Nutrition and Energy Flow I. How Organisms Obtain Energy
advertisement

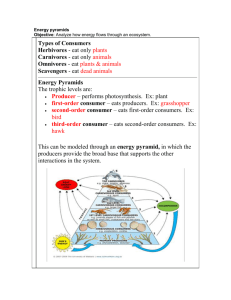
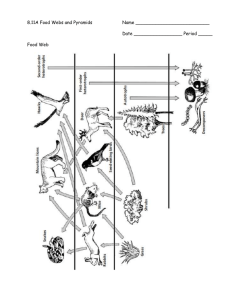
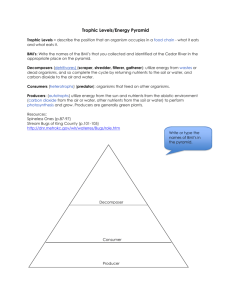
Nutrition and Energy Flow I. How Organisms Obtain Energy -Obtain means to get. -The ultimate source of the energy for life on earth is the sun. -Energy is the ability to cause change. I. How Organisms Obtain Energy 1. Autotrophs: The producers. Producers turn light energy from the sun into food through a process called photosynthesis. Ex: Trees, plants, algae. I. How Organisms Obtain Energy -Photosynthesis happens in the leaves of plants in special organelles called chloroplasts. -Chloroplasts contain a chemical called chlorophyll which helps to capture the sun’s energy. -Photosynthesis is the process of turning light energy into sugar. Equation for Photosynthesis: 6CO + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 carbon + water glucose + oxygen dioxide (sugar) Questions What provides energy for life on earth? -the sun What is energy? -the ability to cause change Is a producer and an autotroph the same thing? -yes What is an example of a producer? -a plant What is photosynthesis? -photosynthesis is when a plant turns light energy into food. Where does photosynthesis happen? -in the leaves of plants in special organelles called chloroplasts. I. How Organisms Obtain Energy 2. Heterotrophs: The consumers. A consumer can’t make it’s own food so it has to eat other organisms. Ex: Lions, Humans, Rabbits. I. How Organisms Obtain Energy Examples of heterotrophs: 1. Herbivore-eats only plants (autotrophs). Ex: Rabbits 2. Carnivore-eats only animals (heterotrophs). Ex: Lions 3. Omnivore-eats plants and animals. Ex: Humans 4. Scavenger-eats dead animals and garbage. Ex: Vultures 5. Decomposer-breaks down dead or dying material. Ex: Bacteria, fungi Questions What is a consumer? -an organism that cannot make its own food. What is an example of a consumer? -humans Is a consumer the same thing as a heterotroph? -yes What kind of heterotroph is this? -carnivore What kind of heterotroph is this? -decomposer What kind of heterotroph is this? -herbivore What kind of heterotroph is this? -scavenger II. Flow of Matter and Energy in Ecosystems -Flow means to move. -Matter flows from producer to consumer. -Energy is transferred from one organism to the next as matter cycles, however, a lot of energy is lost to the environment as heat. Autotrophs Third-order heterotrophs First-order heterotrophs Second-order heterotrophs Decomposers II. Flow of Matter and Energy 1. Food chain - a model that shows how how matter and energy moves through an ecosystem. berries → mice → black bear II. Flow of Matter and Energy -Nutrients/energy move from producer to consumer to decomposer. Example food chain: berriesrabbittiger **The arrows in a food chain show the direction of energy movement. II. Flow of Matter and Energy -Each organism in a food chain is a feeding step, or trophic level in the movement of matter and energy. -Only 10% of energy is passed up each trophic level!!! -Because so much energy is lost at each trophic level, there can only be 3-4 steps in a food chain. II. Flow of Matter and Energy in Ecosystems 2. Food Web-a model which shows all possible feeding relationships at each trophic level in a community. ***A food web is more realistic than a food chain because organisms depend on more than one other species for food. Chihuahuan raven Honey mesquite (pods eaten by beetles) Pronghorn antelope Example Gambel quail Food Web Jackrabbit Long-tail weasel Desert tortoise Prickly pear cactus Coyote (top carnivore) Roadrunner Kangaroo rat (seed eater) ants Texas horned lizard Red spotted toad Mexican whiptail lizard Mojave rattlesnake Questions What does flow mean? -to move Energy flows from _______ to _______ in an ecosystem. -Energy flows from producer to consumer in an ecosystem. What is a food chain? -a model that shows how energy flows in an ecosystem. What is a food web? -a model which shows all the feeding relationships in an ecosystem. Which is more realistic, a food web or a food chain? -a food web is more realistic than a food chain b/c is shows all possible feeding relationships. What is a trophic level? -a feeding step. How much energy can be passed up each trophic level? -10% Why can there only be 3-4 trophic levels? -There can only be 3-4 trophic levels b/c only 10% of the energy is passed up each level, which means that after 3 or 4 levels, energy will run out. II. Flow of Matter and Energy in Ecosystems 3. Ecological Pyramids-a model which shows how energy flows through an ecosystem. Pyramid of Energy -Pyramid of Energy-shows how energy decreases at each trophic level. Only 10% of the energy is passed up each level! Heat Heat 0.1% Consumers 1% Consumers 10% Consu Heat Heat 100 Produ -Pyramid of Biomassshows the weight at each trophic level. Pyramid of Numbers Fox (1) Birds (25) Grasshoppers (250 Grasses (300 Pyramid of Biomass 1 kilogram of human tissue 10 kilograms of beef 100 kilograms of grain -Pyramid of Numbers shows the number of organisms eaten by the animal above it on the pyramid. Questions What is the Pyramid of Energy? -the Pyramid of Energy is an ecological pyramid which shows how much energy is in each trophic level. Does the amount of energy increase or decrease as you go up each trophic level? -decrease Why does the amount of energy decrease? -energy is lost to the environment as heat. What is the Pyramid of Numbers? -the Pyramid of #’s is an ecological pyramid which shows how many organisms exist at each trophic level. What is the Pyramid of Biomass? -the Pyramid of Biomass is an ecological pyramid which shows how much weight exists at each trophic level.