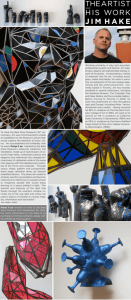
Analysis of Bata Reports
advertisement

PROJECT REPORT ON “FINANCE & ACCOUNTING OF BATA INDIA LTD.” F.B.M & F.R.M FOUNDATION-B 2009-10 SUBMITTED TO: Mr. Rahul Jain Mr. S.C Kapoor Faculty, Pearl Academy of Fashion SUBMITTED BY: ANKIT BEHL SOURABH KUMAR ADITI MALHOTRA SAMAR RAJPUT Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 1 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT This report has been insightful and erudite experience that we have undergone. The credit for the completion of this report goes to Mr. Rahul Jain and Mr. S. Kapoor who has taught us and made us competent of understanding the intricacies. Without her help this report could not have been possible. ANKIT BEHL SOURABH SAMAR ADITI Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 2 CONTENT PARTICULARS Overview of Footwear Industry… Export and Import Over view Role of Government in Industry Organizational Profile… Company profile Management Structure History Key Milestone Product Profile . Page No. 6-8 9-11 12-13 14 15-19 20 21 22-25 26-31 Internal And External Environments… 32 Human Resource Policy 33 34 Corporate social responsibility Marketing Initiative of the company Strategy of Company Technology and Manpower Distribution Channel Award won and Expansion Plan Government approvals in last decade 35 36-37 38 39 40 41 Manufacturing Process 42-43 Competitors 44-46 PEST Analysis 47-50 Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 3 Financial Condition… 51 Analysis of Bata Report (Charts and Graphs) 52-56 Competitor Analysis of Bata (Charts and Graphs) 57-58 Horizontal Analysis of Balance Sheet of Bata 59-60 Horizontal Analysis of Profit & Loss Account 61-62 Analysis of Economic Environment… 63 Factor that will affect the organization demand 64-67 Factor that will affect the organization supply 68-72 Recent Trend in Industry 73 Implication of Fiscal Policy 74-77 Implication of Monentary Policy 78-81 SWOT Analysis Recommendation Competitor Profile… 82-83 84 85 Lakhani Company Profile 86 History 87 H R Policy and Products 88 Liberty Company Profile 89 History 90 H R Policy, Award Won and Products 91 Minimum wages Chart… Bata India Pvt. Ltd 92-93 Page 4 Recent News Article Annexure … 94-96 Product Profile of Bata 98-105 Balance sheet of Bata 106-107 Profit And Loss Account of Bata 108-109 Quarterly Result of Bata 110-111 97 Mutual Fund Activities of Bata 112 F I Activities of Bata 113 Profit & Loss Account of Lakhani Balance sheet of Lakhani Profit & Loss Account of Liberty Balance sheet of Liberty References… Bata India Pvt. Ltd 114-116 117 118-120 121 122-123 Page 5 OVERVIEW OF Indian Footwear Industry The Footwear Industry is a significant segment of the Leather Industry in India. India ranks second among the footwear producing countries next to China. The industry is labour intensive and is concentrated in the small and cottage industry sectors. While leather shoes and uppers are concentrated in large scale units, the sandals and Chappals are produced in the household and cottage sector. India produces more of gents’ footwear while the world’s major production is in ladies footwear. In the case of Chappals and sandals, use of non-leather material is prevalent in the domestic market. The major production centers India are Chennai, Ranipet, Ambur in Tamil Nadu, , Mumbai in Maharashtra, Kanpur in U.P. , Jalandhar in Punjab, Agra and Delhi. The following table indicates concentration of units in various parts of the country: Region Tamil Nadu Large & Medium Scale 64 Delhi & up North SSI Household 31 7 4 8 2 Agra, Kanpur 9 34 14 Calcutta 1 3 19 Bangalore 6 3 4 Mumbai 3 11 Others 13 10 3 The estimated annual footwear production capacity in 1999 is nearly 1736 million pairs (776 million pairs of leather footwear and 960 million pairs of non-leather footwear). Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 6 Region-wise share of total estimated capacities is as follows: Region Leather Shoes Non-leather Leather Shoe Shoes Uppers Leather Sandals Non Leather Sandals Percentage Tamil Nadu 26 5 54 1 0 Delhi & up North 10 77 4 1 60 Agra, Kanpur 45 0 32 62 0 Calcutta 12 0 2 3 0 Bangalore 3 3 4 0 0 Mumbai 4 2 1 32 0 Others 0 13 3 1 40 Total 100 100 100 100 100 Shoes manufactured in India wear brand names like Florsheim, Gabor, Clarks, Salamander and St. Micheal’s. As part of its effort to play a lead role in the global trade, the Indian leather industry is focusing on key deliverables of innovative design, consistently superior quality and unfailing delivery schedules. India in itself has a huge domestic market, which is largely untapped. The Indian footwear industry is provided with institutional infrastructure support through premier institutions like Central Leather Research Institute, Chennai, Footwear Design & Development Institute, Noida, National Institute of Fashion Technology, New Delhi, etc in the areas of technological development, design and product development and human resource development. The availability of abundant raw material base, large domestic market and the opportunity to cater to world markets makes India an attractive destination for technology and investments. Source: Secretariat For Industrial Assistance Department of Industrial Policy & Promotion Ministry of Commerce and Industry Govt. of India Udyog Bhawan, New Delhi - 110 011 SIA Website : http://indmin.nic.in (http://www.indianshoebazaar.com/ind_india.asp) Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 7 Production capacity of Shoe Industry The leather industry is spread in different segments, namely, tanning & finishing, footwear & footwear components, leather garments, leather goods including saddlery & harness, etc. The estimated production capacity in different segments is as under Hides:64 million pieces Skins:166 million pieces Footwear & Footwear Components Shoes:100 million pairs Leather shoe uppers:78 million pairs Non-leather shoes/chappals etc:125 million pairs Leather Garments:6 million pieces Leather Products:70 million pieces Industrial Gloves:40 million pairs Saddlery:6000 pieces The major production centers for leather and leather products are located at Chennai, Ambur, Ranipet, Vaniyambadi, Trichi, Dindigul in Tamil Nadu, Calcutta in West Bengal, Kanpur in Uttar Pradesh, Jalandhar in Punjab, Bangalore in Karnataka, Delhi and Hyderabad in Andhra Pradesh. Raw material supplies: There exists a large raw material base. This is on account of population of 194 million cattle, 70 million buffaloes, 95 million goats. According to the latest census, India ranks first among the major livestock holding countries in the world. In respect of sheep with 48 million sheeps, it claims the sixth position. These four species provide the basic raw material for the leather industry. The annual availability of 166 million pieces of hides and skins is the main strength of the industry. This is expected to go up to 218 million pieces by the end of year 2000. Some of the goat/calf/sheep skins available in India are regarded as specialty products commanding a good market. Abundance of traditional skills in training, finishing and manufacturing downstream products and relatively low wage rates are the two other factors of comparative advantage for India. http://leather.indiabizclub.com/info/indian_leather_industry_overview Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 8 Export and Import overview India's export of Leather & Leather Products has reached US $ 3.47 billion in dollar terms and Rs.14,000 crore in rupee terms. In dollar terms, there has been an export growth of 13.67% and in rupee termsl.13%Footwear alone holds a major share of 42.44% in India's total leather products export trade. As against the export target of US $ 3042 million for the financial year 2007-08, the achievement was 114.32% Footwear is the engine of growth for the entire Indian leather industry and India is the second largest global producer of footwear after China, accounting for 14% of global footwear production. of 14.52 billion Pairs. India Produces 2065 million pairs of Different Categories of Footwear (Leather Footwear 909 million pairs, Leather Shoe uppers 100 million pairs and Non-leather footwear 1056 million pairs) India exports about 115 million pairs. Thus, nearly 95% of its production goes to meet its own domestic demand. Footwear exported from India are Dress Shoes, Casuals, Moccasins, Sport Shoes, Horrachies, Sandals, Ballerinas, Boots, Sandals and Chappals made of rubber, plastic, P.V.C. and other materials. MNC Brands sourced : Acme, Clarks, ColeHann, Deichmann, Ecco, Elefanten, Florsheim, Gabor, Hasley, Hush Puppies, Double H, Justin, Marks from India & Spencer, Nautica, Nike, Nunn. Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 9 MNC Brands Sold in India : Bally, Clarks, Hush Puppies, Lee cooper, Lloyd, Marks&Spencer, Nike, NineWest, NewBalance, Reebok, StacyAdams Indian Brands sold in India : Red Tape, Bata, Liberty , Khadims, Lakhani, Action Nearly 75% of India’s Export of Footwear is to the European Countries and the USA. The Indian Footwear Industry provides employment opportunities to a total of 1.1 million people, mostly from the weaker sections of the society. Out of this, about 0.2 million are employed in the organized sector, 40% of whom are women. Remaining 0.9 million people are engaged in unorganized footwear sector like rural artisans, cottage and household units etc. The Footwear Sector is now de-licensed and de-reserved, paving the way for expansion of capacities on modern lines with state-of-the-art machinery. To further assist this process, the Government has permitted 100% Foreign Direct Investment through the automatic route for the Footwear Sector. Footwear export has increased from US$40.15 million in 1977-78 to US$ 1475.83 million in 2007-08 Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 10 Chart showing Global Import of footwear Vs. Indian Export of Footwear India ’s Exports of Footwear – Country-wise Share in Total Exports (2007-08) Source: DGCI& S The European Union and the USA are the major markets for Indian Footwear accounting for 79.95% and 9.22% share respectively in India’s total footwear export. The major markets for Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 11 Indian Footwear are Germany 16.66%, UK 16.31%, Italy 15.32%, USA 9.22%, France 7.81%, Spain 5.10%, Netherlands 4.91%, Portugal 2.50%, UAE 2.48% and Denmark 1.18%. These 10 countries together accounts for nearly 81.49% of India’s total leather products export. (http://footwearsinfoline.tripod.com/export_import.htm) NOTE:- 20% of total Indian shoe production come from Bata. i.e about 8crorte pairs. ROLE OF GOVERNMENT IN SHOE INDUSTRY IN INDIA Jairam Ramesh Minister of state for Commerce has announced Rs.1.6-billion (Rs.160-crore) package to boost the local shoe industry, but the state government, chief minister opposed this. Ramesh made the announcement on Saturday when he was inaugurating an international fair on leather, footwear components and technology at the Kalakriti Grounds near the Taj Mahal. The package comprises of Rs.600-million Leather Park, Rs.200-million footwear design development centre, Rs.100-million design studio, a testing laboratory and a permanent exhibition ground to be developed on investment of Rs.500-600 million, on similar to Pragati Maidan exhibition in New Delhi. Local shoe manufacturers have been asked to look for land. But there’s a problem the land for the projects has to be released by the state’s ruling party (which is the Congress’s opposition party). Agra’s old shoe industry directly and indirectly supports 100,000 families, mostly from the dalit community. Mayawati of BSP opposed to Ramesh of Congress Party that heads the United Progressive Alliance (UPA). According to shoe industry sources, Mayawati won’t be in a hurry to release land for any of the projects announced. But the industry believes once the schemes starts, exports could reach Rs.30 billion (Rs.3000 crore) from the present level of around Rs.8 billion (Rs.800 crore). More than 200 national and international components and raw materials manufacturers have put up their stalls at the exhibition. (http://www.thaindian.com/newsportal/politics/big-boost-for-agras-shoe-industry-if-state-governmenthelps_100116975.html#ixzz0XAkn7VPx) Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 12 Design-cum-Resource Centre for Footwear & Leather Industry: Leather goods and shoes as well as items of fur are being manufactured in the Small Scale Industry/Tiny sector traditionally in Srinagar and Jammu. The Central Government would make an initial contribution of Rs. 1.00 crore as grant for setting up a Design/Resource Centre and National Leather Development Programme (NLDP) will provide assistance for machinery, training and salaries of professionals. Under the National Leather Development Prograramme, exclusive assistance will be provided to market finished leather products of the artisans of the State in the form of buyer seller meets and exhibitions. (jammu.gov.in/departments/.../Central-Policy%20and%20Procedures.pdf) RAW MATERIAL FOR SHOES Synthetic leather Shoe leather PU leather Air blown PVC soles PU welted sole TPR soles for men PU sleeper sole PVC gents sole PU shoe sole Emulsion polymers (latexes) Pell ethane thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers Polyurethanes Voralast polyurethane system Microfiber leather (www.tradeindia.com/seller...38/shoes-materials-accessories. html) (www.dow.com/products-services/division/textiles.html) Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 13 Organizational Profile Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 14 COMPANY PROFILE Business Type: Footwear Main Market: India Founder : Tomas Bata Chairman: P.M Sinha Turnover: 1012 Cr. Employees: 6800 approx. Company Address: 22/4, Nukuleshwar Bhattacharya Road, Kolkata-700026 Phone: 033-24631657/8 Fax: 91- 124 4100883 Site URL: www.Bata.in Face Value: 10 Share Price: Bata India listed on BSE and NSE Current Price- NSE Price Rs 191.90 (As on 22/1/2010) BSE Price Rs192.90 ( As on 22/1/2010) Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 15 Share Holding Pattern: Promoter Holding-51.02% Non Promoter Holding-13% Public and Other-23.06% FII-11.50% 13% Promoters 11.50% Public and Other 51.02% FII Non Promoter Corparate 25.06% (Bata India Ltd.) Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 16 Board Of Director: As per company records, the board of directors of the company presently comprises the following. Name Mr. P M Sinha Mr. Marcelo Bravo Mr. Pradip Kumar Date Of Appointment April 16, 2004 Feb 11, 2005 August 25, 2001 Mr. Jaswant Singh Mr. A. K. Thakur Mr. V. Narayanan Mr. Constantin Designation Chairman Managing Director Deputy Managing Director Director Marketing Nominee Director UTI Director Director Mr. Shaibal Sinha Mr. Amit Mitra Mr. N. Sankar Director Finance Director Director Feb 2, 2005 Feb 2, 2005 Feb 2, 2005 August 1, 2002 December 11,, 1996 January 2, 1995 March 10, 2004 Brief Details of Board of Directors Mr. P. M. Sinha Mr. Sinha is the former CEO of Pepsi Cola International South Asia and was the Chairman of Pepsico India Holdings and President of Pepsi Foods Limited. He was also on the Management Committee & Director of Hindustan Lever Limited for eleven years, before he joined Pepsico in 1992. He is currently on the Boards of ICICI Bank, Wipro Limited, Indian Oil Corporation Limited, Lafarge India Pvt. Limited. Mr. Marcelo Villagran Bravo Mr. Marcelo Villagran Bravo has more than 34 years of experience with the Bata group. Before joining the Company as a Managing Director, he was working with one of the most successful companies in the Bata group, i.e. Bata . Chile. He has wide operating and sales experience. He is a commercial engineer and a Bachelor of Business Administration. Mr. Pradip Kumar Nag Mr. Nag graduated in Commerce with Honours from Goenka College of Commerce and Business Administration under Calcutta University and is a member of All India Management Association. Mr. Nag has a rich experience in multifarious areas of Accounting, Financial Management, Taxation,Costing Principles and Methods and Administrative functions encompassing over three decades. He held the position of Senior Vice President, Finance in the Company for over 5 years. Mr. Nag undertook training in Toronto, Chicago, Ottawa and Philadelphia in various areas of Retailing, Financial Accounting and Management Reporting in connection with .SAP. Project for North American BSO Companies. He was appointed by Bata Limited, Toronto, Canada (The International Headquarters of Bata Shoe Organisation) as Director .Enterprise Controlling. for Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 17 Integrated Business Systems and was closely massociated with successful implementation of .SAP. Integrated Business Systems in Retail Canada and User Support Programme. Mr. Jaswant Singh Mr. Singh joined the Company in 1971 as a Management Trainee . Marketing and had also undertaken training for 18 months in the Retail and Wholesale Departments. Mr. Singh started his career with the Company way back in 1971, and in the year 2000, he was made Managing Director, Bata Shoe Co. Uganda Limited, which position he held till his transfer to Bata India Limited in the year 2004. Mr. Singh has wide experience in Retail, Wholesale, Brand Management, Production, Merchandising and General Management. During his career he has attended various courses being MARKETCO, Monssey, France, 1983, ADVANCO, Chicago, Toronto, 1990, EMP (Executive Management Programme) NYC, Toronto, 1998, Company Managers Programme Toronto, 2000 and has represented the Company at several Shoecons, namely Milan, Padova, Prague and Chicago. Mr. Singh was awarded an Achievement Award by Mr. Thomas G. Bata at Milan in 1990 for North Star. Mr. A. K. Thakur Mr. A. K. Thakur is a B.Com from Calcutta University and a Chartered Accountant. He is the former Executive Director of Unit Trust of India. He has worked in almost all the key areas of Unit Trust of India and actively participated in formulating various corporate policies, procedures and strategic decisions. Mr. V. Narayanan Mr. Narayanan is the former Chairman and Managing Director of Pond.s (India) Limited. He is a product of the Lawrence School at Lovedale and the Loyola College, Chennai. Mr. Narayanan began his career in 1959 as a Management Trainee in Hindustan Lever Limited (HLL). In his ten years with HLL, he specialised in Sales and Marketing, both in India and in the UK. He joined Chesebrough Pond.s Inc in 1968 as its Marketing Director and became Chairman and CEO of Pond.s (India) Ltd. in 1978. After his retirement from Pond.s (India) Limited, Mr. Narayanan is on the Board of several leading companies. Mr. Constantin Salameh Mr. Salameh has worked for 19 years with Hewlett Packard, which he joined in 1984. He has worked in a number of senior management positions in this company in sales, marketing and financial services in Europe and Asia Pacific. The last two positions held in Hewlett Packard were Vice-President and Managing Director of Financial Services in Asia Pacific (1996-1999) and in Europe, Middle East and Africa (2000-2003) with full P & L responsibilities for a US$ 2.5 billion financing business. Mr. Salameh completed his University degrees from King.s College, England (B.Sc Engg. with 1st class honours in 1979), M. Sc. Engg. from M.I.T. in 1980 and his MBA from Stanford University (USA) in 1984. His board affiliations are with the American University of Beirut and the University of Geneva. Mr. Salameh frequently addresses external audiences . including the Management Centre Europe, Euromoney, International Technology Management, Asia International and World Bank Conferences on operational aspects of captive Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 18 finance entities, business planning and financial management practices from a global perspective. Mr. Shaibal Sinha Mr. Shaibal Sinha qualified as a Chartered Accountant in 1986. He has worked with Eicher Limited, Toyota (in Muscat) and with Shaw Wallace and Company Ltd. His last assignment was with Reckitt Benckiser in U.K. and in India, where he has worked for the last eight years. Dr. Amit Mitra Dr Amit Mitra did his Masters in Economics from Delhi School of Economics in 1970 and further attained the Doctorate Degree in Economics from Duke University, USA in 1978. Later he taught in major Universities in the United States over a decade and received the prestigious SearsRoebuck Foundation Award for Distinguished Teaching, 1990. Furthermore, he has wide Post Doctoral Research experience as senior consultant. In addition to the Company, he is also on the Board of Directors of Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL), GAIL (India) Limited and Principal PNB Asset Management . He is also a Member on the Advisory Board of The India Fund of The Unit Trust of India (UTI), Member of the Central Advisory Committee, Central Electricity Regulatory Commission, Member of the Life Insurance Council, Member of the "India-China Eminent Persons Group" from the Indian side, Member of the Central Listing Authority constituted by SEBI, Member of the Advisory Committee to Union Commerce Minister of India on International Trade (WTO), and Member of the "Indo - EU Roundtable" from the Indian side (initiated by Government of India and the European Union (EU)). He is and also has also been a part of several committees and sub-committees constituted by various ministries in the Government of India. Mr. N. Sankar Mr. N Sankar (59) holds a Masters Degree in Chemical Engineering from the Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, USA. He is the Chairman of The Sanmar Group and its associates, which operates in diverse areas such as Chlorochemicals, Speciality Chemicals, Shipping, Engineering, Insurance, and Cement. The turnover of the Sanmar Group (including its associates) is close to Rs.30,000 million. The Sanmar Group has long-standing and well-established joint ventures with leading international corporations like Emerson Electric, Tyco, Flowserve and Cabot of the USA, and AMP of Australia. The Sanmar Group currently has nine joint ventures. Mr. Sankar also serves on the Board of a few institutions outside the Sanmar group, such as F.L. Smidth Limited. Over the years, Mr. Sankar has held office in several public bodies representing trade and industry, such as the President of Assocham and the Chairman of the Indo-US Joint Business Council. He has also received awards recognizing his services to business and industry, including the ‘Lala Shriram National Award for Leadership in Chemical Industry. from the Indian Institute of Chemical Engineers. Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 19 Management Organisation Structure: Managing Director M Velligran Special Projects Dy. Managing Director H Vengali P K Nag Commercial Internal Audit Harpreet Singh Human Resources Finance Shaibal Sinha Special Projects P P Dasgupta Sujit Sen Corporate/Admin./ Legal/Tax Personnel & H.R. M J Z Mowla S Ganguly S Chakravarty P Gupta S D Singh Finance, H.O. Kisor Sen Bataganj T R Salaria Mokamehghat Finance Hemant Sultania S R Raha Faridabad S D Singh Company Secretary A B Anand Marketing & Commercial Family & Bazaar Stores Flagship & City Stores J Singh R Hotte E Tonolli Wholesale V Anand Exports S Dixit Retail Flagship & City C C Ponnappa Retail Flagship(West) S K Dwivedi Retail Family (North) Retail Flagship(West) S K Dwivedi G P Sahu Retail Family (South) Retail Flagship (East) A Nandy R Sengupta Retail Family (East) & Bazaar C Roy Product Development F Ferraris Merchandising Insurance Sandak B S Das Opender Singh GGGFFFFF Information Systems BS AHM Ehsanuzzaman Batanagar Production Merch.Coord Special Projects Production Southcan Retail Family (West) S Nagarajan Vinesh Singh Retail Analysis S Chakraborty S Maitra K Raman g Advertising & Comm. Costing & Efficiency Tumpa Roy S Ranjan Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 20 HISTORY All About Bata: Bata India is the largest retailer and leading manufacturer of footwear in India and is a part of the Bata Shoe Organization. Incorporated as Bata Shoe Company Private Limited in 1931, the company was set up initially as a small operation in Konnagar (near Calcutta) in 1932. In January 1934, the foundation stone for the first building of Bata's operation - now called the Bata. In the years that followed, the overall site was doubled in area. This township is popularly known as Batanagar. It was also the first manufacturing facility in the Indian shoe industry to receive the ISO: 9001 certification. The Company went public in 1973 when it changed its name to Bata India Limited. Today, Bata India has established itself as India's largest footwear retailer. Its retail network of 1250 stores gives it a reach/ coverage that no other footwear company can match. The stores are present in good locations and can be found in all the metros, mini-metros and towns Bata's smart looking new stores supported by a range of better quality products are aimed at offering a superior shopping experience to its customers. And the new face of Bata India is now visible to the industry as well as its customers. Today, backed by a brand perception of experience, the company is working towards positioning itself as a vibrant and contemporary young brand. It has significantly transformed its retail formats to become more lifestyleoriented, which has helped change consumer perceptions to a large extent. (http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/DetailedReport.aspx?Type=COMP-HIS&SSKICode=BATA) Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 21 Key Milestones: Date/Year Event 1894 The Bata Shoe Organisation was founded by Tomas J. Bata, a ninth generation shoe maker 1931 The Company was incorporated in India. 1933 The production of footwear commenced in a rented premises at Konnagar, a few miles away from Kolkata, where for the first time rubber and canvas shoes were manufactured in India. October 28, 1934 The foundation stone was laid on land purchased from the Port Commissioners and small landowners in the outskirts of Kolkata and the first manufacturing unit was set up, at a place now known at Batanagar. The factory shifted from Konnagar to Batanagar The construction work at the Batanagar factory was completed, and factory operation shifted from Konnagar to Batanagar. Towards the end of 1936, the factory produced leather footwear for the first time 1936 1937 Batanagar tannery became operational towards the end of 1937 1939 The Batanagar factory was complete in terms of every activity related to footwear. The Batanagar township grew to become self-sufficient with the acquisition of more land and the erection of schools, places of worship, hospitals, entertainment and recreational centres. 1940-45. During the World War II the factory’s production was geared to meet war requirements. 1942 A footwear manufacture plant, a machinery department was set up at Batanagar, which produced the first India-made major shoe machine. Simultaneously, several auxiliary departments were started. This was followed by the setting up of the factory at Bataganj, Bihar. 1950 Bata successfully launched the brand .Hawai.. 1951 The rubber/canvas factory was set-up at Faridabad, Haryana. 1952 One of Asia’s largest tanneries was set-up at Mokemehghat, Bihar. 1988 The Bata factory was set-up in Peenya, Bangalore Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 22 1994 The Company’s factory at Hosur in the State of Tamil Nadu became operational, which was originally an Export Oriented Unit, but now caters to the domestic Indian market 1993 Batanagar factory became the first Indian shoe-manufacturing unit to receivethe ISO 9001 certification. (http://www.sebi.gov.in/dp/bata.pdf) Our Values Constant innovation in design and product development Superior customer service Excellence in operational and commercial execution Entrepreneurial spirit and passion to win Teamwork in international environment Trust and respect for our employees Adding value to the community Delivering on our commitment to shareholders (http://www.bataindia.com/page.php?kon=5_2_1) Our commitments Your Purchase Guarantee In case of any problem, bring back the pair shoes with in the next 15 days from the date of purchase and we will replace it with another pair. Condition apply. Wide collection With more than 1000 different designs to choose from, we have one of the widest selection shoes, handbags and accessories. Assured Quality Strict quality measure are followed during and often the production of all our products. We have our own factories and warehouse that are supervised by trained and experience personas. Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 23 Personalized Attention In all our stores, our trained professional sales staff is at your service. In case you have any query about Bata products or services, please feel free to ask for any assistance. Product Detail We ensure that you get complete detail of all our products in the most convenient way. Each item carries tags that clearly mention type, price, size or other necessary information. It not only saves your time but also helps you in your selection. (http://www.bataindia.com/page.php?kon=4_0) Bata India - Today Sells over 45 million pairs of footwear every year Serves over 120,000 customers every day Sells through over 1200 retail stores Operates 5 manufacturing facilities Employs more than 6800 people (http://www.bataindia.com/page.php?kon=5_2_1) Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 24 bata global Subsidiary Bata India Pvt. Ltd Companys Of Bata India Page 25 . Products Profile Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 26 PRODUCTS Bata India Ltd. has a large variety of shoes for all the sections. They also make accessory for men’s and women’s. Bata India Ltd. make products of the following categories: 1.) Men`s Wear: They make products of preferably for service men and also have Segment of sports shoes for young men under a different company name POWER . they have a large . Variety of products such as: Closed dress Closed casual Sandals Chappals Sports wear Closed dress range starts from 699 to 2699 Closed casual range starts from 399 to 1999 Sandals range starts from 399 to 1899 Chappals range starts from 169-1799 Sports shoes range start from 699-1799 Closed dress . Bata India Pvt. Ltd (http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=11) Page 27 Closed casual (http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=21) Sandals . . . (http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=31) Chapels (http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=41) Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 28 2.) Women’s wear: They make products of preferably missy and have large variety Of products such as:- Chappals Closed Sandals Chappals range starts from 139 to 1249 Closed range starts from 299 to 1299 Sandals range starts from 299 to 1249 Chappals (http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=12) Closed ( http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=22) Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 29 3.) Kid`s wear : they make products of the age group 6-17 years Infants Closed Sandals Infant range from 199 Closed range from 159 to 699 Sandals range from 199 to 599 Infants (http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=23) Closed (http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=33) Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 30 Sandals (http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=43) order to increase their product offering, they are planning to add new variety of shoes. For example, they proposing new technology of sports shoes to be in a competition from Rebook and Addidas. Bata India Pvt. Ltd Page 31 . . . INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 32 Internal Environment The Internal factors include strengths and weaknesses focuses of the firm . Strengths refer to core competencies that give the firm an advantage in meeting the needs of its target markets. Company strengths should be market oriented/customer focused because it assists the firm to understand customer needs. Weaknesses refer to any limitations a company faces in developing or implementing a strategy. Weaknesses should also be examined from a customer perspective so that they can understand there weaknesses from customer point of view. HUMAN RESOURCE POLICY: when they set-up their factory in India, their approach was to hire local labor and trained them making shoes. As a technology advanced they trained their employees on machine. But , for special tasks they hired person who were in occupation of shoe making. As the demand increased they develop their vends in places like Agra, Noida, Gurgaon etc gave them their requirements to manufacturers per their quality standard. The policy in this regard was to frame their vendor. The company has lot of welfare schemes for their employs to encourage stability. Regular training programs are held for the employs and the lower level minimum wages