Hinduism (1) - payaptruthandservice
advertisement

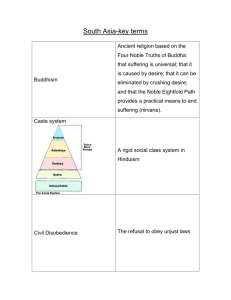
Hinduism IGE101: Truth and Services By: Sukanya Radanachaless 5305020140 Quick facts about Hinduism • The religion of most people in India and Nepal. • It has over 900 million followers around the world. • The oldest living religion • The third largest religion • No single founder • No single scripture http://nemf.org Defining Hindu …………………………………………………………… • The word ‘Hindu’ was from the Sindhu. • ‘Tellingly, Hindus cannot even agree on what to call their religion. One of the most common claims among Hindus in the west is that Hinduism is a way of life rather than a religion’ from the book God Is Not One. • Hinduism is also closely associated with the other Indian religions such as Jainism, Buddhism and Sikhism. Their deities • ‘Hindus worship many gods through many different paths(margas), disciplines(yogas), and philosophies(darshanas). Their deities appear as powerful kings, starving ascetics, brave monkeys, graceful dancers, blue-faced flute players, and impersonal stones.’ • From the book God Is Not One Their deities (con.) • ‘Some Hindus believe that there are many gods but only one is supreme. Still other says there are many gods and all are equal. Some Hindus even say there is no god.’ • From the book God Is Not One The Hindu trinity 1. Brahma • Brahma's job is creation of the world and all creatures. http://simple.wikipedia.org 2. Vishnu • The second god in the Hindu triumvirate. • The preserver and protector of the universe • His role is to return to the http://silkpaintings.wordpress.com earth in troubled times and restore the balance of good and evil. 3. Shiva • The third god in the Hindu triumvirate • His role is to destroy the universe in order to recreate it. • Shiva is therefore seen as the source of both good and evil http://zimbio.com Worship • You must have the image, or icon, which can be worshipped either at home or in the temple. • Mostly an individual action • Family often worships together • At a Hindu temple, different parts of the building have a different spiritual or symbolic meaning. Problem : The nature of reality • Samsara is the problem. • Samsara refers to the cycle of life, death, and rebirth. • Hindus have seen that it is a problem rather than a reward for human. • It is a cycle of impermanent happiness. Philosophical Hinduism • The philosophical Hindus believe that ‘Inside each of us, there is unchanging and eternal soul. And we are that soul. But our souls are trapped in the prisons of our bodies and in the illusions (maya) these bodies are conjuring up. As long as we inhabit flesh and bones, we are destined to suffer. Yet death offers no release either because, after we die, we will be reborn in other bodies and repeat again and again.’ • From the book ‘God Is Not One’ The goal • The goal is not to leave this world and go to heaven but rather to escape from heaven and earth altogether. • This Hindus goal is called moksha which means ‘release’. • It’s not salvation. How to achieve the goal? There are three different disciplines 1. Discipline of action 2. Discipline of wisdom 3. Discipline of devotion Sannyasins : The earliest exemplars • ‘ Philosophical Hinduism also introduced various meditative and yogic techniques designed to awaken liberating insight in practitioners willing to withdraw from the world into lives of celibacy and other austerities. These mystics, known as renouncers(sannyasins), become Hinduism’s earliest exemplars. ’ • From the book ‘ God Is Not One’ Characteristics of a good person in Hinduism ‘ Hinduism now recognizes dharma(duty), artha(power), and kama(sensual pleasure) as a legitimate aims of life.’ From the book ‘ God Is Not One’ 1. Dharma: Living ethically and correct your life 2. Artha: Working hard to achieve the success 3. Kama: Pleasure 4 fundamental questions • What is real ? • The cycle of life, death, and rebirth are things we cannot avoid. • What is the quality of life ? • To have a material success and whatever happiness is possible in this imperfect world. 4 fundamental questions • What is truly good person? • ‘ It affirms that neither priestly sacrifice nor philosophical knowledge is necessary for release from the bondage of samsara. All that is needed is love heartfelt devotion to the god of your choosing.’ • From the book ‘God Is Not One’. 4 fundamental questions • How do you become a good person ? • Achieving moksha • Renouncing worldly things • Having good karma The dimensions of religion • Ritual • Narrative • Material Cites • • • http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/hinduism http://www.religionfacts.com/hinduism/index.htm http://uwacadweb.uwyo.edu/religionet/er/hinduism/hrlif e.htm