Societies at the Crossroads
advertisement

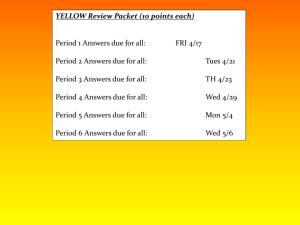
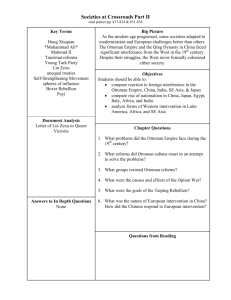
C 31: Societies at the Crossroads: Ottoman Empire, Russia, Japan and China Issues that they share • military weaknesses • vulnerable to foreigners who could often force their way in • propose reform modeled on the West (education, responsive govt, Written constitutions, limit power of rulers, guarantees of equality) • Suffered from internal pressures (population/ declining crop production/ Falling income ) Issues where they differ • Ottoman Empire, Russia China = elite rulers did not embrace or support reform • Japan = Tokugawa Shogunate fell, emperor was restored, reform is thorough and embraced industrialization Territorial Losses of the Ottoman Empire (1800-1914) Muhammad Ali (r. 1805-1848) Societies at the Crossroads: The Ottoman Empire 1750-1914 Geography Religion Achievements Political Geographically diverse- for centuries controlled trade routes from East to West _____________________________ Islam Some resistance to reform by conservative clerics/ internal conflict (Christians, Muslims, Jews) ______________________________ Turkish made the official language even With Arabic and Slavic speakers See Tanzimat Era/ Young Turks ___________________________ Territorial Losses from Russia, the Balkans Loss of Egypt (Muhammad Ali) 1820, Greece 1830, Serbia 1867 Semi-independent war lords are a problem Corrupt leadership/ private armies Military weak/ technologically weak Internal conflict ethnic/ nationalist groups = REVOLT then Authority under Sultan Mahmud II(1808-1839) (however undermined authority of the ulama Tanzimat Era: 1839-1876 (conservative critics) Reform accelerated, restructuring of military Based on European models, attacked Ottoman sharia laws educational reform, centralized Societies at the Crossroads: The Ottoman Empire 1750-1914 Economic Social Increased economic pressure from Europe Loss of control (and revenue) from trade due to shifting focus on Atlantic trade Reluctance to embrace modern technology Led to fiscal insolvency, economic dependence, foreign loans (high interest) 1882 CAPITULATIONS = humiliating Deprived Ottomans of income (GB didn’t have to pay taxes) Extraterritoriality imposed________ YOUNG TURKS: 1889-1908 (Social and Political) (Parisian Exiles): Universal suffrage Equality before the law, Freedom of religion emancipation Free public education, Nationalistic (Turkish independence within empire=Arab resistance united in mistrust of Europe 1908: Inspired an Army Coup Mehmed V Rashid (r. 1909-1918) puppet sultan DECLINE: continued to lose wars, subject peoples wanted autonomy, survived b/c Europe didn’t know how to divide empire w/o Upsetting their own balance of power Sultan Mahmud II 1808-1839 Tanzimat Reforms 1839-1876 The Crimean Wars: 1854-1856 Sultan Abdul Hamid II 1876-1901 The Young Turks 1889-1908 Proclamation for the Ottoman Empire (Young Turks 1908) 1. The basis for the Constitution will be respect for the predominance of the national will. One of the consequences of this principle will be to require without delay the responsibility of the minister before the Chamber, and, consequently, to consider the minister as having resigned, when he does not have a majority of the votes of the Chamber. 2. Provided that the number of senators does not exceed one-third the number of deputies, the Senate will be named as follows: one-third by the Sultan and two-thirds by the nation, and the term of senators will be of limited duration……… 7. The Turkish tongue will remain the official state language. Official correspondence and discussion will take place in Turkish……… 9. Every citizen will enjoy complete liberty and equality, regardless of nationality or religion, and be submitted to the same obligations. All Ottomans, being equal before the law as regards rights and duties relative to the State, are eligible for government posts, according to their individual capacity and their education. Non-Muslims will be equally liable to the military law. The Russian Empire 1801-1914 Peter I the Great (r. 1682-1725) Catherine II the Great (r. 1762-1796) Alexander I (r. 1801-1825) Nicholas II (r. 1894-1917) Nicholas I (r. 1825-1855) Alexander II (r. 1855-1881) Sergei Witte Societies at the Crossroads: The Russian Empire 1750-1914 Geography Religion Achievements Political Extremely geographically diverse_______ Russian Orthodox Christianity (1/2) Judaism (pogroms) Extreme multi-culturalism _____________________________ Industrialization Sergei Witte (Trans- Siberian Railroad) (however peasant discontent: low wages, long hrs, uprooted from agrarian lifestyle) __________________________ Romanov tsars ruled as autocrats w/ support of church and nobility Russian military (although backward) expanded empire to E, S and SW (threat to Ottoman Empire upset European balance of power = Crimean War (18531856)= Russian LOSS) Tsars attempt to censor intelligenisa (radicals/socialists) (latter 20th C) Nationalism gains support (Baltics, Poland, Ukraine, Georgia, central Asia)= tsarist threat REFORM under Alexander II (regional assemblies: zemstovs) but subordinate to tsar/1876 terrorists arm of an anarchist group assassinated Alexander II (no more reform) Societies at the Crossroads: The Russian Empire 1750-1914 Political Economic Social Tsar Nicholas II (1894-1917): further police control, further expansion into Manchuria/Korea = Russo-Japanese War 1905 (Japan destroys Russian navy) Tsars agree to some political concessions = The Duma (national legislature) by October 1905 (failed for now- lacked authority) ______________________________ Industrialization with a fundamental agrarian economy (motivation different than in WEST: Why??) Key to modern success = emancipation of the serfs (WHY?) Tsar