Study Guide - Long Branch Public Schools
advertisement

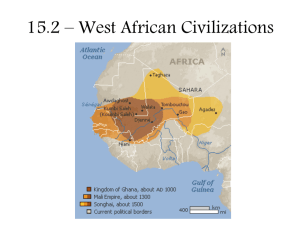
NAME__________________________________________CLASS_________DATE_________ EARLY AFRICAN CIVILIZATIONS STUDY GUIDE 13.1 Geography and Early Africa pp. 380-385 1. In West Africa, what do the different regions running east and west have in common? 2. List the four regions of West Africa in order from most rainfall to least? 3. Which two factors contributed most to the survival of early West African villages? 4. Why did farming in Africa improve around 500 BC? 5. What were extended families? Explain three benefits? 6. Explain the importance of Animism in early West African society. 1 7. Why do you think many people lived in West Africa? What geographical feature presents obstacles to humans living and traveling in North Africa? Why? 8. Analyze the “Crossing the Sahara” map on pages 384-385 of our World History textbook. List five goods that were traded across the Sahara. Explain why salt was a valued trade good. 13.2 The Empire of Ghana pp. 386-389 1. List three main characteristics of the Soninke people? 2. Explain the main advantage of silent barter? 3. What is one way that Ghana’s rulers became wealthy? 4. Who were the Almoravids and how did they affect Ghana? 2 13.3 Later Empires pp. 390-395 1. Who conquered Ghana, took over the salt and gold trades, and improved agriculture with new farmlands of beans, onion, and cotton? 2. What was an important similarity between the development of the Ghana and Mali empires? 3. What method did Sundiata use to gain more power in Mali? 4. List three ways that Mansa Musa spread Islam and education throughout Mali? 5. How did Mansa Musa become such a great ruler? What accomplishments did he make that have left a lasting impact on African society? 6. What was the significance of Timbuktu to the spread of learning and Islam? 3 7. How did the salt trade influence the rise of this African capital of Timbuktu? 8. How did Sunni Ali’s rule affect West Africa? 9. What affect did the shared Muslim religion of the Songhai leaders and African Berbers have on the Songhai Empire? 13.4 Historical and Artistic Traditions pp.396-399 1. Why was an oral history so important to the African culture? 2. What is a proverb? Give an example of an African proverb. 4 ANSWERS 13.1 1. In West Africa, what do the different regions running east and west have in common? They are all warm. 2. Which list of regions is in order from most rainfall to least? rain forest, savannah, Sahel, Sahara 3. Which two factors contributed most to the survival of early West African villages? work and family 4. Farming in Africa improved around 500BC because people learned how to make iron tools. 5. What were extended families? What were three benefits? Age sets helped people of the village to work together. Extended families helped farm, hunt, and raise livestock. Loyalty to family helped keep society together. 6. Define Animism The belief that bodies of water, animals, trees and other natural objects have spirits 7. People lived in West Africa because the Niger River provided people living the region with water, food, and transportation. There are other resources such as gold, forests, and salt for trade from the Sahara Desert. The geographical feature that presents an obstacle to humans living and traveling in North Africa is the Sahara Desert because of its vast size, extremely high temperatures, bandits trying to steal from traders, and lack of water. 8. silk, spices, salt, gold, ivory, salt helped to preserve food, flavor food, and help people survive the hot climate 5 13.2 1. They lived in small groups and farmed along the Niger River. After AD 300, they began to band together to protect against attacks from nomadic hunters. They were among the earliest people in West Africa. 2. Which of the best explains the usefulness of the practice of silent barter? Silent barter ensured that trading was peaceful and that locations of mines remained secret. 3. What is one way that Ghana’s rulers become wealthy? Traders had to pay taxes when they passed through Ghana. 4. Who were the Almoravids? Muslims who attacked Ghana and cut off trade routes. 13.3 1. After conquering Ghana and taking over salt and gold trades, who improved agriculture and had new farmlands of beans, onion, and cotton? Sundiata of Mali Empire 2. Which of the following best illustrates a similarity between the development of the Gana and Mali empires? Both empires lay along the upper Niger River, where fertile soil made food plentiful. 3. Which of the following is a method Sundiata used to gain more power in Mali? He took power away from local chiefs and leaders, including important religious leaders. 4. Mansa Musa He hired artists and architects to build mosques in Mali. He sent scholars to study in Morocco and then to set up schools in Mali. He stressed the importance of reading and writing in Arabic, the language of the Qur´an. 6 5. Mansa Musa was a skillful leader who made a pilgrimage to Mecca. He sent scholars to study in Morocco and later established schools to teach the Qur’an. Mansa Musa stressed the teaching and learning of he Arabic language, and hired Muslims to build mosques in Mali, Mali’s people likely became more knowledgeable about the Qur’an and Arabic. 6. What was the significance of Timbuktu to the spread of learning and the impact on Islam? The African capital of Timbuktu had a strategic location along the Niger River where goods were traded, there were mosques, and scholars came to study Islam and the Arabic language. 7. Salt trade was key to the rise of the African capital of Timbuktu because of its strategic location along the Niger River rulers were able to increase goods to trade and build armies to protect traders. 8. Sunni Ali brought peace and stability to the area.” 9. The Songhai Empire grew richer. 13.4 1. Why was an oral history so important to the African culture? It helped pass down African history to future generations. Africa did not have a written history. Griots helped unite African communities with stories from the past. 2. What is a proverb? Give an example of an African proverb? Short saying of wisdom or truth. It takes a whole village to raise a child. 7