are given but incentives are linked and outcome. Same way the company has their outlet for sale where the employs are on the pay role of Bata. The functions of any management are planning, organizing, staffing, directing and controlling. The management of Bata performs these functions efficiently. All divisions of Bata are taken care of by different set of managers. The management at Bata knows the importance of customers to its business. It has a good image in the minds of the customers. It caters to a large class of customer for middle class and lower middle class customers. The management of the brand performs many functions e.g. it takes up the work of brand repositioning very often. It also works for social causes such as it employs physically challenged people and it is also working towards women empowerment by employing more and more women. The management also takes care of the environment. The organization always gives importance to its employs. It provides many facilities to its employees such as the crèche facility, medical facilities, transportation etc. the industry also Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 33 celebrates birthdays long service etc. All these motivates the employees to achieve the goals and objectives of the organization. Employee Categorisation: Employees of the Company are categorized along the following grades, in descending heirachical order • Directors • Senior Managers (Senior Vice President, Vice President, General Manager) • Middle Managers • Junior Managers • Selling personnel • Shop Managers • Shop Employees Additionally, the Company employs direct and indirect workmen on its factory sites. The number of permanent employees currently on the payroll of the Company is 9,969 as on January 31, 2005. CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY: The following CSR activities were undertaken by the Company during the year: - Sponsorship of Rain Water Harvesting Project in Gurgaon. - Donation to Bihar Flood Relief Fund. - Free shoes to Orphans on Republic Day. - Free medical camp for under privileged caretakers of Kolkata Maidan and physically handicapped. - lnauguration of Bata Cricket School in October 2008. - The Company operates two Higher Secondary Schools, one for boys and one for girls and three Primary level Schools " and also one Nursery School. The children of our employees and neighbouring localities get educational facilities from these institutions. - The Company encourages entrepreneurial spirit in the small scale businesses located in the vicinity of its factories so that they become independent associates and partners in progress with the Company. This generates large employment in the area and gives people the opportunity to grow in their businesses. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 34 - The Company maintains a temple, -a church and a mosque where employees and people from the different communities in the neighbourhood participate in prayers. - The Company actively participates in organizing Blood Donation Camps and distribution of fruits and sweets to the ailing patients at the Batanagar Hospital and Ramakrishna Mission Residential School at Batanagar. (http://content.icicidirect.com/Research/DirectorsReport.asp?icicicode=BATIND) Marketing Initiatives of the Company: In addition to products manufactured by it, the Company also sells footwear, accessories, garments etc. manufactured by international and domestic agencies/ entities. The Company has entered into an arrangement with international shoe-manufacturers such as Reebok, Adidas, M&B Footwear Private Limited, Tej International Private Limited, Sierra Industrial Enterprise Private Limited for marketing their products though the Company.s retail outlets. The Company has the entered into following keyarrangements: • Reebok: Under this arrangement, the Company will purchase shoes from Reebok as per its requirement and earn a gross margin of 36% of the retail price. • Adidas Marketing Private Limited: Adidas Marketing Private Limited has agreed to provide the Company with its products in footwear, apparel, accessories at a Gross margin of 40% for footwear and 42% for apparel and accessories. Margins offered to Bata are subject to change in event of changes in the tax structure and business scenario. • M&B Footwear Private Limited: M&B footwear Private Limited to provide the Company on an outright sale basis stocks of its brands .Lee Cooper. and .ID. at a margin of 40% of the retail price. M&B Footwear would advertise and promote Bata as its business partner. The term of this arrangement extend for three year starting April 30, 2003. • Sierra Industrial Enterprise Private Limited: Sierra Industrial Enterprise Private Limited has agreed to supply the Company their products .Lotto., which launched in almost 50 flagship stores of Bata by mid-February 2005 and is expected to reach 250 stores by mid-August 2005. Bata has agreed to purchase the products at an agreed Gross margin of 42% of the Retail price. • Planet Sports Private Limited: The Company has entered into a Consignment Agreement dated February 29, 2004 for a period of three year extending till February 29, 2007 with Planet Sports Private Limited for supply of footwear, apparel and accessories by the brand name Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 35 .PUMA. at the maximum retail price or at a discounted price as provided by Planet Sports Private Limited and Bata will be entitled to a commission of 35% on the sales net of taxes. (http://www.sebi.gov.in/dp/bata.pdf) Strategy of the Company: The Company.s management has evolved the strategy of the Company after considering the Company’s strengths and weaknesses. The Company believes that this strategy will enable the Company to build on the opportunities in the market. Cost optimization and margin improvement The Company is focusing on margin improvement and cost effectiveness programmes which have started yielding results. The Company has initiated strict control on costs in purchases and outsourcing and is looking at global sourcing for raw materials to improve the net realization. The Company has also been clearing old merchandize through discount sales, write-offs, etc. which will enable it to focus on improving sales. Logistics and demand based production To optimize utilization of production facilities a new logistics team focuses on obtaining specific orders from the market for best selling designs and sizes and ensures that all raw materials are available in the factories well in time so that the Company can produce and place in shops the products that consumers want. Thus the Company has been focusing on consumers and market demand which will reduce inventories and improve sales-to-stock turnover. The Company has closed five depots and converted them into C&F (carrying and forwarding) agents. It is also renegotiating transport costs to ensure a competitive transportation cost of the Company.s products to the sales outlets. Tax-free zone manufacturing base A part of the outsourcing of manufacturing is now routed by the Company from contract manufacturers based in Himachal Pradesh and Uttaranchal which are both states offering concessions in excise, sales tax and corporate tax. The Company is also looking at and negotiating with third party manufacturing facilities in two other tax-free states of Assam and Jammu and Kashmir. The Company is thus aiming to maximize its margin improvement programme. Rationalizing and re-engineering As part of the rationalization of work practices, processes and modernization the Company offered Voluntary Retirement Scheme (VRS) to its work force. 1520 employees have accepted the VRS in year 2004. The Company plans to introduce a new VRS in year 2005. The VRS is Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 36 expected to reduce the Company.s employee cost in the medium term. The Company has modernized seventeen stores, opened twenty new stores and closed down sixty unviable stores. Focus on collecting old outstanding dues The Company.s sales team is fully focused on collecting old outstanding amounts from wholesalers thus reducing working capital. The Company is adopting a dual policy to collect the old outstanding. On one hand the Company is negotiating settlement with the wholesalers and offering discounts to those willing to pay the reduced amount. At the same time the Company is filing legal cases against those who are not willing to settle and pay. Training and restructuring the frontline sales force The Company has reorganized its front line sales force and has promoted its best performing shop managers as district managers. It has undertaken an intensive training programme for its shop assistants and managers to ensure excellence in service to the customers. The Company has also undertaken a rural marketing thrust where the market is growing faster than the urban markets. The Company is bringing in young managers with fresh ideas to inspire and empower the workforce with the requisite skills. Brands and designs The Company is consistently trying to leverage on its established brands like Mocassino, Super Stride, Quo Vadis, Jubliee etc. at the same time create a niche for its new brands like Azaleia, Toppers, Bubblegummers, Weinbrenner and Power International. The Company has been focusing on specialty value added products for better margins. It has been continuously introducing new designs in shoes for men, ladies and children. The Company is endeavouring to break the myth of the price factor, by Introducing an economy range of products that will encompass both style and quality. Borrowings of the Company The shareholders of the Company have in the Annual General Meeting held on June 17, 2004, given the authority to the Board of Directors to borrow up to Rs.1,000 mn against the security of the Company.s assets. Details of the borrowing of the Company . Secured and Unsecured loans is given in the Section tiled .Financial Performance of the Company. on page 60 of this draft Letter of Offer. (http://www.sebi.gov.in/dp/bata.pdf) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 37 Manpower: Bata have more than 65oo employs. Bata has a supportive manpower policy. Bata received the “Great place to work award” on 9 June 2009. Bata does not indulge in human right abuses. There is no form of forced or compulsory labor Bata. The industry has a labor union and also has a mutual agreement with the union. Bata do not indulge in child labor and also does not let its suppliers to do so. The company does not discriminate anyone on the basis of sex, disability etc for employment as per Bata code of conduct. 4% of Bata workforce are people with disability and measures are taken to take care of their special needs. Measures are also taken to avoid any kind of bribery and extortion. TECNOLOGY: They use “dynamic spring prods” that act as cushion for your feet. They use “in- built-air circulation technology” that allows your feet to breath and ensure that you stay fresh am to pm. Use technology “built-in massage paints” , inspired by Chinese reflexology. In it shoe has flexi sole with arch grip system. (http://www.scribd.com/doc/15233456/bata-marketingproject) The company has entered into an agreement with Bata Ltd of Toronto (Canada) for the supply of technical know-how and services such as footwear technology and design, brand development, product development, retailing and information system for a period of ten years from January 1, 2001. (http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/DetailedReport.aspx?Type=COMP-HIS&SSKICode=BATA) Distribution Channels: Bata India markets its products through three distinct channels. • Company operated retail outlets The Company operates its own retail network of over 1,100 retail stores spread across the country. These outlets are serviced through six distribution centres spread out geographically and each responsible for a particular region The process flow begins with the transportation of the finished products from the Company’s manufacturing units and contract manufacturers. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 38 plants to the distribution centres through the services of third party carrying and forwarding agents. The distribution centres in turn transport these products to the Company operated retail outlets based on specific demand requirements. These retail outlets are manned by the Company.s employees and exclusively market the Company.s footwear brands. As part of its strategy to provide complete footwear solutions to customers, the retail outlets also market accessories like shoes laces, socks, shoe polish. In certain outlets, the Company also provides cosmetic services like pedicures, etc. Out of the 1,100 retail stores, the Company has designated 84 stores as factory outlets which are used to sell merchandise at marked down prices. These factory outlets are used primarily by the Company to sell surplus or non-moving products and factory seconds stocks. Institutional sales as well as supplies to the civil and defence agencies are also taken care of through the Company.s distribution network. The Company has designated specific senior managers to oversee the marketing to this segment of buyers. The requirements are directly supplied from the Company.s distribution centres. • Dealer Network The Company also uses the dealer network of the footwear industry to market its products. Through this channel, the Company supplies its products to non-exclusive wholesale distributors who in turn distribute the Company.s products to independent dealers across the country. The dealers covered under this channel are non-exclusive Bata dealers and hence sell footwear and related products of other companies also. • Market Extension Programme The Company is undertaking steps to generate volume business in semi-urban markets and markets which are un-represented and under-represented footwear markets, pursuant to its Market Extension Programme, through authorised Bata dealerships. Under this programme, the Company appoints authorised dealers, subject to certain selection criteria who run outlets which exclusively market the Company.s products and adhere to rules and regulations of the Company. As on date, there are 470 such outlets in the country. The dealer outlets are not manned by Bata employees but are manned by the employees of the private dealer. (http://www.sebi.gov.in/dp/bata.pdf) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 39 Award Won: 1.) The company bagged the Retailer of the year award for the year in footwear category as a part of the Reid and Taylor Award for Retail Excellence which was presented during the Indian Retail Summit 2006. 2.) They received the country`s most coveted Retail Award at the 4 th Images Retail Award (IRA) 2007 3.) Bata was honored with most admired brand of the year 2006-2007 in footwear category. 4.) They have been rated as one of the Top 10 super brand in India and Awarded Super Brand award on April 12,2007. 5.) In February 21, 2008 , they have been given AMITY corporate Excellence Award 2008. This award has been given for Bata`s excellent performance and retail growth during 2007. ( http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/DetailedReport.aspx?Type=COMP-HIS&SSKICode=BATA) Expansion Plan and Future Plan: Bata India, among the oldest organized retailers of the country, in a shift of retail strategy is now focusing on opening large format stores. “Bata India has opened over 150 new large format stores since 2006 and will continue to open 60 new stores every year Bata India to focus on large format stores across tier II & III cities. (http://www.indiaretailbiz.com/blog/2009/03/16/bata-to-focus-on-international-style-large-format-store) Footwear major Bata India Limited has informed that it has sold-off its ‘Hawai’ brand to Brazilian company 'Alpragatas' for Rs 3.90 crore. The reason behind selling off ‘Hawai”the popular brand was stated as its cheaper duplication in the unorganized sector. (http://www.stockwatch.in/bata-india-sell-its-%E2%80%98hawai%E2%80%99-brand-brazilian-firm-rs-390crore-2882) Add new machines to produce sophisticated new designs and comfortable shoes. (http://content.icicidirect.com/Research/DirectorsReport.asp?icicicode=BATIND) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 40 Governmental Approvals And Licensing Arrangements In Last Decade: The Company has the following approvals from the Government authorities as required to carry on the present business. However, certain approvals have expired in respect of which, the Company has applied or is yet to apply for renewals, as indicated corresponding to the relevant licenses. Licences/Permission/Approvals in respect of factory located at Sipcot, Batashatak, Hosur, Tamilnadu. 