2. Trophic Levels & Quiz- sub
advertisement

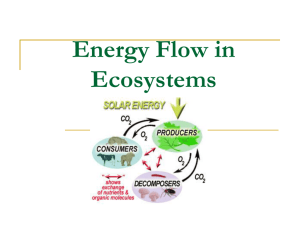
Bell Work HAVE SLATE, MARKER, AND ERASER ON DESK 1. Draw a food chain for your critter. Include at least 5 organisms. 2. Label each organism with vocab from Thursday (phototroph, herbivore, scavenger, etc.) ***If you finish early, describe how your critter gets its food (does it hunt? Does it hide? Explain) 1 Instructions for notes/participation When you see this pencil symbol next to something, you must write it in your notes When you see the marker, answer the question on your slate & wait for the guest teacher to ask everyone to show (No marker? Participate on scratch paper) Behold! I come to speak to you of… Title for today’s notes (lined paper) Trophic Levels and the Rule of Ten What does the Praying Mantis gain from eating the cricket? But is some of the energy in the cricket destroyed, when the mantis demolishes the cricket? NO! 1st Law of Thermodynamics: Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it is only transferred. Ten days later… According to the 1st Law of Thermodynamics no energy is destroyed in this short food chain. Discuss with your partner: does the lizard gain all of the energy that was in the cricket? Why or why not? Secondary Consumer The different levels we looked at in food chains and food webs are called Trophic Levels Primary Consumer Producer These levels have different names based on how far up they are from the base. Who is always going to be at the base? The producer is the producer. ( HAS TO BE AN AUTOTROPH) The primary consumer is the first consumer. (HAS TO BE A HETEROTROPH) The secondary consumer is the second consumer. Energy is lost between trophic levels in a number of ways. I used energy to move! I used energy in cellular respiration! I lost energy in my poo! (Did you cook with it?) Trophic level = an organism’s level in a food web/chain I lost energy as heat! Yo tambien! Me as well! Where is all this heat coming from? Any biological process that requires energy such mating, hopping, growing, changing colors, growing hair, urinating, swimming, smelling, hunting, being endothermic, biting, digesting, eating, and avoiding being eaten releases heat. Transfer of Energy • When a zebra eats the grass, it does not obtain all of the energy the grass in the ecosystem. Some is not eaten, some of what is eaten is not absorbed, some energy is lost as heat during digestion. • Lions eat zebras, but they do not get all of the energy from the zebra population. (much of it is lost as heat, bones, uncaught zebras) Transfer of Energy • The two (2) previous examples of energy transfer show that no organism EVER receives all of the energy from the organism they just ate • Only 10% of the energy from one trophic level is transferred to the next The Rule of Ten 1,000 cal 100 cal 10 cal 1 cal Rule of Ten: Only 10% of the energy gained by one trophic level is available to the next level. Rule of 10 Model • Flip your notes over & draw a circle at the top center of your page. • This represents a red tail hawk, a top-level predator in our local food web. Label your “hawk” a tertiary consumer. • Are red-tail hawks autotrophs or heterotrophs? Heterotrophs! Rule of 10 Model • Hawks eat pack rats. There must be at least 10 pack rats to support each red tail hawk. • Display this by drawing 10 smaller circles in a pile or row beneath the “hawk”. • Pack rats are considered to be secondary consumers. Label the “pack rats” as secondary consumers. Rule of 10 Model • Pack rats in this area eat grasshoppers. Since the model now has 10 pack rats, how many TOTAL grasshoppers would you expect to find in this area? 100! • Grasshoppers are represented by smaller circles of another color. Make 100 small dots in a separate level under the “pack rats”. • “Grasshoppers are primary consumers ___________ in this food web.” Rule of 10 Model • Grasshoppers in this area eat, well… grass. • For the number of grasshoppers you modeled in this population how many grass plants would you expect to find? 1000! • You do NOT have to draw the grass plants on your model. Just write the NUMBER of dots you would have to draw & label it as “grass” • As the only auto _____trophs in this food web, grass in classified as a producer. (fill in the blank on slate) 12 word summary • Underneath your Rule of 10 model write a 12 word summary about how the Rule of 10 is related to population sizes of different species. What Is Life? Quiz • No one can sit right next to anyone else – 1 person per lab table & in middle section – 3 people @ counter • If you finish early- turn into front basket & quietly read/draw/listen to MP3 until everyone is finished If 10 mins+ extra time practice on next two slides • Take food web cards out to lab • Use the trophic vocab cards to label each organism (phototroph, chemotroph, etc.)