Plant Reproduction

First Five
Silently, answer the following question in your notebook:
Explain the difference between each of the following pairs of words
1.
cell membrane, cell wall
2.
osmosis, diffusion
3.
enzyme, substrate
4.
respiration, photosynthesis
Announcements
Past Due:
Plant Nutrition Packet
Respiratory System Packet
Circulatory System Problems
Today:
Fill out Guided Notes
Plant Reproduction HW is on the final page
Due next class period.
Plant Reproduction
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CkBNEM2mD30
Plant Reproduction
1.
Get your assigned ipad
2.
Go to my Weebly(ctompkinsasuprep.weebly.com)
Coordinated Science II
3.
Click on “Classwork: Plant Reproduction”
4.
Open the Powerpoint and use it to answer the questions on the handout
Plant Reproduction
Flowers are the reproductive organs of plants
Many flowers have both male and female reproductive parts
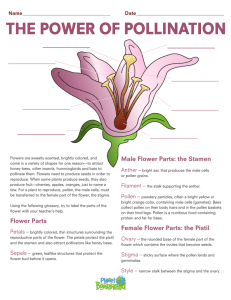
Structure of a Flower
1. Pistil/Carpel
2. Stigma
3. Style
4. Ovary
5. Stamen
6. Filament
7. Anther
8 . Petal
9. Sepal
10. Receptacle
11. Stem
Male Reproductive Structure
The stamen consists of two parts: Anther and
Filament
The anther is where meiosis occurs to produce haploid pollen
The filament is a stalk that supports the anther
• Pollen
Grain
• Anther
Sac
Female Reproductive Structure
The pistil (or carpel) consists of the stigma, style and ovary
Meiosis occurs in the ovary to produce haploid ovules
The sticky stigma receives the pollen
(male gamete structure) from the anther
The pollen grows a tube down through the style
Fertilization
After pollen lands on the stigma, a pollen tube grows down through the style to ovary
The pollen tube passes through the micropyle (opening) into the ovule
Fertilization
Male gametes travel along the pollen tube and into the ovule
The male gamete fuses with the female gamete – fertilization has taken place
Seed and Fruit Development
After fertilization, the petals and sepals fall off flower
Ovary “ ripens ” into a fruit
The ovule develops into a seed
Other Reproductive Structures
Petals : colorful structures that attract pollinators.
Sepals : surround and protect the flower bud.
Reflect
[Write your answer on the worksheet.]
In which part of a flower are male gametes made?
In which part of a flower are female gametes made?
Pollination
Wind, insects or other animals transfer pollen from the anther (male structures) of one flower to the stigma (female structures) of another
Flowers vary depending on pollination mechanism
Pollination Vectors
Wind Pollination : Dull, scentless flowers with reduced petals
Bees/Butterfly Pollination : Bright color, nectars, scent.
They sip nectar, get pollen on coats, transfer pollen from flower to flower
Bird Pollination : Nectars bright colors, tube-like flowers
Moth Pollination : White petals, open at night
Fly Pollination :Rank odor, flesh colored petals
Reflect
[Write your answer on the worksheet.]
After pollination, how does the male gamete reach the ovule?
Seed Dispersal Mechanisms-
Allow plants to colonize new areas and avoid shade of parent plant
Wind Dispersal - Flight mechanisms, like parachutes, wings, etc.
Ex. Dandelion, maples, birch
Animal Dispersal - Fleshy fruits which animals eat, drop undigested seeds in feces or burrs which stick to animals ’ coats
Gravity Dispersal -
Heavy nuts fall to ground and roll ex. acorns
Water Dispersal - Plants near water create floating fruits ex. coconuts
Cambridge Practice
Questions
Complete the Cambridge Practice Questions at the end of the handout.