1. Industrial Licence issued by the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India vide letter dated July 27, 2000 bearing number CLR- 4412000 for the purpose of establishing a new industrial undertaking for the manufacture of leather footwear located at Plot No.73 & 74, SIPCOT, Industrial Complex Phase . I, District Hosur (Dharampuri) in the State of Tamil Nadu. The date of expiry of this industrial license is July 27, 2002, and the Company had to commence commercial production by that date. This license was issued subsequent to the Hosur factory.s conversion from an Export-oriented unit to a domestic producer, and the Company continued with commercial production in the aforesaid period. Thus, renewal application in respect of the same is not applicable. 2. Registration Certificate issued under the Central Excise Rules, 1944 by the Registering Authority dated November 29, 2001 for the purpose to cure, produce, manufacture, carry on wholesale trade/business/broker or commissioner agent or otherwise deal in excisable good, act as a user of excisable goods for special industrial purposes. This registration certificate is valid until factory carries on the activity for which it is issued or until surrendered. 3. Authorisation and consent issued by Tamil Nadu Pollution Control Board dated September 12, 2003 bearing number 8179A for the purpose of operating the industrial plant in an Air Pollution Control Area and to continue discharge of emission from the stacks under Section 21 of the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981. This authorisation/consent is valid until March 31, 2005. 4. Renewal of consent order issued by District Environmental Engineer, Tamil Nadu Pollution Control Board bearing number 11325 A for the purpose of discharge of sewage under Section 25 of the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974. This consent is valid until March 31, 2005. 5. Factory Running Licence issued by Block Development Officer under the provisions of the Tamil Nadu Panchayat Rules bearing number 1543 for the purpose of running the industry for manufacture of leather footwear. This licence is valid until March 31, 2005. 6. Factory Licence issued by Deputy Chief Inspector of Factories bearing number 29290 for the purpose of using premises at Sipcot Industrial Complex, Hosur as a factory. This licence is valid until December 31, 2005. (http://www.sebi.gov.in/dp/bata.pdf) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 41 Manufacturing process: (Used in Faridabad plant), Bata use batch production system. Although it only manufacture canvas shoes but with in that it has various size variants. With in the batch production system, assembly line process is followed. The plant has 2 assembly line working simultaneously, one for the stitching of shoes upper and other is a semi-automated conveyor belt for assembly of the shoes, at the end of which we get the shoe. Simultaneously, there are other process like the production of adhesive cement and rubber latex, shoe binding etc are done simultaneously at different workstations. The plant in all has 6 conveyor belt and 6 stitching line but presently the management is operating only 3 of them, in view of the low demand for their products in year. One conveyor belt requires 35 people to work and 6 people are required on the stitching conveyor. The factory employs 450 people. One set of conveyors (i.e both stitching and assembly included) produces about 1800-1900 pairs of shoes in one day. The gross monthly production of the plant average around 5 lack pairs. (http://www.scribd.com/doc/21040194/production-and-operations-management-at-Bata) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 42 Process flow chart Raw Material Stock compou u chemic out Threa Binding Make Sole Pull Cement advresive Folding Rubber Latex Cutting Make Binding Stamping Stitching Assemble Vulcanizing Controlling Canvas Shoes Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 43 Boxe EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT The External Analysis contains or examines opportunities and threats that exist in the company. Opportunities and threats are independent factors of the firm. If we understand our Opportunities properly it refer to add favorable conditions in the firm that could produce rewards for the organization .Threats refer to conditions or barriers that may prevent the firms from reaching its objectives. The following area analyses are used to look at all external factors affecting a company: Competitors:The footwear manufacturing industry globally and in India, is highly fragmented, with a large number of small and medium sized manufacturers having a local presence in China and India. Their principal competitors in their manufacturing operations are: Country Competitor India India India India India India Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 44 PERCEPTUAL MAPPING PRICE HIGH QUALITY LOW HIGH LOW In comparison to its competitors, Bata is a reasonably priced brand with reasonable product quality. With respect to its international competitors, it is the most affordable as can be seen in the above illustration. All the competitors have better quality with higher prices. woodland has the highest price and quality in comparison to all the competitors of Bata. Whereas, relative to its Indian competitors, it is the highest priced but also offers the highest product quality. In case Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 45 of Indian competitors, Relaxo and Lakhani is placed just a little below Benetton for its price and quality, and Sparks is the lowest priced with lowest quality with respect to the Indian competitors of Bata. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 46 Pest Analysis This is imperative that an organization considers its environment before beginning the marketing process. In fact, environmental analysis should be continuous and feed all aspects of planning. The organization's marketing environment is made up of: 1. The internal environment e.g. staff (or internal customers), office technology, wages and finance, etc. 2. The micro-environment e.g. our external customers, agents and distributors, suppliers, our competitors, etc. 3. The macro-environment e.g. Political (and legal) forces, Economic forces, Sociocultural forces, and Technological forces. These are known as PEST factors. Political Factors The political arena has a huge influence upon the regulation of businesses, and the spending power of consumers and other businesses. You must consider issues such as: 1. How stable is the political environment? 2. Will government policy influence laws that regulate or tax your business? 3. What is the government's position on marketing ethics? Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 47 4. What is the government's policy on the economy? 5. Does the government have a view on culture and religion? Economic Factors Marketers need to consider the state of a trading economy in the short and long-terms. This is especially true when planning for international marketing. You need to look at: 1. Interest rates. 2. The level of inflation Employment level per capita. 3. Long-term prospects for the economy Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita, and so on. As we all are aware of the last FY in the globe, so there were many companies who suffer from the market condition. Bata desperate and long overdue search to make a style statement in the Indian shoe market for (formals shoe wear). Exchange 52 Week High 52 Week Low BSE 208 76 NSE 209.40 75 The last report by the company is showing the dynamic condition of the market and it shows the way it climbs up and get down. Bata at BSE on Dec 7, 2009 Current: 191.40Rs; Volume: 30,363; Change (%):+1.74. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 48 Sociocultural Factors The social and cultural influences on business vary from country to country. It is very important that such factors are considered. Factors include: 1. What is the dominant religion? 2. What are attitudes to foreign products and services? 3. Does language impact upon the diffusion of products onto markets? 4. How much time do consumers have for leisure? 5. What are the roles of men and women within society? 6. How long are the population living? Are the older generations wealthy? 7. Do the population have a strong/weak opinion on green issues? Bata India has a clearly defined policy for Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). As part of the company’s CSR initiative, the manufacturing units of shoes Divisions have acquired the certifications ‘ISO 9001: 2000 Quality Management System Standards’ and ‘ISO 14001:2000 Environment System standard’ emphasizing the efforts to be an ecologically responsible organization. The company’s diverse CSR initiatives include: Children’s education Enabling the disabled Women’s empowerment Environment management programmes Miscellaneous community initiatives Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 49 Technological Factors Technology is vital for competitive advantage, and is a major driver of globalization. Consider the following points: 1. Does technology allow for products and services to be made more cheaply and to a better standard of quality? 2. How is distribution changed by new technologies e.g. books via the Internet, flight tickets, auctions, etc? 3. Does technology offer companies a new way to communicate with consumers e.g. banners, Customer Relationship Management (CRM), etc? Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 50 FINANCIAL CONDITION OF BATA Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 51 Graphs and Charts Analysis of Bata Reports The following graphs made by referencing the Balance Sheet, Profit & Loss Account of Bata, which is attach in the annexure of the report. The following graphs show the year-wise growth of different category Total Income 1200 1012.85 934.06 1000 823.96 Figure in crores 800 600 400 200 0 2008 years 2007 2006 The total income of Bata in 2006 is 823.96 cr. which is less than from 2007 by 9.17% and income of 2007 which is 934.06 cr. is less than income of 2008 by 6.57% and income of 2008 is 1012.85 which is the highest. Hence, 2008>2007>2006 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 52 Tax Paid 11.1 12 9.03 Figure In Crore 10 8 6 3.75 4 2 0 2008 2007 2006 year Bata tax paid graph shows that in year 2006 Bata paid tax which is 9.03 cr. which is 44% more than year 2007 and tax paid in year 2007 is 3.75 cr. which is 61.25% less than year 2008 and 44% less than in year 2006, and highest tax paid is 11.1 cr. in year 2008. Hence, 2008>2006>2007 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 53 Figure in Crore Expenditure on the salary of employees 184 182 180 178 176 174 172 170 168 181.47 183.21 173.22 2008 2007 2006 year Bata expenses on the salary of employees is 183.21 in 2006 which is more than 2007 by 0.94%, and expenses in 2007 is 181.47 which is more than year 2008 by 4.49% and expenses. Hence, 2008<2007<2006 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 54 Profit Margin 70 60.74 Figure in Crore 60 47.44 50 40.15 40 30 20 10 0 2008 2007 2006 year Bata profit margin in year 2006 is 40.15 cr. which is less than in year 2007 by 10.41%, profit margin in year 2007 is 47.44 cr. is less than from 2008 by 19% and maximum profit margin is in year 2008 which is 60.74 cr. Hence, 2008>2007>2006 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 55 Total Assets 400 350 335.78 303.18 300 Figure in Crore 272.52 250 200 150 100 50 0 2008 2007 2006 year Bata total assets in year 2006 is 272.52 cr. which is less than 2007 by 7.67%, total assets in year 2007 is 303.18 cr. which is less than 2008 by 8.14% and total assets in 2008 is maximum which is 335.78 cr. Hence, 2008>2007>2006 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 56 Competitor analysis of Bata By using the Balance sheet and Profit and Loss Account of Bata, Lakhani and Liberty which is attach in annexure. Total Income 1200 1012.85 Figure in Crore 1000 800 600 400 230.98 152.36 200 0 Bata Lakhai Liberty year Bata has maximum total income rather than Lakhani and liberty and after Bata, liberty has highest total income and then Lakhani’s total income which is 152.36 cr. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 57 Profit 70 60.74 60 Figures in Crores 50 40 30 20 8.42 10 3.5 0 Bata Lakhani Liberty year . Bata has maximum profit. Bata record 60.74 cr profit and lakhani has 8.42 cr which is .more than liberty Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 58 Horizontal Analysis of Balance Sheet (Bata) PARTICULARS (Current year) 2008 (Dec ) (Amt in Crores) (Base year) 2007 (Dec) (Amt in Crores) 291.15 ABSOLUTE CHANGE % CHANGE 251.38 39.77 15.82 64.26 64.26 0 0.0 Reserves and Surplus 226.89 187.12 39.77 21.25 Secured loans Unsecured loans Total Debt Total Liabilities 35.91 8.72 45.07 6.73 -9.16 1.99 -20.32 29.57 44.63 335.78 51.80 303.18 -7.17 32.6 -13.84 10.72 349.33 324.88 24.45 7.53 Less: Depreciation/ Amortisation Net Block 232.31 220.96 11.35 5.13 117.02 103.92 13.1 12.60 Capital Work in Progress 0.86 0.31 0.55 177.41 SOURCE OF FUNDS Total Share holder's Funds Share Capital APPLICATION OF FUNDS Gross Block Bata India Pvt. Ltd. COMMENTS There is no change in the amount as compared to previous year Due to the increase in firm's Reserves and Surplus firm will be able to run its business in uncertain conditions There is an increase in company's fixed assets. Therefore, outflow of cash is taking place. It is according to the total amount of Fixed Assets they own. As there is an increase in Net Block but the % is low than Gross Block as there will be more depreciation due to increased value There is an increase in capital work in progress because of purchase of Fixed Assets so they would be under Page 59 construction Investments CURRENT ASSETS , LOAN & ADVANCES Inventories Sundry Debtors Cash & Bank Balance Loan and Advances LESS: CURRENT LIAB. & PROV. Current Liabilities Provisions Net Current Assets Miscellaneous Eepenses not w/0 Total Assets Contingnet Liabilities Bata India Pvt. Ltd. 17.25 17.25 0 0 292.23 25.89 303.74 22.86 -11.51 3.03 -3.78 13.25 26.75 32.72 -5.97 -18.24 96.75 53.23 43.52 81.75 194.36 198.4 -4.04 -2.03 54.26 193 33.65 180.50 20.61 12.5 61.24 6.92 7.65 1.2 6.45 537.5 335.78 45.28 303.18 76.52 32.60 -31.24 10.75 -40.82 Page 60 Horizontal Analysis of Profit & Loss Account (Bata) PARTICULARS (Current year) 2008 (Dec ) (Amt in Crores) (Base year) 2007 (Dec) (Amt in Crores) 1012.33 11.2 10.68 INCOME Sales Turnover Other Income Stock Adjustment Total Income EXPENDITURE Raw Material Excise Duty Power & Fuel Cost Other Manufacturing Expenses Employs Cost Selling and Administration Expenses Miscellaneous Expenses Less: Preoperative Expenditure Capitalized Profit before interest, depreciation & tax Interest & Financial Charges Profit Before Tax Depreciation Profit Before Tax Bata India Pvt. Ltd. ABSOLUTE CHANGE % CHANGE 890.79 14 29.27 121.54 -2.80 -18.59 13.64 -20 -63.51 1012.85 934.06 78.79 8.43 455.33 22.86 28.22 437.63 23.58 25.74 17.7 -0.72 2.48 4.04 -3.05 9.63 29.22 29.74 -0.52 -1.74 173.22 184.71 181.47 141.73 -8.25 42.98 -4.54 30.32 16.45 16.41 0.04 0.24 0 0 0 0 102.08 77.76 24.32 31.27 11.24 10.56 0.68 6.43 90.84 67.2 23.64 35.17 19 71.84 16.01 51.19 2.99 20.65 0.18 40.34 COMMENTS Page 61 Depreciation Profit Before Tax Tax Profit After Tax Adjustment Below Net Profit P&L Bal. brought forward Appropriation P&L Bal. Carried down Equity Dividend Preference Dividend Corporate Dividend Tax Equity Dividend (%) Earning Per Share Bata India Pvt. Ltd. 19 71.84 16.01 51.19 2.99 20.65 18.67 40.33 11.1 60.74 3.75 47.44 7.35 13.3 196 28.03 0 0 0 0 69 40.15 28.85 71.85 24.87 104.87 18.59 69 6.28 35.87 33.78 51.99 16.07 12.85 3.22 25.05 0 0 0 0 2.73 2.18 0.55 25.22 25 20 5 25 9.03 7.04 1.99 28.66 Page 62 ANALYSIS OF ECONOMIC ENVIRONMENT Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 63 Factors That Will Affect The Organization Demand The demand of products at Bata can be affected by various factors: -Product: Shoes( Men’s and Women) 1. Price Of The Commodity: If the prices of the shoes at Bata increases (decreases), then the demand for the shoes will decrease(increase). This happens because the price of the shoes and its demand are inversely related. It implies that lower the price of the commodity larger is the quantity demanded and higher the price lesser quantity is purchased. For example:- A closed dress category shoe of Bata Style no: 801-6210 New price: Rs 979 Old price: Rs 1300 (http://www.bata.in/catdetail.php?