL CORPORATE BUSINESS INDIVIDUAL WORSHIP I sit here and worship my god alone…this is my temple. I perform all the rites of worship to gods like Ganga, etc…in the morning and evening. Cont. Transparency High trust societies have a higher social capital High social capital compels transparency Transparency reduces corruption Roots of corruption Familism P Power o w e r Lack of social capital