Plant Reproduction
advertisement

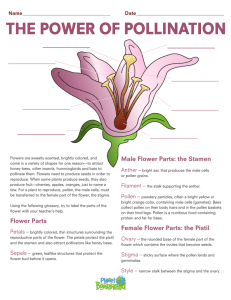
Plant Reproduction Ferns, Mosses and Liverworts Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms – the dominant terrestrial vegetation today Structure and function of the flower stigma anther style stamen filament ovary ovule petal sepal peduncle receptacle carpel Flower Structure Quiz • What is the name of the structure labelled X in the diagram? A. carpel B. sepal C. stamen D. peduncle X Flower Structure Quiz • Where is pollen made? A. stigma B. sepal C. anther D. ovary Flower Structure Quiz • Where is the ovule found in a flower? Flower Structure Pollination A. petals B. style C. nectary D. ovary Fertilisation Seed Dispersal Germination Test Flower Structure Quiz • Which parts of the flower are labelled below: X A. X = style, Y = stigma B. X = filament, Y = anther Y C. X = stigma, Y = style D. X = anther, Y = filament Pollination The pollen grain contains the male sex cell (gamete) Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma Male gamete is contained within a pollen grain. The hard outer coating protects them both physically and from desiccation. Pollen can be carried between flowers by insects or by wind Wind-pollinated flowers are different in structure to insect pollinated flowers as they do not have to attract insects to them but do need to be exposed to the wind. Pollen grains are very small and light. They occur in very large numbers Anthers are exposed to the wind so that pollen can easily be blown away Stigmas are feathery to catch pollen carried in wind Petals are small and green as there is no need to attract insects Flower Structure No scent or nectary Pollination Fertilisation Seed Dispersal Germination Test Insect-pollinated flowers are adapted to attract insects to enable the transfer of pollen Pollen has barbs for hooking onto insect fur nectar and a scent present Anthers positioned to rub pollen onto insects Sticky stigma to collect pollen Flower Structure Pollination Brightly coloured petals Fertilisation Seed Dispersal Germination Test Eggs are enclosed and protected within an ovary. After fertilisation of the egg the embryo develops inside a structure with food reserves and a protective coat. Angiosperms have formed successful relationships with animals And also the wind Pollination Quiz • Pollination is the transfer from….? A. stigma to anther B. style to stamen C. ovule to filament D. anther to stigma Pollination Quiz • Two mechanisms for pollination are? A. Wind and water B. Insect and wind C. Insect and water D. Wind and birds Pollination Quiz • Contains food to support initial embryo plant growth A. Testa B. Radicle C. Cotyledon D. Plumule Pollination Quiz • Flowers are adapted for wind-pollination by… A. Having bright petals and a scent B. Having a nectary C. Having feathery stigmas D. Having sticky stigmas