Peripheral Arterial Thromboembolism_FINAL_2-Dec-2013
advertisement
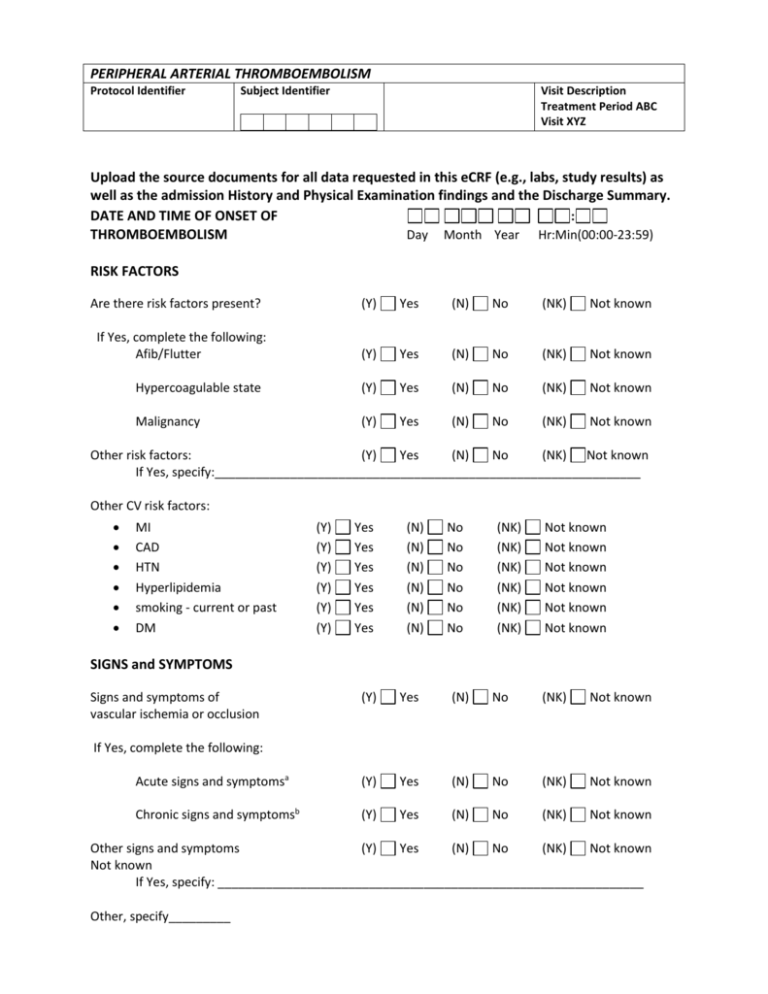
PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL THROMBOEMBOLISM Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description Treatment Period ABC Visit XYZ Upload the source documents for all data requested in this eCRF (e.g., labs, study results) as well as the admission History and Physical Examination findings and the Discharge Summary. DATE AND TIME OF ONSET OF : THROMBOEMBOLISM Day Month Year Hr:Min(00:00-23:59) RISK FACTORS Are there risk factors present? (Y) Yes (N) No (NK) Not known (Y) Yes (N) No (NK) Not known Hypercoagulable state (Y) Yes (N) No (NK) Not known Malignancy (Y) Yes (N) No (NK) Not known If Yes, complete the following: Afib/Flutter Other risk factors: (Y) Yes (N) No (NK) Not known If Yes, specify:______________________________________________________________ Other CV risk factors: MI CAD HTN Hyperlipidemia smoking - current or past DM (Y) (Y) (Y) (Y) (Y) (Y) Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes (N) (N) (N) (N) (N) (N) No No No No No No (NK) (NK) (NK) (NK) (NK) (NK) Not known Not known Not known Not known Not known Not known SIGNS and SYMPTOMS Signs and symptoms of vascular ischemia or occlusion (Y) Yes (N) No (NK) Not known Acute signs and symptomsa (Y) Yes (N) No (NK) Not known Chronic signs and symptomsb (Y) Yes (N) No (NK) Not known If Yes, complete the following: Other signs and symptoms (Y) Yes (N) No (NK) Not known Not known If Yes, specify: ______________________________________________________________ Other, specify_________ PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL THROMBOEMBOLISM Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description Treatment Period ABC Visit XYZ a Acute limb ischemia is defined as a sudden decrease in limb perfusion that causes a potential threat to limb viability (manifested by ischemic rest pain, ischemic ulcers, and/or gangrene) in patients who present within two weeks of the acute event. The five "P's" of acute ischemia or large vessels include pain, pulselessness, pallor, paresthesias, and paralysis. In addition, small vessel occlusion can cause the blue toe syndrome. b Patients with lower extremity chronic ischemia present with longstanding symptoms of peripheral artery disease that can include rest pain, which is pain across the base of the metatarsal heads at rest relieved by dependency, or with tissue loss, which can be ulceration, dry gangrene or wet gangrene. Chronic signs and symptoms may include claudication with ambulation, nocturnal and/or resting pain, ischemic ulceration, and/or frank gangrene PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL THROMBOEMBOLISM Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Test Performe d Diagnostic Test Name Visit Description Treatment Period ABC Visit XYZ Consistent with peripheral arterial thromboembolis m Y=Yes N=No If yes, is Thromboembolis m within a peripheral stent? Y=Yes N=No Date of Test Day Location 1= Extremity 2= Aorta 3=Cerebrovascular 4=Renal Y=Yes N=No Time of Test Hr:Mi n 00 0023:59 Mont h Year Ultrasound CT MRI Angiograph y : : : : THERAPY Did the subject require medication? (Y) Yes Was peripheral revascularization (Y) Yes (N) (N) No (NK) No Not known (NK) Not known performed? If Yes, complete the following: Specific Procedure Procedure Performed Y=Yes N=No e.g., Y Bypass surgery Percutaneous revascularization intervention Elective/Urgen t 1=Electived 2=Urgente or Emergentf 1 Location 3= Extremity 4=Aorta 5=Cerebrovascula r 6=Renal 5 Date of Procedure Time of Procedure Day Month Year Hr:min 00:0023.59 01 Jan 11 10:35 PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL THROMBOEMBOLISM Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description Treatment Period ABC Visit XYZ Complete a new row if procedure was performed on more than one location. d Elective: An elective procedure is one that is scheduled and is performed on a patient with stable disease, or in whom there is no urgency and/or increased morbidity or mortality associated with a planned procedure. Urgent: An urgent procedure is one that is not emergent but required to be performed on a timely basis (≤ 24 hrs) (e.g., a patient who has been stabilized following initial treatment of acute limb ischemia, and there is clinical consensus that a definitive procedure should occur within the next 24 hours). e f Emergent: A procedure that is performed immediately because of the acute nature of the medical condition (e.g., acute limb ischemia, acute aortic dissection), and the increased morbidity or mortality associated with a temporal delay in treatment.