Summary2005F
advertisement

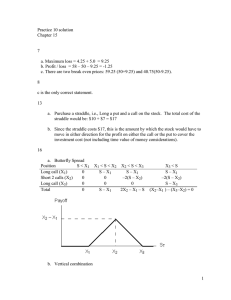
FIN9797 Options Markets Midterm Topic Review Forwards and Futures Definitions: Forward price, value of forward position, delivery price, maturity Pricing is based on replication: The cost of buy and carry. o Pricing formula: Forward price F=S*exp(r-q)*t (r –interest rate, q-dividend yield for stock, foreign interest rate for currency). o In the presence of discrete dividends (benefits), costs (such as storage), F=S*exp(r-q)*t – Future Value of Dividends (& other dollar benefits) + Future Value of Dollar Costs (e.g., storage) o If the market price differs from replication cost, you can do an arbitrage trade: Buy the cheap one, sell the expensive one. Values of forward positions: N*exp(-r (T-t))(F-K), where N is the size of the position, negative for short. Appreciate the difference between forward price and the value of a forward contract, the difference between the forward price F and the delivery price K Payoff at expiration (S-K for long, K-S for short), Can make adjustments for stock splits, can plot the payoff function as well as answering questions on payoffs at given situations Options Definitions: Call/put, long/short, American/European, strike, expiry o Moneyness: At the money, out of the money, in the money – Focus on the definition based on forward instead of spot o Intrinsic versus time value: Option Value = Intrinsic Value+ Time Value o Call option intrinsic value = max(0, exp(-r (T-t))(F-K)) o Put option intrinsic value = max(0, exp(-r (T-t)) (K-F)) o Payoff (max(0, S-K) for call, max(0,K-S) for put, negative for short) Strategies o Given a portfolio, understand the payoff: Can plot the payoff function, and answer questions on payoffs under specific situations o Given a payoff plot, know how to create it using options/forwards/bonds o Understand the names, payoffs, usages of the common combo contract: bull spread, bear spread, butterfly, straddle, strangle, risk reversal Option behavior o Strike/maturity relation creates arbitrage bounds o Exposure (to forward and volatility): Understand how option prices move with the underlying forward (spot, interest rate, dividend) and volatility o Lower/upper bounds, put-call parity: Arbitrage trading when bounds/relations are violated