File
advertisement

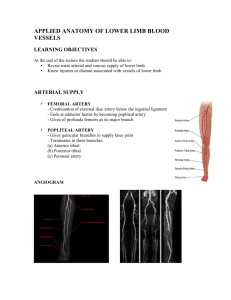
Blood Flow of Upper and Lower Extremities Arteries and Veins of Upper and Lower Extremities Arteries of Upper Extremities • Subclavian Artery • Axillary Artery • Brachial Artery • Radial Artery • Ulnar Artery • Deep Palmar Arch • Superficial Palmar Arch • Digital Arteries Arteries of the Upper Extremities • Subclavian artery supplies blood to each upper limb. After passes over lateral boarder of the first rib, it is renamed the: • Axillary Artery – extends branches to the shoulder and thoracic region. • Has many branches (supreme thoracic artery, thoracoacromial artery, lateral thoracic artery, humeral circumflex arteries and subscapular artery). • When passes the inferior boarder of the teres major muscle it is renamed the: • Brachial Artery – Travels alongside humerus. • Supplies blood to most brachial (arm) muscles. • Divides into Ulnar and Radial Artery Arteries of the Upper Extremities • Radial and Ulnar Arteries • Both supply the forearm and wrist before they form two arterial arches in the palm: superficial palmar arch and deep palmar arch. • Superficial Palmar Arch – formed primarily from the ulnar artery • Deep Palmar Arch – formed primarily from the radial artery • Digital arteries emerge from the arches and supply the fingers Veins of Upper Extremities • Superficial Venous Drainage: • • • • Dorsal Venous Arch Basilic Vein Cephalic Vein Median Cubital Vein • Deep Venous Drainage: • • • • • • Palmar Venous Arch Radial Vein Ulnar Vein Brachial Vein Axillary Vein Subclavian Vein Veins of the Upper Extremities • Superficial Venous Drainage of the Upper Limb: • On the dorsum of the hand, a Dorsal Venous Arch (or network) of veins drains into both the basilic vein and cephalic vein. • The basilic vein runs adjacent to the medial surface of the upper limb and eventually helps form the axillary vein. • The cephalic vein runs alongside the lateral aspect of the upper limb and drains into the axillary vein. Veins of the Upper Extremities • Superficial Venous Drainage: • The Median Cubital Vein connects the cephalic and basilic veins. • Common site for venipuncture. • All superficial veins are highly variable among individuals. Veins of Upper Extremities • Deep Venous Drainage: • The digital veins and palmar venous arches drain into pairs of radial and ulnar veins that run parallel to arteries of the same name. • At the level of the cubital fossa, the radial and ulnar veins merge to form a pair of brachial veins that travel with the brachial artery. • Brachial veins and the basilic vein merge to form the axillary vein. • Superior to the lateral boarder of the first rib, the axillary vein is renamed the subclavian vein. Arteries of Lower Extremities • External Iliac Artery • Femoral Circumflex Arteries • Femoral Artery • Popliteal Artery • Anterior Tibial Artery • Posterior Tibial Artery • Fibular Artery • Medial Plantar Artery • Plantar Arch Arteries of Lower Extremities • The external iliac artery is the main arterial supply for the lower limb. • Travels inferior to the inguinal ligament, where it is renamed to the Femoral Artery. • The Deep Femoral Artery emerges from the Femoral Artery to supply the hip joint and many of the thigh muscles before traversing posteromedially along the thigh. • The Deep Femoral Artery enters the posteriorly placed popliteal fossa where it is renamed the Popliteal Artery, which supplies the knee joint and muscles in this region. Arteries of Lower Extremities • The Popliteal Artery divides into: • Anterior Tibial Artery – supplies anterior compartment of leg • At anterior surface of ankle, is renamed Dorsalis Pedis Artery • Posterior Tibial Artery – supples the posterior compartment of the leg • Extends a branch called the fibular artery – which supplies the lateral compartment leg muscles. • On planar side of foot, Posterior Tibial Artery branches into: • Medial and Lateral Plantar Arteries • The Dorsalis Pedis Artery and a branch of the Lateral Plantar Artery unite to form the Plantar Arch of the foot • Digital Arteries extend from the Plantar Arch to supply the toes. Veins of Lower Extremities • Superficial Venous Drainage • Dorsal Venous Arch • Great Saphenous Vein • Small Saphenous Vein • Deep Venous Drainage • • • • • • • Anterior Tibial Veins Posterior Tibial Veins Fibular Veins Popliteal Vein Femoral Vein External Iliac Vein Common Iliac Vein Veins of Lower Extremities • Superficial Venous Drainage: • On the dorsum of the foot, a Dorsal Venous Arch (or network) of veins drains into the: • Great Saphenous Vein • Originates in the medial ankle and extends adjacent to the medial surface of entire lower limb before draining into femoral vein. • Small Saphenous Vein • Extends adjacent to the lateral ankle and then travels along the posterior calf, before draining into popliteal vein. • These veins have branches that connect to the deeper veins. • If the valves in these veins become incompetent, varicose veins develop. Veins of Lower Extremities • Deep Venous Drainage: • The digital veins and deep veins of the foot and ankle drain into pairs of: • Anterior Tibial Veins and Posterior Tibial Veins that parallel the arteries of the same name. • A pair of Fibular Veins that travel alonside the Fibular Artery merge to form the: • Popliteal Vein that accompanies the Popliteal Artery, once in the anterior portion of the thigh, it is renamed: • Femoral Vein, once this vein passes superior to the inguinal ligament it is renamed once again to: • The External Iliac Vein – this vein merges with the internal iliac vein in the pelvis to form the: • Common Iliac Vein, there is a left and right – which merge to form the inferior vena cava.