Alexander II (1855-1881) abolished serfdom (landowners compensated for their loss BUT freed serfs not happy: WHY?) ______________________________ Military defeats (Crimean War, Russo-Japanese War 1905) Russification: attacks on ethnic minorities led to riots: Bloody Sunday (January 1905 march on Winter Palace) Social discontent leads to October 1905 Revolution Bloody Sunday 1905: Soldiers shot into the crowd Civilian Deaths= 96-4000 Strike for fair pay, Suffrage, shorter Work day But…… China and Japan: 19th century Pressures CHINA: Opium Wars and Unequal Treaties 1838-1842 Since 1759: European trade Limited to port of Guangzhou Foreign merchants forced to deal with Chinese firms called cohongs: ONLY trade in silver buillon WAR! 40,000 chests of opium a year shipped to China by 1838 Commissioner Lin Zexu rejected by Queen Victoria Lin Zexu confiscated and destroyed 20,000 chests of opium Forced to grant extraterritoriality status UNEQUAL TREATIES/ Spheres of Influence Unequal Treaties • • • • According to the 1842 Treaty of Nanjing, the Chinese were to: Reimburse Britain for costs incurred fighting the Chinese Open several ports to British trade Provide Britain with complete control of Hong Kong Grant extraterritoriality to British citizens living in China REACTION? Taiping Rebellion 1850-1864 Opposed the Manchus: wanted radical Social change, no footbinding, no private property, free public ed, no concubinage (men and women equal) 20-30 million lives lost Massive decline in economy/ food 1885 France took Vietnam 1895 Japan forced Korean independence 1898 Spheres of Influence China: The Boxer Rebellion 1899-1900 Chinese Empress Dowager Cixi Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists University of Pennsylvania 49 lb flawless crystal spheresecond largest in the world Societies at the Crossroads: China 1750-1914 Geography Extremely geographically diverse_______ Religion unequal treaties allowed Christian missionaries ______________________________ Achievements Political __________________________ Qing Dynasty (Manchus) 1644-1911 British introduced opium to end cohong system Opium War (1839-1842)- Chinese easily defeated unequal treaties Treaty of Nanjing 1842 lost tribute states of Vietnam, Burma, Korea, Taiwan Societies at the Crossroads: China 1750-1914 Political Economic Social 1896 Spheres of Influence 1899-1900 Boxer Rebellion (Empress Dowager Cixi supported militia against foreigners) 1900- Chinese leaders no longer in control of economy 1912- collapse of the Qing Dynasty _____________________________ BEFORE: tight control of foreign trade/ foreign contact/ cohong system agrarian/ little demand for foreign goods AFTER: unequal treaties ultimately severe economic decline (eating grass, human flesh) "Self Strengthening" Movement (1860-1895) failed _____________________________ popular uprisings 1850-1860s Taiping Rebellion defeated by Qing and foreign troops (1864) government slaughtered 100,000 Taipings Hundred Days reforms 1898 Deshima, known as Dejima in Japanese, was a small artificial island in Nagasaki Bay (approximately 150 feet by 500 feet) on the southwestern Japanese island of Kyushu. From 1641 to 1845, Deshima served as the sole conduit of trade between Europe and Japan, and during the period of self-imposed Japanese seclusion (approximately 1639-1854) was Japan's only major link to the European world. Closed Country Edicts 1635 and 1639 JAPAN: Commodore Perry 1853 and Unequal Treaties Japan had a history of successful imitation and China did not. Meiji Restoration 1868 ended Tokugawa Shogunate European style military Modernized the infrastructure New public health measures/ population increase 1872 Mass public education system 1890s Massive industrialization (zaibatsu) Supported consumer culture/ department stores History of feudalism may have helped them understand the military aspects of the Western challenge/ created group loyalties Treaty of Kanagawa: March 31, 1854 1. Peace and friendship between the United States and Japan. 2. Opening of two ports to American ships at Shimoda and Hakodate 3. Help for any American ships wrecked on the Japanese coast and protection for shipwrecked persons 4. Permission for American ships to buy supplies, coal, water, and other necessary provisions in Japanese ports. Societies at the Crossroads: Japan 1750-1914 Geography Religion Achievements Political isolation Extremely geographically diverse_______ Shintoism/ Neo-Confucianism/ Buddhism unequal treaties allowed Christian missionaries ______________________________ universal education (primary and secondary) competitive universities __________________________ Tokugawa shogunate failing to end crisis foreign pressure to reverse closed door policy 1840s bakufu plan to attack foreign interests 1853 Commodore Matthew Perry unequal treaties = humiliation = end of Tokugawa rule 1868 Meiji Restoration = end to military rule constitutional government 1889 (parliament, Diet, political parties) Emperor still theoretically in charge) daimyo and samurai lose power government supported industrial growth/ outlawed unions and labor reform Societies at the Crossroads: Japan 1750-1914 Political political stability linked to industrial growth defeated China 1895, Russia 1904 ____________________________ Economic Social tax system reorganized (grain taxes to fixed money) industry: govt take over of industry to modernize it- then sold some to private investors (zaibatsu) railroads, telegraphs, steamships, postal systems, banking systems, munitions production) 1899 unequal treaties ended- no limits on Japanese in trade either ___________________________ peasant class suffer under tax burden uprisings quickly suppressed Confucian social order dismantled Almost all Japanese became legally equal as commoners- still female infanticide