&catItem=11&selId=&action=&techId=&brandId=&size=&price=&art_number= &a_page=3&tipslist=) In above example Bata reduce the price of shoe by 25%, it will lead to the increase in demand of that shoe. Because the discount of particular item attract the customer. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 64 2. Price Of Related Goods: a) complementary Good- A change in the price of polish and socks will affect the demand of the shoes. If the prices of the polish and socks will decrease(increase) then the demand for the shoes will increase(decrease). Complementary goods are those goods which are complementary to one another in the sense that they are jointly used or consumed together like car and petrol ,leather and polish and gas and gas stoves. For instance if the price of leather shoes increases then the demand for polish will decrease and vise a versa. This happens because the price of the complementary good ( socks and polish0 is inversely related to the demand of the shoes. b) Competitive/ Substitute Goods- A change in the price of shoes at Action and lakhani will affect the demand of the dresses at Bata. An increase (decrease) in the price of shoes at Action and Lakhani will increase(decrease) the demand of dresses at Bata. Substitute goods are those goods which satisfy the same type of demand and hence can be used in place of one another. This happens because the price of the substitute good (Shoes at Bata) is directly related to the demand of the dresses at Bata. For instance if the price of lakhani leather shoes increases consumers will prefer buying bata leather shoes as they will be cheaper therefore the demand for bata leather shoes will increase. 3. Income Of The Consumer: a) Normal Goods- They are those goods the demand for which increases with increase in income of the consumers and decreases with fall in income. For instance a consumer may increase his demand for clothes ,shoes, accessories etc. if his income increases. Normally an increase(decrease) in the real income of the consumer will increase (decrease) the demand of shoes. This happens because the income of the consumer is directly related to the demand of the shoes. b) Inferior Goods- They are those goods the demand for which falls with increase in income of the consumer. For instance if a consumers income increase he would prefer buying shoes from woodland than bata. In case of the inferior goods, such as shoes of very low cost an increase (decrease) in the real income of the consumer will decrease(increase) the demand of such shoes. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 65 See the following chart to understand the consumer expenditure capacity. Per Capita Income The Per Capita Income in India was Rs 19040. The Per Capita Income in India was Rs 20982. The Per Capita Income in India was Rs 23241. The Per Capita Income in India was Rs 37490. Year 2002-2003 2003-2004 2004-2005 2008-2009 ( http://www.tradechakra.com/indian-economy/per-capita-income.html) The above chart show that per capita income in India increase year by year. Since 2002-2003 to 2008-2009 there is a increasment of 50.78%, which is a very good growth in its self. It show the buying power of consumer also increase. Hence the demand of shoes, normal goods and inferior goods also increase. 4. Tastes And Preferences: These depend on social customs habits of people fashion general lifestyle of people. For instance if converse shoes are in fashion then consumers will prefer buying that to any other shoe. If there is a favorable(unfavorable) change in the tastes and preferences of the consumer for the particular type of shoes it will lead to an increase(decrease) in the demand of the shoes at Bata. This happens because the taste and preferences of the consumer is directly related to the demand of the shoes. The taste and preference of the consumer can be affected by many factors: a) Advertisements. b) Consumer Satisfaction c.) Fashion Trend etc. For example:- According to 2001 census male literacy rate is 86.9% and female literacy rate is 72.9%. Hence more males able to get the job, Bata is a company known for its closed dress wear or formals. So they manufacture more men’s shoes compare to female’s shoes. (http://www.censusindia.gov.in/census_data_2001/India_atglance/literates/aspx.) 5. Other Factors: a) Size Of Population- Market demand for a commodity depends on the size of the population. Larger the population larger the demand as they will be more consumers . Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 66 size of population in a way means the number of consumer. Hence, as the size of the population increase(decrease) the demand for the shoes will also increase(decrease). For example:year 1981 1991 2001 Population 68,33,29,097 84,63,02,688 1.02,87,37,436 (http://www.censusindia.gov.in/census_Data_2001/India_atglance/variation.aspx) According to the census of last three decade done by government of India, there is a increasment in population. From 1981 to 1991; there is increasment of 20% in population and from 1991 to 2001; there is a increasment of 18% in population . Hence the population increases the demad of the shoes also increases because shoes are the part of daily need of an human being. b) Composition Of Populationcomposition of population relates to specifically either or male population from the total population. Composition of population affects demand because the types of goods demanded by different people are different. For example if in a country the composition of working men is large then the demand for leather shoes will be more. Hence, if there will be an increase(decrease) in the female population it will lead to an increase(decrease) in the demand for the shoes. This happens because composition of the population and the demand for the shoes are directly related. c) Distribution Of Income--If the distribution of income in a country is unequal there will be more demand for luxury goods and if the distribution of income is evenly distributed then the demand for luxury goods will be less and more demand for necessities. The way the income is distributed in the economy also affects the demand of the product, which in our case is the shoes at Bata. If the income will be distributed equally (unequally) amongst all the sections of the socity then demand for the shoes will increase(decrease). Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 67 Factors That Will Affect The Organization Supply The supply of the product at Bata can be affected by various factors: Product: Shoes(Men’s and Women’s) 1. Price Of The Commodity: If the price of the shoes at Bata increases(decrease), then the supply for the shoes will also increase(decrease). This happens because the price of the shoes and its supply are directly related. Given other things larger quantity will be supplied at a higher price and smaller quantity at a lower price. This will be because higher the price given per unit cost of production higher is the per unit profit .The higher profit would motivate the suppliers to supply more in order to earn more profits. 2. Prices Of Factor Inputs: This relates to the cost of production. An increase (decrease) in one input of production will cause a consequent increase (decrease) in the cost of production of that commodity which will lead to a decrease (increase) in the supply of that product. For eg:- Raw material, Transportation cost, etc. So, an increase (decrease) in the price of raw material like leather and fabric will cause a consequent increase (decrease) in the cost of production of the dresses which will lead to a decrease (increase) in the supply of dresses. This happens because the price of factor input is inversely related to the supply of the product. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 68 3. Price Of Related Goods: a) Complementary Goods- A change in the price of polish and socks will affect the supply of the shoes. If the prices of the polish and socks will decrease (increase) there will be a decrease (increase) in the supply of the shoes too because this will lead to a decrease (increase) in the profit margins of the supplier. This happens because the price of the complementary goods ( socks and polish) is directly related to the supply of the shoes. b) Competitive/ Substitute Goods- A change in the price of the shoes at “Action” and “Libarty” will affect the supply of the shoes at Bata. An increase (decrease) in the prices of shoes at “Action” and “Liberty” will decrease (increase) the supply of the shoes at “Bata” because this change in the price will tempt the suppliers to divert their available recourse to the production of the substitute good i.e the shoes at “Action” and “Liberty”. This happens because the price of the substitute goods ( shoes at Action) is inversely related to the supply of the dresses at Bata. 4. State Of Technology: The supply of a commodity depends upon the state of technology. Over-time if there is an increase (decrease) in the infrastructure and the technology i.e the technology has become more advanced it result in low-production cost ( high production cost) and hence will increase (decrease) the supply of the shoes. For eg:-Better Machinery, up-to-date infrastructure, etc. This happens because the state of technology is directly related to the supply of the shoes. For instance new machines are invented to the bata factory then the supply would increase and there is a chance of the profits increasing. 5. Expected Future Price: If the future price of the shoes at Bata are going to decrease (increase) it will increase ( decrease) the current supply of the shoes at Bata because in the future the profit margins of the supplier will decrease (increase). For instance if the suppliers of bata know that the demand Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 69 for leather shoes will increase next year then they will produce less this year in order to earn more profits next year so the supply of leather shoes will increase next year. This happens because the expected future price is inversely related to the supply of the shoes. 6. Number OF Firms Producing That Product: If the number of firms producing increase (decrease) then Bata will get more (less) competition from other firm and hence the supply of Bata will increase (decrease). This happens because the number of the firms products a product is directly related to the supply of shoes at Bata. For instance if bata is the only producer of leather shoes then they will restrict their supply in order to earn more profits and if they have competition then there supply would be more. 7. Goals OF The Firm: The supply of a commodity depends upon the goals of firms producing that commodity. So, the supply of shoes at Bata depends upon the goals of Bata. Mostly all firms sell their products such that they attain maximum profits. But at times some products are supplied not to attain more profit but because they are a source of status and prestige for the company in the society. For example if the goal of Bata is to earn maximum profits they would supply more in order to earn more profits. 8. Taxation Policy: Imposition of heavy (less) taxes on a commodity decreases (increases) its supply. So, if the government increases (decreases) the taxes on the production of shoes it will lead to a decrease (increase) in the supply of the dresses. Also, tax concession would help in stimulating the supply of shoes at Bata. Foe eg:- a) Tax deduction for workers in the industry. b) Exemption from consumption tax ( sales tax or V.A.T), etc This happens because the taxes and the supply of the dresses are inversely related to each other. If Heavy taxes are imposed on bata then there supply would be less but if the government spends money on supplying bata machines etc then there supply would increase. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 70 Recent Policy Initiatives: Specific Industry Associations viz. Council for Leather Exports, Central Leather Research Institute ,Footwear Design and Development Institute declares various schemes on an ongoing basis to promote specific activities viz. Export promotion, Training Design Inputs , etc. The States Governments of Himanchal Pradesh, Uttranchal , Jammu and Kashmir and Assam are promoting manufacturing by offering Tax holiday for a period of ten years on full Excise duty and Income Tax and a subsidy in sales Tax, Land/ Building and Plant/ Machinery. 9. Tastes And Preferences: If there is a favorable (unfavorable) change in the tastes and preference of the consumer for the shoes it will lead to an increase (decrease) in the supply of the shoes at Bata. This happens because the taste and preference of the consumer is directly related to the supply of the shoes. The taste and preference of the consumer can be affected by many factors: a) Advertisements. b) Consumer satisfaction, etc. 10. Natural Factors: a) Size of Populationsize of population in a way means the number of consumer. Hence, as the size of the population increases (decreases) the supply for the shoes will also increase (decrease) This happens because the size of the population and the supply for the shoes are directly related. b) Composition Of PopulationComposition of population relates to specifically either female or male population from the total population. Hence, if there will be an increase (decrease) in the female population it will lead to an increase (decrease) in the supply for the shoes. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 71 This happens because composition of the population and supply for the shoes are directly related. 11. Availability Of Labour : there are times when labour has conflicts with the management, within themselves, they might go on strike or even leave jobs for some reason, which effects work and hence reduces productivity. Due to such reasons of scarcity of labour, supply gets affected. 12.Transpotation Cost: As the transportation costs are to be beared by the supplier, his costs increase with the increase in transportation costs. Hence, the supplier is not willing to supply at increased costs. This is another factor that leads to decreased supply of Bata shoes. 13. Demand: As the demand for Bata shoes decreases or increases, the supply also decreases or increases respectively. When the consumer demands increase, the supplier needs to provide more products to fulfill the demand. When the consumer does not need a particular product, then there is no use of the supply as it will not sell. Hence, demand of Bata shoes is one of the major reasons affecting its supply. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 72 Recent Trends in the Industry Role of Technology:Technology has expanded operations of the apparel and footwear industries to a more global scale. It has also provided closer working relationships between retailers and manufacturers. Technology has improved efficiency and has reduced the amount of manual labor. Computer Technology:-Rapid improvements in computer technology have helped to shorten the new product development phase from years to practically months, especially in the fashion/style/high- performance areas. apparel marketers who are linked with retailers through quick-response programs and other technology go a long way toward making themselves indispensable to their customers. EDI Technology collects information (such as the bar code that is attached to each item sold, the price of the product(s) sold, and details such as color and size) from the retailers’ checkout counter and relays the information back to the manufacturer. The data is then used for manufacturers to automatically reorder the stock of merchandise to replenish their shelves in a timely manner. EDI also makes distribution and shipping information more efficient. