Nervous System Part 2
advertisement

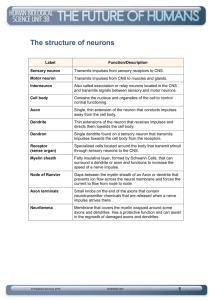
Nervous System Part 2 Synapse • The gap between different neurons is called a synapse. • Definition: The gap between the axon of a previous neuron and the dendrites of the next neuron. • We have established how an impulse can travel down a neuron (electricity). How does the impulse travel between different neurons? How does an impulse travel across a synapse? Chemical, not electric • The way an impulse was passed down a single neuron was electrical (meaning the impulse related to positively and negatively charged atoms). • The way an impulse is transmitted across a synapse is chemical, not electric. Transmission at the Synapse • The axon terminal contains many tiny sacs containing chemicals known as neurotransmitters. • When the impulse reaches the end of an axon (the axon terminal), it causes the axon to release these neurotransmitters into the synapse. Neurotransmitters • These neurotransmitters cause some of the dendrite’s sodium channels to open. • This causes sodium to rush in, making that area of the neuron more positive, causing the nearby voltage-gated-sodiumchannels to open, and the cycle begins. Neurotransmitter Breakdown • After the neurotransmitters stimulate the next dendrite, they must be removed or they will continue to send impulses down the next neuron. • To do this, there are enzymes that destroy the neurotransmitters in the synapse. Multiple Synapses • The nervous system is actually much more complex than that. • Each dendrite can have up to 1000 synapses with different axons. • The nervous system is not a direct path – it is much more twisted and interconnected than a single straight line. 2 Types of Neurotransmitters Excitatory Neurotransmitters• These chemical start impulses in the next neuron. These make the next dendrite more permeable to sodium. These would be sent when you want muscles to contract. Inhibitory Neurotransmitters• These chemical prevent impulses in the next neuron. These make the next dendrite less permeable to sodium. These would be sent when you want muscles to stop contracting. What happens if a dendrite receives contradictory messages? • The dendrite has synapses with multiple axons. • Sometimes, different axons tell a dendrite different things. • When this happens, the cell body (headquarters) takes the average of all of the incoming impulses. If the majority are excitatory, then it will send the impulse down its axon. If the majority are inhibitory then it will not send an impulse down its axon.