Honey Bee Worksheet
advertisement

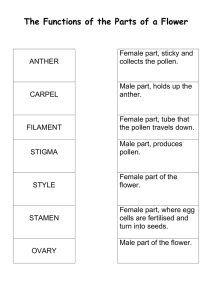
Name _____________________________________ Date _____________________________________ THE POWER OF POLLINATION Flowers are sweetly scented, brightly colored, and come in a variety of shapes for one reason—to attract honey bees, other insects, hummingbirds and bats to pollinate them. Flowers need to produce seeds in order to reproduce. When some plants produce seeds, they also produce fruit—cherries, apples, oranges, just to name a few. For a plant to reproduce, pollen, the male cells, must be transferred to the female part of the flower, the stigma. Using the following glossary, try to label the parts of the flower with your teacher’s help. Flower Parts Petals – brightly colored, thin structures surrounding the reproductive parts of the flower. The petals protect the pistil and the stamen and also attract pollinators like honey bees. Sepals – green, leaflike structures that protect the flower bud before it opens. Male Flower Parts: the Stamen Anther – bright sac that produces the male cells or pollen grains. Filament – the stalk supporting the anther. Pollen – powdery particles, often a bright yellow or bright orange color, containing male cells (gametes). Bees collect pollen on their body hairs and in the pollen baskets on their hind legs. Pollen is a nutritious food containing protein and fat for bees. Female Flower Parts: the Pistil Ovary – the rounded base of the female part of the flower which contains the ovules that become seeds. Stigma – sticky surface where the pollen lands and germinates. Style – narrow stalk between the stigma and the ovary.