Revolutionary Battles PP
advertisement

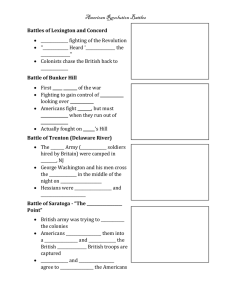
The American Revolution 1775-1783 The Shot Heard Round the World The Combatants • British Advantages – Army of Regulars – Top Navy – 30,000 Hessians – 50,000 American loyalists – Large industrial base – Money and supplies • American Advantages –3,000 miles of ocean –Home Turf (defensive war) –Fighting for independence –Leadership –Possible French assistance –Guerilla tactics American Advantages • Most important element of American victory was their determination to be free. Battles Lexington and Concord “The shot heard round the world” –Unclear start to a revolution –Approves “Olive Branch Petition” Battles Breed’s Hill/ Bunker Hill • British driven from Mass • England ‘wins’ but loses ½ its men • British realize the scope of the revolution Battles Trenton • NJ:Washington attacks during winter with limited success. Defeats Hessians • Battle of Saratoga: –Turning point –French have the confidence to support the Patriots with supplies Washington Crossing the Delaware Valley Forge • Low point for Continental Army. Suffered the winter without food or supplies. 3,000 soldiers die from starvation and disease. Battles Yorktown • Marks last major battle – Cornwallis cornered between land and sea – French-American army surround British “The World Turn’d Upside Down” First Continental Congress • Convened in Phil. in ‘74 –Statement of grievances to King –Preparations for fighting –Boycott –Agreed to meet again in ‘75 Common Sense Thomas Paine • Published Jan.’76 • Sold 100,000 copies in first four months • Called for complete split from Britain and its constitution Declaration of Independence • Written by Jefferson • Formal break with the crown When in the Course of Human Events… Reactions to July 4… Conducting the War: States v. Central government • Despite individual states vying for power, Congress given power to coordinate the war but –State militias –States volunteering money New York City in Flames War and Economy Trade with Britain cut No protection at sea • Diversified by the 1780s –New trading partners –Formation of navy –Some industry forms Imports/Exports Treaty of Paris of 1783 • U.S. bordered by Mississippi, Canada, Atlantic, and Florida • Diplomatic recognized by British • British promised to evacuate Ohio Valley • U.S. promised to pay debts War and Society • Loyalists harassed –Left behind property and estates –Many moved to Canada or Britain • Native-Americans generally opposed the Revolution • Mixed bag for African-Americans Toleration and Slavery • Where it was not used, usually abolished • SC and GA refused to halt slave trade • Separation of Church and State (Statute of Religious Freedom by Thomas Jefferson of VA) Washington Resigns from the Army State Constitutions • Guiding principle: Do the opposite of Britain • Republicanism • CN & RI simply changed their colonial charters • Limited executive branch • Most had bicameral legislatures • Property required for voting Articles of Confederation (’81-’89) • Federal Gov’t consisted of a unicameral Congress (9 out of 13 votes to pass a law) • 13 out of 13 states needed to amend • Representatives frequently absent • Could not tax or raise armies • Northwest Ordinance a success • Shays’ Rebellion shows weaknesses