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 73 Implication of Fiscal Policy Fiscal policy, also know as Keynesian economics proposed by British economist john Maynard Keynes. The theory basically states that government can influence macroeconomic productivity levels by increasing or decreasing tax levels and public spending. There are two main instruments of fiscal policy:1) Government spending 2) Taxation The changes in both have impact on following variables in the economy: Aggregate demand Level of economic activity To counter the negative fallout of global slowdown of Indian economy, government responded by providing three focused fiscal stimulus packages in form of tax relief and increased expenditure on public projects along with RBI taking a number of monetary easing and liquidity enhancing measures. GOVERNMENT SPENDINGS: INFRASTRUCTURE: According to government budget 2009-2010, infrastructural development will be given a big boost. IIFCL (INFRASTRUCTURE FINANCE CO.) will evolve a takeout financing scheme in consultation with banks to facilitate incremental lending to the infrastructure sector. A new scheme, Rajiv Awas Yojna will be introduced with the aim to make the country slum free in next 5 years. Footwear industry plans to raise fund from domestic and overseas economic sectors in form of joint venture, association, establishment of shareholding companies, issuance of shares and bonds in stock market. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 74 Footwear industrial parks will be built, encompassing good infrastructure conditions and environmental treatment facilities, in a bid to draw and facilitate investment in footwear industry. TYPICAL PROJECT PROFILES OF FOOTWEAR INDUSTRY: PROJECT COST (in millions) COST (in Euros) Leather Shoes 50.00 0.898 Polymer shoes 152.00 2.732 Leather shoe uppers 35.00 1.438 Finished Leather Shoes 420.00 7.551 EMPLOYMENT: Although India’s share in global economy is low, however being a labourintensive industry, its contribution to employment is significant. In recent study, it was highlighted that the total employment in footwear sector would amount to 2.5 million ( 30%of which are women). Footwear industry provides employment to uneducated population-40% of employment is represented by unskilled workers doing table work operation in assembly line. The footwear industry has potential to provide employment across all sections of the economy. The estimated employment potential of footwear industry is to provide 3 lakh jobs in next 3 years. INTREST PAYMENTS: Due to fiscal consolidation in last four years, interest payments as percentage of total revenue receipts (net) of central government has shown a significant improvement. According to the budget estimation 2009-10 it is estimated as 36.7% from 36.7% in 2008-09. The 2% interest subvention scheme provided by Indian government for certain labour intensive sectors, has been extended from september30, 2009 to march31,2010 which includes footwear sector of the industry. This will facilitate reduced interest rate @BPLR minus 4.5% for leather footwear sector on pre-shipment and post-shipment rupee export credit. TRANSFER OF PAYMENTS: are the form of government spending .It is defined as redistribution of income in market system. Eg:-for welfare(financial aid),social security and government subsidies for certain business(firms).The boost the footwear industry the Indian federal government has earmarked a Rs.4.5 billion Grant to be made available to the industry Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 75 over a span of 5years but that’s not without any string. The fund availability is conditional upon the sector’s attracting an annual investment of 2.2 trillion. SUBSIDIES: Government plan to spend Rs.1,11,276 crore (us $23.03 bn.) on providing subsidies in budget 2009-2010. There are various subsidies provided by Indian government to boost footwear industry in India. The lowering of value addition norms under DFRC scheme from 33% to 25%, would benefit the exporters of leather goods including leather footwear. Funding is available to enable tanners to modernise manufacturing facilities in footwear sector. Machinery also benefits from duty free/concessional import regulation. There is concessional rate of interest on export credits to mitigate the effects of rupee appreciation which has led to tightening of credit. On the smaller scale, there is a scheme known as “support to rural artisans scheme, marketing and technical support for traditional and ethnic Indian footwear products such a mojpuri, jooti and kohlapuri is being provided. Government also provided support in terms of improved infrastructure .Duty free import of raw material (namely raw skins, hides etc...) EXPORT GROWTH: Exports can become engine of growth for the entire economy as it develops. India is largest producer footwear producer after China. It comprises 42.44% export of footwear. In this view to boost exports Indian government has taken various measures: Adjustment assistance scheme to provide enhanced exports credit and guarantee corporation (ECGC) cover at 95% to badly hit sectors extended upto march 2010. Interest subvention of 2% on preshipment credit for 7 employment oriented export sectors extended beyond the current deadline of september30, 2009 to march31, 2010. To facilitate flow of credit at reasonable rate, Rs.4000crore provided as special fund out of rural infrastructure development fund to small industry development of India, This will incentivise banks and state finance corporation to lend to micro and small enterprises by refinancing 50% of incremental lending to MSE’s during current financial year. PUBLIC DEBT: Due to the slowdown in the economy in few last years government raised its borrowings. Footwear industry shall raise funds from domestic and overseas economic sectors in form of shares and bonds in the stock market. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 76 FDI (FORIEGN DIRECT INVESTMENT): Liberalizing FDI was another important part of India’s reform, driven by belief that this would increase total volume of investment in Indian economy. A list of investment projects will be prepared in bid to call for investors at home and abroad encouraging the involvement of domestic foreign economic sector in investing in footwear industry. EXCISE DUTIES: According to the government policies in India, excise duties and many other miscellaneous taxes are not levied on the apparel products, but they are categorized as restricted imports. Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) Scheme: The EPCG scheme is provided for those export companies and traders who inform the Government of India about the type and value of capital goods being imported by them and the exports they expect to produce using those imports. The Government of India provides a license to the exporters allowing them to import capital goods either duty free or at very low rates of duty, on the basis of the export commitment made at the time of import of goods. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 77 IMPLICATION OF MONENTARY POLICY The Indian economy has been developing at a considerable growth rate since independence, but it has never been able to achieve the targets set up. In the first quarter of the year 2009-10, the Indian economy was growing at a rate of 6.1%, which is higher than that of 5.8% in the fourth quarter of the financial year 2008-09, but lower than 7.8% in the first quarter of the year 2008-09. The year-on-year (y-o-y) deceleration in growth was broad-based covering all the three major sectors, viz., agriculture, industry and services. Real GDP Growth (%) Financial Year Sector 2007-08 2008-09 Quarterly Growth Rates (y-o-y) 2008-09 Q1 2009-10 Q4 Q1 Agriculture 4.9 1.6 3.0 2.7 2.4 Industry 7.4 2.6 5.1 (-) 0.5 4.2 Services 10.8 9.4 10.0 8.4 7.7 9.0 6.7 7.8 5.8 6.1 Overall GDP Source: Central Statistical Organisation (CSO). In the Indian economy, clear signs of revival from recession and growth of the industrial sector have been seen in the recent months. The index of industrial production (IIP) showed an increase by approximately 5.8% during April-August 2009 as compared with a growth of 4.8% in the corresponding period of the previous year. While the basic, intermediate and consumer durable goods sectors (that includes the apparel industry) witnessed higher growth, the performance of the capital goods and consumer non-durable sectors was relatively modest. The core infrastructure sector experienced a growth of 4.8% during April-August 2009, as compared to 3.3% in the corresponding period of the previous year. The leading indicators of industrial production, both quantitative and qualitative, also point to revival of industrial activity in the months ahead. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 78 The results of the Industrial Outlook Survey done by the Reserve Bank of India that tracks the business expectations for the current quarter and the business outlook for the following quarter, conducted in July-August 2009 showed a turnaround in the business sentiment. The assessment for the second quarter of 2009-10 showed continuing upturn with a 7.8% increase in the Business Expectations Index (BEI) over the previous quarter. Also considerable improvement was shown in key indicators such as production, order books and capacity utilisation. The financing conditions have also become better. Inflation that is measured by year-on-year variations in the wholesale price index (WPI), remained negative during June-August 2009 due to the base effect, but returned to a positive figure in September 2009. Inflation based on the CPI for industrial workers (IW) and urban nonmanual employees (UNME) has also witnessed a one-time step-up reflecting significant upward revision in imputed prices of rent-free houses emanating from the Sixth Pay Commission Award. The Central Government has already completed net market borrowing of Rs. 3,19,911 crore (as much as 80.4 per cent of the budget estimate) through dated securities during 200910 (up to October 26, 2009). Contribution of Footwear industry in National Nncome: Footwear industry has major contribution in country’s national income. The sector is pride of India’s leather industry and ranks second in the world, next to China. Global trade in leather footwear is US$30 Billion and non leather is US$ 18 Billion. The footwear industry has made a strong contribution to Indian economy. India’s share in global trade remains low, however being labour-intensive industry, It has a strong contribution in employment. The sector provide 2.5million employment(of which 30% women).By reduction in unemployment the growth of economy increases and hence per capita income increases which lead to higher standard of living. In total national income of the economy increases FDI(FORIEGN DIRECT INVESTMENT): play an important role in increasing national income. As India is developing economy it has an attractive profit making opportunities for the foreign investors. Because of its production strength it attracts more international players and also duty free or concessional imports and reduction in excise duty help in increasing FDI. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 79 Pre- and Post-Shipment Financing: Pre-shipment financing is provided by the Reserve Bank of India to Indian exporters through commercial banks for purchasing raw material, packaging material and other required material by presenting a confirmed order or letter of credit. Also RBI provides post-shipment financing through commercial banks at preferential rates to Indian exporters presenting export documents. These programs make a financial contribution to Indian firms to the extent of the difference between benchmark short-term interest rates and the preferential interest rates. BANK CREDIT: Non-food credit by scheduled commercial banks decreased considerably, with the growth rate (y-o-y) falling to 11.2% as on October 9, 2009 from 29.4% in the corresponding period of the previous year. On a financial year basis (up to October 9, 2009) too, the growth in scheduled commercial banks’ non-food credit at 4.3% is drastically lower than the growth of 10.5% in the corresponding period of the previous year. The various factors that have contributed to the slowdown in non-food bank credit are as follows: 1. Overall credit demand from the manufacturing sector slowed down reflecting a decrease in commodity prices and drawdown of inventories. 2. Corporates were able to access non-bank domestic sources of funds and external financing – which had almost dried up during the crisis – at lower costs. 3. Oil marketing companies reduced their borrowings from the banking sector as oil prices moderated. 4. A significant amount of bank finance has gone to the corporate sector through banks’ investment in units of mutual funds. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 80 5. Banks have also reined in credit to the retail sector due to the perceived increased risk on account of the general slowdown. This credit cutback was more pronounced in the case of foreign banks and private banks. Interest Rates: In response to the crisis, the Reserve Bank has effected a substantial reduction in policy rates beginning October 2008: the repo rate by 425 basis points and the reverse repo rate by 275 basis points. The CRR was also reduced by 400 basis points of NDTL of banks. Monetary Easing by the Reserve Bank since October 2008 Item Early October Reduction October 2009 (basis 2008 points) Repo Rate 9.00 4.75 425 Reverse Repo Rate 6.00 3.25 275 Cash Reserve Ratio (% of NDTL) 9.00 5.00 400 Taking cues from the reduction in the Reserve Bank’s policy rates and easy liquidity conditions, all public sector banks and most private sector banks have reduced their deposit and lending rates. http://rbi.org.in/scripts/NotificationUser.aspx?Id=5326&Mode=0 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 81 SWOT ANALYSIS OF BATA STRENGTHS Targeting all income segments. Footwear for the entire family. Nationwide retail network. Brand Image. Good quality at low or reasonable price. Shoes available are in varied quality and price. The brand ‘Bata’ is closely identified with footwear by consumers. An extensive retail network of owned and franchisee stores enables the Company to reach out to consumers across the length and breadth of the country. The Company’s own tanneries located in Batanagar and Mokamehghat ensures uninterrupted supply of raw materials. Six manufacturing locations enable the Company to schedule production to meet demand for a large number and varied categories of footwear. Being a part of the Bata Shoe Organization gives the Company access to new designs, brands and production technologies. WEAKNESSES No continuity of leadership. No proper planning regarding Advertisement No variety in Fashionable shoes. Lack of variety in sports shoes. Lack of futuristic approach. Lack of variety in sports shoes. The Company has a large labour force resulting in high employee costs The Company has been in existence for more than seven decades and faces a challenge in switchingto new production technologies OPPORTUNITIES Great market channels. Exchanging or expending in offer rural market. Innovative Products New mediums for advertisements Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 82 Acquired, Partnership with small players Entering new segments of Markets Rising potential in the domestic market Growing fashion consciousness globally The Indian footwear retail market is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 20% for the period spanning from 2008 to 2011, and also expected to comprise of 60% of the total leather exports by 2011.(india-reports,2008) Footwear retailing in India remain focused on men’s shoes, there exists plethora opportunities in the exclusive ladies and kids footwear segments with no organized retailing chain having a national presence in either of these categories.(indiareports,2008) For leather industry, duty free entitlements of import trimmings, embellishments and footwear components is increased to 3% of FOB value of exports, for leather sector, duty free import increased to 5% of FOB value of exports and the machinery and equipment for effluent treatment plants are to exempt of custom duty.(Indianindustry, 2009) India is a very large market and offers good demand potential for footwear which is an item of mass consumption. Low per-capita footwear consumption in India provides opportunity to the Company which has large production capacity spread over six locations The Company sees potential in leveraging the .Bata. brand for marketing other merchandise consumer products. (http://www.indianindustry.com/trade-information/foreign-tradepolicyhighlights.html) THREATS Too many players will dilute the market & the profit margin goes down because of Low priced Chinese or local products. The Company faces competition from the unorganized market which is able to sell footwear at low cost due to lower overheads and manufacturing costs. Opening of the Indian market to imports has resulted in the Company facing competition from cheap imports. Due to growing inflation, there has been an increase in the cost of raw materials and transportation The decreasing fashion cycle is one of the major threats as new collections need to be brought in very frequent Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 83 Recommendations The recommendation for the company to maintain the consistency, good will, brand image, uniqueness and cost effective methods for production are as follows:- In Asia luxury spending was expected to grow between 6 and 7 percent in the year starting July, compared to a decline of up to 15 percent in the United States and a drop of up to 5 percent in Europe. Bata retailers need to educate potential customers about their wares, especially during this crisis, when they're more reluctant to buy on the spur of the moment. Bata sales teams should appeal to customers' emotions, online or at the store, to succeed. Bata should adopt recycling of textiles. It is cost effective process and company input cost will be reduced. It should inculcate “Lean Sigma” adopting the latest technology of waste reduction and improving efficiency level. This is cost cutting and time saving adoption. Strengthening the pre production processes as apart of over all supply chain to enhance the operational efficiency. Many industries are adopting the strategy of going green highlighting their initiatives and future plans towards a cleaner environment. Though the initial investment in setting up a green factory is about 30%-40% higher, the investment pays back in couple of years through various savings achieved as a part of this initiatives. Bata should also adopt this as it will enhance its brand image. Bata should also show some advertisement on T.V, newspaper so that more people aware about it. Indian market is dominated by men’s footwear i.e. about 58% so there huge untapped sector of women and children footwear in India thus Bata should try tapping these sector. Worldwide epidemiological studies shows that the employment in the shoe industry is associated with high risk of cancer so Burberry should keep records of his workers health.(joem,2009). (http://www.ijoem.com/temp/IndianJOccupEnvironMed917-5037142_135931.pdf) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 84 Competitor Profile Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 85 Lakhani Company Profile: Business Type: Footwear Main Market: India Chairman and M.D: Mr. Parmeshwar Payal Lakhani Market Value: 46 cr Company Address: B-106, Sector-2, Noida, Uttar Pradesh . Tel. no: 91-0120-4015810 Fax: Site URL: Employees: 2702 Share Price: company only listed on BSE Current price - 34.80 Rs Share Holding Pattern: Promoter – 66.20% Non-Promoter-25.32% Public Holding- 7.42% M.F & Other- 1.06% Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 86 1.06% 7.42% Promoter 25.32% Non-promoter Public Holding M.F & Other 66.20% History: Originally incorporated as Lakbros Shoe Company Pvt Ltd in Dec.'81, Lakhani was converted into a deemed public limited company on 14 Jul.'89 and its name was changed to Lakhani India in Sep.'94. Promoted by K C Lakhani, P D Lakhani and J C Arora, LIL belongs to the Lakhani group. It manufactures and markets shoes and chappals. In Jun.'95, LIL came out with a public issue of 38.4 lac equity shares at a premium of Rs 110, aggregating Rs 46.08 cr, to partfinance the expansion-cum-modernisation of its non-leather shoe unit from 30 lac to 61.65 lac pairs pa at Faridabad, Haryana, and its diversification into the manufacture of 3 lac pairs of leather shoes. The other companies in the Lakhani group are Lakhani Rubber Udyog, Lakhani Footwear, Lakhani Shoe Company, Lakhani Shoes, etc. The group is the largest manufacturer of beach slippers and the second-largest manufacturer of canvas shoes in India. It exports goods to UK, Sweden, Italy, France, Germany, Ireland and Western Australia. The manufacturing units of LIL are at Bhiwadi( Rajasthan); Noida(Uttar pradesh) ; Faridabad(Haryana); and Indore (Madhya Pradesh). The Lakhani group is one of the largest suppliers of rubber components to automobile manufacturers like Maruti, TELCO, Escorts, Sona Steering, DCM Daewoo. (http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/DetailedReport.aspx?Type=COMP-HIS&SSKICode=LAKHANI) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 87 Human Recourse Policy: Employer relations continued to remain cordial during the training and development of employees continue to be an area of importance. The devotion and commitment of our employees has enabled the company fulfill its target and deadlines in time. The total number of employes in the company as on 31st march,2008 was 2702. (http://www.indiainfoline.com/market/company) Product Profile: PRODUCT RANGE- RetailPrice: Rs. 1150 Retail Price: Rs. 1090 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 88 LIBERTY Company Profile: Business Type: Footwear Main Market: India CEO: Mr. Adesh Gupta Market Cap: 180 cr Company Address: A-40, II flore, Phase-II, . . Naraina Industrial Area, Near Batra Banquat Hall, N.D-110025 Tel. no: 91-11-41410592 Employees: 1332 Share Price: Company listed on BSE as well as on NSE Current price- BSE- 106 Rs ( As per the closing on 22/1/2010) NSE-106.90 Rs (As per the closing on 22/1/2010) 52 week High- 113.45Rs 52 week low- 35Rs Share Holding Pattern: Promoters-61.94% Public-32.58% Non-Promoter Corporate Holding-5.16% Mutual Fund-0.32% Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 89 0.32% 5.16% Promoters 32.58% Public Non-Promoter 61.94% M.F History: Liberty Shoes (LSL), incorporated in Sep.'86 as a public limited company, engaged in the business of manufacturing and selling leather & non-leather shoes, leather shoe uppers and leather garments. In 1991, LSL set up a joint venture to manufacture shoes, and in Dec 1995 it was discontinued. facility for 6 lac pairs of leather shoes and 9.6 lac pairs of non-leather shoes. The company has commenced commercial production of non-leather shoes in Dec.'93. LSL has well established network of retail stores, and markets it's products under the well known brand 'Liberty'. LSL serves all major segments of the footwear market, it's product range consists of Gliders and Coolers range of footwears under Casual Footwear segment, GeoSport in Sports shoes. Liberty Shoes Ltd. is the only Indian company that is among the top 5 manufacturers of leather footwear in the world with a turnover exceeding U.S. $100 million. With 50 years of excellence, today Liberty produces footwear for the entire family and is a trusted name across the world. In the domestic market it is one of the most admired footwear brands and holds the largest market share for leather footwear. (http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/DetailedReport.aspx?Type=COMP-HIS&SSKICode=LIBERTYS) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 90 Human Resource Policy: Company has been consisted in following the prudent polocirespect of H.R and industrial relations by duly complain the all the applicable industrial law and code of conduct as laid for the protection of the workers. The company believes in harmonious and cordial relationship with its work force and as such, always committed to provide generous support to its workforce. Proway for a better work environment and the attainment of large bro objectives in efficient and specialized manner, As on 31 st march,2009,the company employ strength is 1332. (http://www.indiainfoline.com/market/company) Award Won: "A1+"(meaning highest safety) rating for its commercial paper in 1999-2000 by ICRA. Product Profile: Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Brand : Fortune Article : 2031-21 Color : BLACK MRP : Rs.1099 Brand : Senorita Article : 2020-104 Size : 36-41 Color : COPPER MRP : Rs.699 Page 91 Minimum Wages Chart By The State Governments MINIMUM WAGES IN DELHI (FEB 1,2009) S.N O 1 2 scheduled employment Ready-made garments Textile , including handloom , thread, manufacturing labels, dyeing & printing UNSKILLED Basic minim um wages V.D. A. 141.00 141.00 CATEGORY OF WORKERS SEMI- SKILLED SKILLED Total minim um wages Basic minim um wages V.D. A. Total minimum wages 10.0 Total Basic V.D. minim minim A. um um wages wages (RS PER DAY) 151.00 148.00 10.0 158.00 158.00 10.0 168.00 10.0 151.00 158.00 158.00 10.0 168.00 148.00 10.0 MINIMUM WAGES IN HARYANA S.N O CATEGORY OF WORKERS Scheduled employment Unskilled Semiskilled (A) Semi-skilled (B) Skilled (A) Skilled (B) highly skilled (RS PER DAY) 1 2 COTTON & GINNING & PRESSING INDUSTRY. READY MADE GARMENTS Bata India Pvt. Ltd. 147.69 152.6 157.69 165.69 167.69 172.69 147.69 152.6 157.69 165.69 167.69 172.69 Page 92 MINIMUM WAGES IN MADYA PRADESH S.N O 1 2 scheduled employment COTTON , GINNING & PRESSING HANDLOOM INDUSTRY UNSKILLED Basic V.D. minim A. um wages CATEGORY OF WORKERS SEMI- SKILLED Total Basic V.D. Total minim minim A. minim um um um wages wages wages (RS PER DAY) SKILLED Basic V.D.A. minim um wages Total minimum wages 47.38 54.1 101.49 43.15 54.1 97.26 39.00 54.11 93.11 47.38 54.1 101.49 43.15 54.1 97.26 39.00 54.11 93.11 MINIMUM WAGES IN UTTAR PRADESH S.N O scheduled employment 1 HANDLOOM INDUSTRY 2 WEAVING OF SILK SAREE & ZARI WORK 3 READYMADE GARMENTS Bata India Pvt. Ltd. CATEGORY OF WORKERS UNSKILLED SEMI- SKILLED Basic V.D.A. Total Basic V.D.A Total minimum minimu minimu . minimu wages m m m wages wages wages (RS PER DAY) SKILLED Basic V.D.A minimu . m wages 129.73 29.69 159.42 137.50 33.85 171.35 171.35 37.54 201.66 129.73 29.69 159.42 137.50 33.85 171.35 171.35 37.54 201.66 129.73 29.69 159.42 137.50 33.85 171.35 171.35 37.54 201.66 Total minimu m wages Page 93 Recent News Related To Footwear Industry A step for footwear November 6, 2006 Indian Shoe Federation (ISF) has taken a step to create a direct link between manufacturers of components and footwear manufacturers. They had organized a footwear components and accessories exhibition at Rajah Muthiah Hall, Egmore, Chennai. A total of 72 footwear components manufacturers from all over India participated in this exhibition. According to the Council of Leather Export, the footwear industry aims to reach a target of $4 billion, within next five years. There is a huge prospect of employment in the footwear component industry. This will help in enhancing the export opportunity for the footwear industry. (http://www.fibre2fashion.com/news/fashion-news/newsdetails.aspx?news_id=25742) Agra footwear industry facing new challenges April 16, 2009 (India) Arrival of footwear manufacturing units in the infrastructure-rich towns like Noida and Chandigarh as well as slowdown in export orders due to unavailability of credit facilities to the major footwear importers, are the new challenges for Agra footwear industry. This makes footwear units in the town to run at less than 50 percent of their production capacity. Agra footwear industry is already facing a 30 percent decline in export orders due to financial meltdown. First quarter of 2009 has experienced a sharp decline in export orders. Though only a few number of footwear units have come up in Noida and Chandigarh, the business of small exporters of Agra is getting affected. So, there is a need to develop a supporting infrastructure for Agra footwear industry. Big exporters of the town are looking for a substantial share in the economic package announced by the Centre for the leather industry, totaling to Rs. 1,300 crore. According to the experts, though Kanpur is known for utility footwear exports and Chennai has the largest share in men’s footwear, the top position in exports of men’s & women’s fashion footwear rests with Agra. Growth rate of Agra footwear industry was 27 percent for the past few years but this drop down Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 94 in business would make it difficult to maintain that growth rate this year. According to experts, situation will change in the near future, as China faces import restrictions from several countries and cost of footwear manufacturing in the Eastern European Countries is going high. Experts hope that in coming years, bulk buyers will turn to India and country’s share in the world footwear trade will rise, at least to 7 percent from 4 percent. (http://www.fibre2fashion.com/news/daily-textile-industriesnews/newsdetails.aspx?news_id=71426) 26th IFC to help Indian footwear industry September 3, 2007 The countdown for the 26th International Footwear Conference (IFC) has begun and this is the first time when India has been given the honour to organize this prestigious event. The three day conference will be organized from August 30 till September 1, 2007 at Chennai and will be inaugurated by Mr G K Pillai, Commerce Secretary, Government of India. The IFC will witness participation from 9 major footwear manufacturing countries from Asia and large number of footwear importing countries like US, Spain, Italy etc. It will also have country presentations from Brazil, South Korea and India who will address the relevant topics including design inputs while designing comfort footwear, latest technology in sports footwear and emerging trends in retailing in India. IFC being an important event for the global footwear industry is a major initiative by Council for Leather Exports (CLE) to take a step ahead in boosting India’s footwear production in the world market. The event would also provide interactive forum to the participants to discuss various issues like current trends in footwear production, trade and consumption. The conference would be of immense help to Indian industry - in terms of understanding the changes happening in other footwear producing countries. Speaking on the occasion, Mr Mukhtarul Amin, Chairman, CLE said, “The conference would be a gateway for Indian footwear manufacturers to know trade andtechnology practices worldwide especially in Far East nations. This event will also gather opinions from experts and trade analysts on issues concerning leather sector.” With the world trade figure soaring high the global leather and leather products imports has almost doubled to US$ 104 billion in 2005 as against US$ 56 billion in 1992 and out of which footwear alone constitutes 67% of the total leather trade. Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 95 Figures also show that US being the largest importer has a highest share of 27%, the leather exporters from India are creating space for Indian leather in US markets and strengthening our trade relations. With the current trends of footwear manufacturing are declining in Europe and depression in Brazilian industry, the Indian Leather Industry sees an immense potential and growth prospects with new emerging markets in Eastern Europe and Latin America and to cater the same stress is on building capacities, manpower and technology advancement is the main stress. (http://www.fibre2fashion.com/news/fashion-news/newsdetails.aspx?news_id=40328&page=2) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 96 . Bata India Pvt. Ltd. ANEXTURE Page 97 Product Profile of Bata Men`s Wear Variety of products such as: Closed dress Closed casual Sandals Chappals Sports wear Closed dress range starts from 699 to 2699 Closed casual range starts from 399 to 1999 Sandals range starts from 399 to 1899 Chappals range starts from 169-1799 Sports shoes range start from 699-1799 Closed dress Style no. 851-6094 Style no. 854-6003 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. INR 699.00 INR 1699.00 Page 98 Style no. 854-4099 Style no. 854-6074 INR 2299.00 INR 2699.00 (http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=11) Closed casual Style no. 829-6095 Style no. 891-1240 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. INR 399.00 INR 1899.00 Page 99 Style no. 834-4006 INR 1999.00 . (http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=21) Sandals Style no. 861-4053 INR 399.00 Style no. 861-6226 INR 699.00 Style no. 801-4167 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. INR 1499.00 Page 100 Style no. 864-6439 INR 1899.00 (http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=31) Chappals Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Style no. 872-6007 INR 169.00 Style no. 871-4095 INR 249.00 Style no. 874-4036 INR 818.00 Page 101 Style no. 874-6930 INR 1799.00 (http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=41) Sports wear Style no. 861-9224 Style no. 839-8134 Style no. 808-3456 Style no. 808-5499 INR 699.00 INR 749.00 INR 1099.00 INR 1799.00 (http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=5) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 102 Women’s wear: Chappals Closed Sandals Chappals Style no. 571-6121 Style no. 561-5995 INR 499.00 Style no. 673-4061 INR 1199.00 Style no. 674-6051 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. INR 139.00 INR 1249.00 Page 103 Closed Style no. 552-7007 INR 299.00 \ Style no. 581-1840 INR 599.00 Style no. 581-2796 INR 1199.00 Style no. 581-2121 INR 1299.00 ( http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=22) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 104 Sandals Style no. 662-1050 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. INR 299.00 Style no. 661-6088 INR 499.00 Style no. 581-2403 INR 999.00 Page 105 BALANCE SHEET OF BATA Particulars Dec-2008 Dec-2007 Dec-2006 Dec-2005 Dec-2004 64.26 51.42 Sources of funds: Share capital+ 64.26 64.26 64.26 Reserves & Surplus+ 226.89 187.12 147.73 197.21 132.74 Total shareholder Funds 291.15 251.38 211.99 262.47 184.16 Secured loans+ 35.91 45.07 56.1 59.69 112.16 Unsecured loans+ 8.72 6.73 4.43 21.94 12.19 Total Debt 44.63 51.8 60.53 81.63 124.35 Total liabilities 335.78 303.18 272.52 343.1 308.51 Application of funds: Gross block+ 349.33 324.88 306.85 363.43 358.1 Less: Accum. Depreciation 232.31 220.96 227.44 231.98 220.04 Net block 117.02 103.92 79.41 131.45 138.06 Capital work in progress 0.86 0.31 0.84 0.47 1.59 Investments+ 17.25 17.25 17.24 4.98 4.85 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 106 Particulars Dec-2008 Dec-2007 Dec-2006 Dec-2005 Dec-2004 Current Assets, loans & advances Inventories+ 292.23 303.74 276.36 278.76 262.16 Sundry Debtors+ 25.89 22.86 21.61 27.94 48.04 Cash and Bank Balance 26.75 32.72 22.34 20.36 14.65 Loans & advances+ 96.75 53.23 42.33 61.24 61.85 194.36 198.4 173.55 163.87 214.2 Provisions+ 54.26 33.65 14.06 36.31 34.6 Net current Assets 193 180.5 175.03 1 88.12 137.9 Miscellaneous Expenses not w/o + 7.65 1.2 18.08 26.11 Total Assets 335.78 303.18 272.52 343.1 Contingent Liabilites+ 45.28 76.52 119.69 112.5 Less: Current liab. & Prov. Current Liabilities+ 0 308.51 108.35 (http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/CommonGrid.aspx?Type=BA&SSKICode=BATA) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 107 PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT OF BATA Particulars Dec-2008 Dec-2007 Dec-2006 Dec-2005 Dec-2004 Sales Turnover+ 1012.33 890.79 794.82 734.24 724.56 Other Income+ 11.2 14 27.58 18.89 4.77 Stock Adjustments+ 10.68 29.27 1.56 18.78 -12.95 Total Income 1012.85 934.06 823.96 771.91 716.38 Raw Materials+ 455.33 437.63 366.34 349.1 378.37 Excise Duty 22.86 23.58 24.45 27.49 30.51 Power & fuel cost 28.22 25.74 24.03 22.65 22.49 Other Manufacturi Expenses+ 29.22 29.74 34.27 34.38 15.98 Employee Cost+ 173.22 181.47 183.21 178.8 183.68 Selling and Administration Expenses+ 184.71 141.73 110.2 100.69 109.64 16.45 16.41 8.09 20.97 14.92 INCOME: EXPENDITURE: Miscellaneous Expenses+ Less: Preoperative Expenditure capitalized 0 0 Profit before Interest, Depreciation & Tax 102.08 77.76 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. 0 73.37 0 37.83 0 -39.2 Page 108 Particulars Dec-2008 Dec-2007 Dec-2006 Dec-2005 Dec-2004 Interest & Financias charges+ 11.24 10.56 10.57 12.24 11.94 Profit Before Depreciation & tax 90.84 67.2 62.8 25.59 -51.14 Depreciation 19 16.01 13.62 12 12.33 Profit Before Tax 71.84 51.19 49.18 13.59 -63.47 Tax 11.1 3.75 9.03 1.1 -0.72 Profit After Tax 60.74 47.44 40.15 12.49 -62.75 Adjustment below Net Profit+ 0 0 0 0 0 -50.26 -62.75 0 P & L Balance brought forward 69 40.15 Appropriations+ 24.87 18.59 -50.26 0 0 P & L Bal. carried down 104.87 69 40.15 -50.26 62.75 Equity Dividend 16.07 12.85 0 0 0 Preference Dividend 0 0 0 0 Corporate Dividend Tax 2.73 2.18 0 0 0 Equity Dividend (%) 25 20 0 0 0 Earning Per Share (Rs) 9.03 7.04 6.25 1.94 0 . Bata India Pvt. Ltd. 0 (http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/CommonGrid.aspx?Type=PL&SSKICode=BATA) Page 109 Quarterly Result OF Bata Particulars September-2009 June-2009 March-2009 Sales Turnover 260.68 309 233.6 Other Income 1.33 2.03 1.31 Total Income 262.02 311.03 234.91 Total Expenditure 236.64 276.21 212.06 Operating Profit 25.37 34.82 22.85 Interest 0.8 1.07 1.29 Gross Profit 24.57 33.75 21.56 Depreciation 6.38 6.57 5.33 Tax 5.04 8.83 5.9 Reported Profit After Tax 13.15 18.35 10.33 Extra-Ordinary Item 0 0 0 Adjusted Profit After 13.15 Extra- 0rdinary Item 18.35 10.33 EPS (units curr.) 2.05 2.86 1.61 Book value (unit curr.) 0 0 0 Dividend (%) 0 0 0 Equity 64.26 64.26 64.26 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 110 Particulars September-2009 June-2009 March-2009 PBIDTM (%) 9.73224 11.2686 9.78168 PBDTM (%) 9.42535 10.9223 9.22945 PATM (%) 5.0445 5.93851 4.42209 (http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/CommonGrid.aspx?Type=QU&SSKICode=BATA) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 111 MUTUAL FUND ACTIVITIES OF BATA Dated . E Gross Purchase E Gross Sale Nov-2009 6459.19 6053.50 Oct-2009 14915.80 Sep-2009 E Net D Gross Purchase Purchase D Gross Sale D Net Purchase 405.60 21850.50 14008.50 7842.20 20225 -5309.10 72412.30 39127.60 33284.80 14105.50 16346.40 -2241 38589.60 30950.40 7639.60 Aug-2009 16764.70 16106.70 657.60 35460.90 27028.60 8432.30 Jul-2009 21002.60 19848 1154.50 51842.90 23677.70 28165.60 May-2009 17208.50 15606.10 1602.60 25237.20 15248.40 9988.90 Apr-2009 11144.60 11126.30 18 44342.60 18390 25952.90 Mar-2009 10580.70 9731.10 849.90 36771.30 18699.50 18072.10 Feb-2009 4684.80 6522.20 -1837.10 26113.60 9617.50 16496.30 Jan-2009 9329.50 10729.10 -1399.80 30688 12466.90 2008 165942.60 157947.80 7994 375593.50 250582.70 125011.70 2007 2295188.8 2439399.2 144207.4 2535182.1 1846545.4 688645.25 2006 252320.9 225232.49 27088.48 200310.87 142793.51 57517.90 2005 69403.32 56430.06 10173.70 95552.40 60410.06 35161.34 2004 42043.39 43309.58 -1366.14 54889.76 43321.63 1155.01 2003 28096.03 27744.62 274.16 58352.08 38382.54 19959.94 2002 15254.33 18248.17 -2711.52 44879.39 31341.79 13752.38 2001 12792.96 17931.20 -5144.50 28851.62 19647.57 9207.40 18221 (http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/CommonGrid.aspx?Type=MFAct) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 112 F I Activities OF BATA Dates . purchase (Rs Crore) Sale (Rs Crore) Investment (Rs Crore) Sep-2009 65197 46766.40 18430.50 Aug-2009 49306 45191.10 4115.10 Jul-2009 67176.60 56338.90 10837.40 Jun-2009 67277.20 63447 3830 May-2009 74776.40 54659.10 20117.20 Apr-2009 39653.30 33145.10 6508.20 Mar-2009 32377.40 31847.30 530.30 Feb-2009 21341.10 23777.90 -2436.60 Nov-2009 21966.90 19088.40 2878.40 Oct-2009 65441.30 57873.90 7568.10 Jan-2009 27874 32119.10 -4245.30 2008 717377.90 769977.40 -52599.60 2007 1309179.60 1204358.13 99838.70 2006 684534.80 666426.80 18802.50 2005 243570.20 201527.20 42607.63 2004 185664.20 145666.70 47980.80 2003 93988.80 63989.80 30590.40 2002 46479.10 42849.80 3629.60 (http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/CommonGrid.aspx?Type=FIAct) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 113 Profit and Loss Account of lakhani Name March(2008) 2007 2006 2005 2004 Sales Turnover 152.07 44.24 99.23 162.76 119.97 Other Income 0.14 0.25 0.71 1.23 0.32 Stock Adjustment 5.35 9.24 1.2 -2.08 -3.34 Total Income 157.56 53.73 101.14 161.91 116.95 Raw Material+ 93.51 30.09 48.16 81.65 62.6 Excise Duty 5.2 3.37 11.25 16.14 10.35 Power & Fuel cost 9.03 3.41 6.5 9.23 6.38 Other Manuf. Expenses+ 9.92 3.74 9.27 14.3 10.05 Employee Cost+ 17.73 6.6 10.04 15.42 11.03 Sellind & Administ Expenses 8.74 3.64 5.9 10.72 7.06 Miscellan. Expense 0.19 0.02 0.05 0.12 0.91 Less: Preoperative Expenditure 0 0 0 0 0 Profit before Interest 13.23 ,Tax and Pepreciation 2.86 9.97 14.33 8.57 Interest & Financial Charges+ 0.64 2.2 3.9 0.79 2.22 7.77 10.43 7.7 Income: Expenditure: Profit before Depreciation Tax Bata India Pvt. Ltd. 4.81 8.42 Page 114 Name March(2008) 2007 2006 2005 2004 Pepreciation 3.83 1.81 4.81 5.3 3.77 Profit before Tax 4.59 0.41 2.96 5.13 4.01 Tax 3.4 -4.98 1.16 2.03 1.57 Profit After Tax 1.19 5.39 1.8 3.1 2.44 Adjustment below Net Profit+ 0 0 0 0 0 P&L Bal. Brought forward 9.25 3.86 2.11 1.56 1.55 Appropriations 0 0 0.65 2.55 2.43 P&L Bal. Carried down 10.44 9.25 3.86 2.11 1.56 Equity Dividend 0 0 0 2.02 2.02 Preference Divd. 0 0 0 0 0 Corporate Divd. Tax 0 0 0 0.28 0.26 Equity Divid (%) 0 0 0 12 13 Earning per share 0.88 4.01 1.78 1.68 1.62 Book Value 46.42 45.59 41.58 40.25 39.91 Extraordinary items+ 0 0 0 0 0 Debt Equity ratio 1.05 0.51 0.53 0.49 0.49 Long term DebtEquity ratio 0.65 0.09 0.02 0.06 0.09 Current Ratio 1.48 1.24 1.15 1.21 1.31 Key Ratio: Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 115 Name March(2008) 2007 2006 2005 2004 Fixed Assets 2.47 0.74 1.62 1.74 1.75 Inventory 2.53 0.85 2.47 2.61 2.34 Debtors 4.21 2.2 7.78 9.03 10.28 1.64 2.35 2.32 6.08 Turnover Ratio: Intrest cover rate 1.95 PBIDTM(%) 8.7 6.46 10.05 8.8 7.14 PBITM(%) 6.18 2.37 5.2 5.55 4 PBDTM(%) 5.54 5.02 7.83 6.41 6.48 CPM(%) 3.3 16.27 6.66 5.16 5.18 APATM(%) 0.78 12.18 1.81 1.9 2.03 ROCF(%) 7.41 1.19 6.18 8.99 6.04 RONW(%) 1.92 9.19 4.31 4.6 4.54 (http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/CommonGrid.aspx?Type=PL&SSKICode=LAKHANI) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 116 Balance sheet of Lakhani particulars Total Share Capital Equity Share Capital Share Application Money Preference Share Capital Reserves Revaluation Reserves Networth Secured Loans Unsecured Loans Total Debt Total Liabilities Gross Block Less: Accum. Depreciation Net Block Capital Work in Progress Investments Inventories Sundry Debtors Cash and Bank Balance Total Current Assets Loans and Advances Fixed Deposits Total CA, Loans & Advances Deffered Credit Current Liabilities Provisions Total CL & Provisions Net Current Assets Miscellaneous Expenses Total Assets Contingent Liabilities Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Mar '03 Mar '04 Mar '07 13.74 13.74 0.00 0.00 40.10 0.00 53.84 28.95 0.00 28.95 82.79 65.89 25.31 40.58 0.00 0.04 54.70 10.59 0.63 65.92 4.33 0.00 70.25 0.00 26.64 2.11 28.75 41.50 0.67 82.79 1.40 13.45 13.45 0.00 0.00 40.22 0.00 53.67 23.61 0.00 23.61 77.28 71.09 28.54 42.55 0.00 0.04 47.72 12.75 1.90 62.37 5.93 0.00 68.30 0.00 30.56 3.38 33.94 34.36 0.34 77.29 2.40 13.45 13.45 0.00 0.00 47.87 0.00 61.32 29.16 1.96 31.12 92.44 34.86 11.54 23.32 27.97 0.40 48.69 22.26 0.70 71.65 2.01 0.00 73.66 0.00 32.71 0.17 32.88 40.78 0.00 92.47 0.00 Mar '08 13.45 13.45 0.00 0.00 48.99 0.00 62.44 98.52 0.46 98.98 161.42 88.09 15.36 72.73 0.00 14.80 71.51 49.95 1.29 122.75 4.16 0.00 126.91 0.00 52.26 0.75 53.01 73.90 0.00 161.43 0.00 Page 117 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 118 Profit and Loss Account Of Liberty Name March(2008) 2007 2006 2005 2004 Sales Turnover 247.53 257.89 237.54 221.12 194.84 Other Income 1.4 5.51 1.74 1.12 1.25 Stock Adjustment 1.4 5.51 1.74 1.12 1.25 Total Income -11.79 6.91 20.13 6.5 -0.13 Raw Material+ 237.14 270.39 259.41 228.74 195.96 Excise Duty 116.43 131.96 121.22 96.67 81.79 Power & Fuel cost 6.16 9.6 15.65 16.39 17.31 Other Manuf. Expenses+ 4.39 4.61 4.65 5 4.09 Employee Cost+ 20.55 22.28 20.92 19.92 16.41 Sellind & Administ Expenses 51.4 56.8 52.2 48.8 45.32 Miscellan. Expense 5.19 1.06 1.92 1.15 1.06 Less: Preoperative Expenditure 0 0 0 0 0 Profit before Interest 26.43 ,Depreciation & Tax 36.33 33.03 32.6 24.24 Interest & Financial Charges+ 13.35 8.82 4.74 6.99 Income: Expenditure: Bata India Pvt. Ltd. 12.56 Page 119 Name March(2008) 2007 2006 2005 2004 Profit before ,Tax & Depreciation 13.89 22.98 24.21 27.86 17.25 Depreciation 6.59 6.38 4.63 4 3.71 Profit before Tax 7.28 16.6 19.58 23.86 13.54 Tax -0.24 0.64 2.4 4.94 3.75 Profit After Tax 7.52 15.96 17.18 18.92 19.79 Adjustment below NetProfit+ 0 0 0 P&L Bal. Brought Forward 32.86 22.9 11.72 Appropriations 6 6 P&L Bal. down 34.38 Equity Dividend 0 Preference Divd. 0 -0.1 1.69 1.47 8.89 9.47 22.9 11.72 1.64 0 0 2.53 3.04 0 0 0 0 Corporate Divd. Tax 0 0 0 0.36 Equity Divid (%) 0 0 0 50 60 Earning per share 4.41 9.37 10.08 10.89 18.46 Book Value 71.79 67.38 58.03 47.93 122.66 Extraordinary items+ -0.16 2.61 0.12 -0.05 -0.01 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. 32.86 6 0 0.43 Page 120 Name March(2008) 2007 2006 2005 2004 Debt Equity ratio 0.09 1.16 1.11 0.88 1.07 Long term DebtEquity rate 0.12 0.18 0.13 0.1 0.16 Current Ratio 1.18 1.13 1.17 1.31 1.3 Fixed Assets 1.92 2.18 2.5 3.02 3.06 Inventory 3.45 3.39 3.66 4.67 4.56 Debtors 3.47 3.57 3.94 4.67 4.56 Intrest cover rate 1.58 2.02 3.22 6.03 2.94 PBIDTM(%) 10.68 12.95 13.91 14.74 12.44 PBITM(%) 8.02 10.47 11.96 12.13 10.54 PBDTM(%) 5.6 7.77 10.19 12.6 8.85 CPM(%) 5.7 7.65 9.18 10.37 6.93 APATM(%) 3.04 5.18 7.23 8.56 5.02 ROCF(%) 8.63 11.68 14.93 21.13 16.76 RONW(%) 6.34 12.5 19.03 26.3 10.57 Key Ratio: Turnover Ratio: (http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/CommonGrid.aspx?Type=PL&SSKICode=LIBERTYS) Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 121 37.60 39.90 Balance sheet of Liberty Particular 45.58 Mar'05 Mar '06 Mar '07 Mar '08 5.07 5.07 0.00 0.00 57.13 0.00 62.20 22.11 31.45 53.56 115.76 17.04 17.04 0.00 0.00 64.63 0.00 81.67 48.81 21.45 70.26 151.93 17.04 17.04 0.00 0.00 81.82 0.00 98.86 104.03 22.02 126.05 224.91 17.04 17.04 0.00 0.00 97.78 0.00 114.82 103.32 15.06 118.38 233.20 Application Of Funds 66.50 Gross Block 27.39 Less: Accum. Depreciation 39.11 Net Block 0.24 Capital Work in Progress 4.02 Investments 41.01 Inventories 47.26 Sundry Debtors 1.78 Cash and Bank Balance 90.05 Total Current Assets 23.20 Loans and Advances 0.67 Fixed Deposits Total CA, Loans & Advances 113.92 0.00 Deffered Credit 33.27 Current Liabilities 8.27 Provisions 41.54 Total CL & Provisions 72.38 Net Current Assets 0.00 Miscellaneous Expenses 115.75 Total Assets 17.22 Contingent Liabilities 122.67 Book Value (Rs) 79.70 31.22 48.48 0.92 6.43 53.65 48.34 2.14 104.13 30.01 0.81 134.95 0.00 31.48 7.37 38.85 96.10 0.00 151.93 60.14 47.93 110.55 35.55 75.00 8.14 17.10 76.17 72.09 1.55 149.81 29.72 3.07 182.60 0.00 52.74 5.20 57.94 124.66 0.00 224.90 10.55 58.01 126.06 40.61 85.45 1.55 20.34 76.19 72.41 1.20 149.80 27.50 3.29 180.59 0.00 52.47 2.28 54.75 125.84 0.00 233.18 9.71 67.38 Sources Of Funds Total Share Capital Equity Share Capital Share Application Money Preference Share Capital Reserves Revaluation Reserves Networth Secured Loans Unsecured Loans Total Debt Total Liabilities Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 122 REFERENCES Content Overview of Footwear Industry Company profile History Reference List http://indmin.nic.in http://www.indianshoebazaar.com/ind_india.asp Leather supply http://leather.indiabizclub.com/info/indian_leather_industry_overview Export and Import Over View http://footwearsinfoline.tripod.com/export_import.htm Role Of Government In Shoe Industry http://www.thaindian.com/newsportal/politics/big-boost-for-agras-shoeindustry- if-state-government-helps_100116975.html#ixzz0XAkn7VPx Bata India http://www.bataindia.com Lakhani http://www.lakhaniarmaan.com/ Liberty www.libertyshoes.com/ Bata India http://www.sharekhan.com/Marketcorner/Detailedreport.aspx?type=comp_His &SSKIcode=BATA http://www.bataindia.com/page.php?kon=5_2_1 http://www.bataindia.com/page.php?kon=4_0 Lakhani http://www.sharekhan.com/Marketcorener/DetailedReport.aspx?Type=compHIS&SSKIcode=LAKHANI Liberty http://www.sharekhan.com/Marketcorener/DetailedReport.aspx?Type=compHIS&SSKIcode= LIBERTY Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 123 Products Bata Human Resource Policy Balance Sheet: Women’s wear http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=22 http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=12 Men’s wear http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=41 http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=31 http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=21 http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=11 Kids wear http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=23 http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=33 http://www.bata.in/catlist.php?catItem=43 Bata Mr. S C Kapoor Lakhani http://www.indiainfoline.com/market/company Liberty http://www.indiainfoline.com/market/company Bata http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/CommonGrid.aspx?Type=BA&SSKICode=BATA Liberty http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/CommonGrid.aspx?Type=PL&SSKICode=LIBERTYS Profit and Loss Account : Bata http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/CommonGrid.aspx?Type=PL&SSKICode=BATA Lakhani http://www.sharekhan.com/MarketCorner/CommonGrid.aspx?Type=PL&SSKICode=LAKHANI Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 124 Bata India Pvt. Ltd. Page 125